How to restart a Python Script [6 Simple Ways]
Last updated: Apr 13, 2024
Reading time·3 min
# Table of Contents
- How to restart a Python Script
- How to restart a Python Script using os.system()
- Only restarting a Python script once
- Restarting a Python script with psutil
- Restart a Python Script with a bash script
# How to restart a Python Script
Use the os.execv() method to restart a Python script.
The os.execv() method executes a new program, replacing the current
process.
import os import sys def restart(): print('Restarting script...') os.execv(sys.executable, ['python'] + sys.argv) restart()
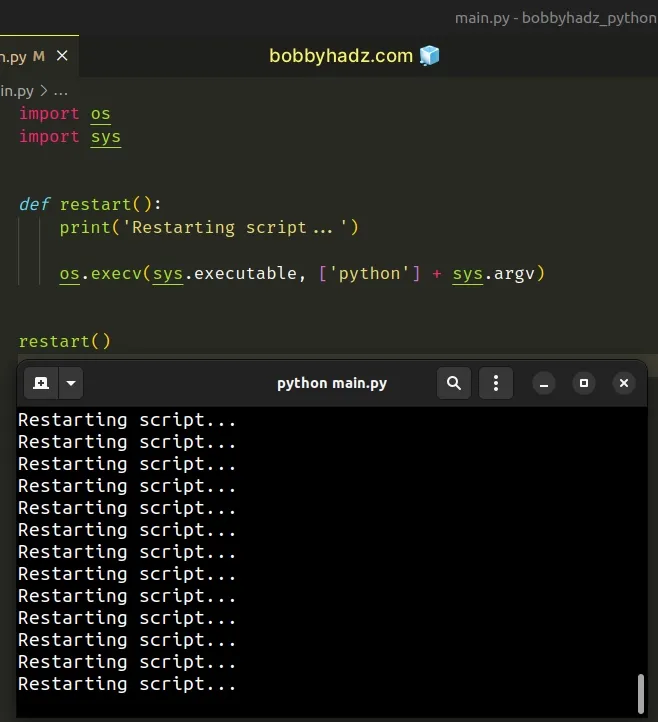
The code sample uses the os.execv() method to restart the Python script.
The sys.executable property returns a string that stores the absolute path of the executable binary for the Python interpreter.
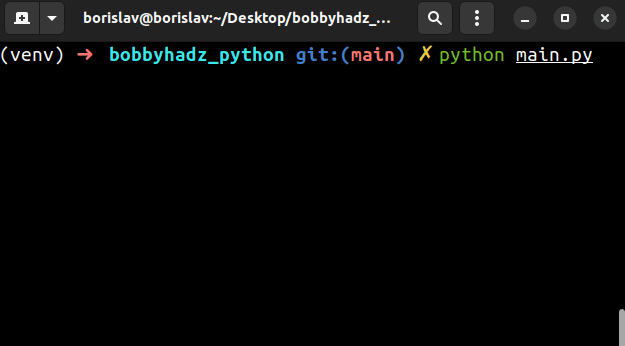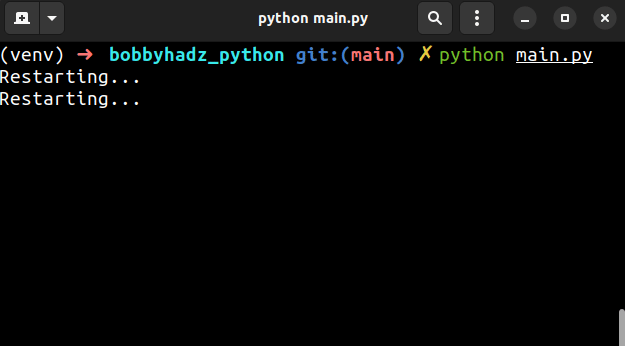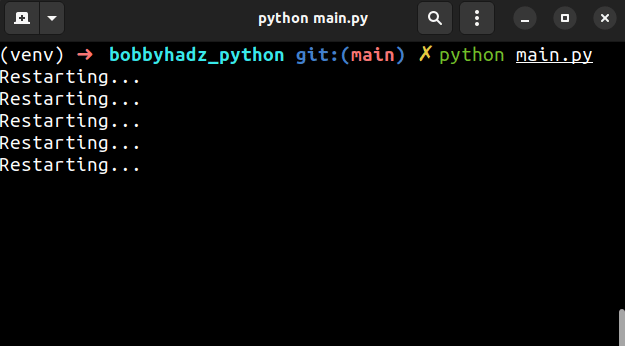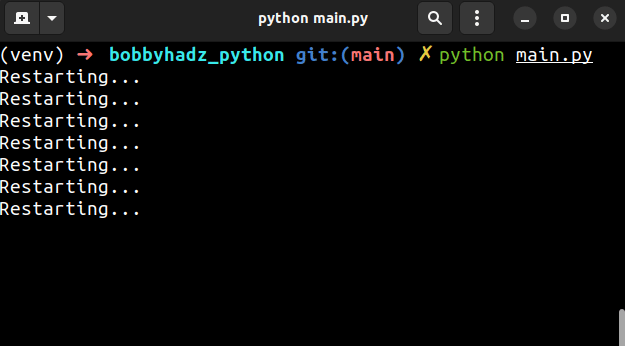
import sys # /home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/venv/bin/python print(sys.executable) # ['main.py'] print(sys.argv)
The sys.argv property returns a list that contains the command line arguments that were passed to the Python script.
The first item in the list is the name of the script.
In other words, the os.execv command executes the python main.py command.
Depending on your Python installation, you might have to use python3 or py
instead of python.
# For macOS and Linux os.execv(sys.executable, ['python3'] + sys.argv) # Using the py alias for Windows os.execv(sys.executable, ['py'] + sys.argv)
You don't necessarily have to wrap the logic into a function.
import os import sys print('Restarting...') os.execv(sys.executable, ['python'] + sys.argv)
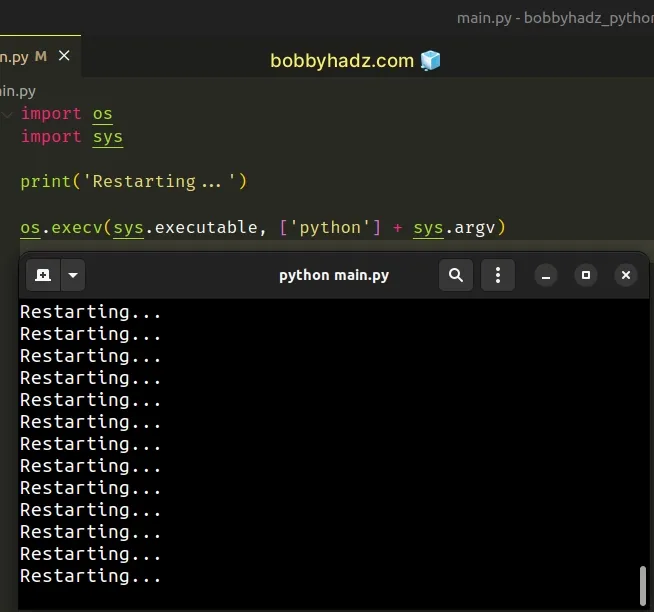
If you want to delay execution for a given number of seconds before calling
os.exec() use the
time.sleep() method.
import os import sys import time print('Restarting...') time.sleep(1) os.execv(sys.executable, ['python'] + sys.argv)
The time.sleep() method suspends execution for the given number of seconds.
# How to restart a Python Script using os.system()
You can also restart a Python script using os.system().
import os print('Restarting...') os.system('python main.py')
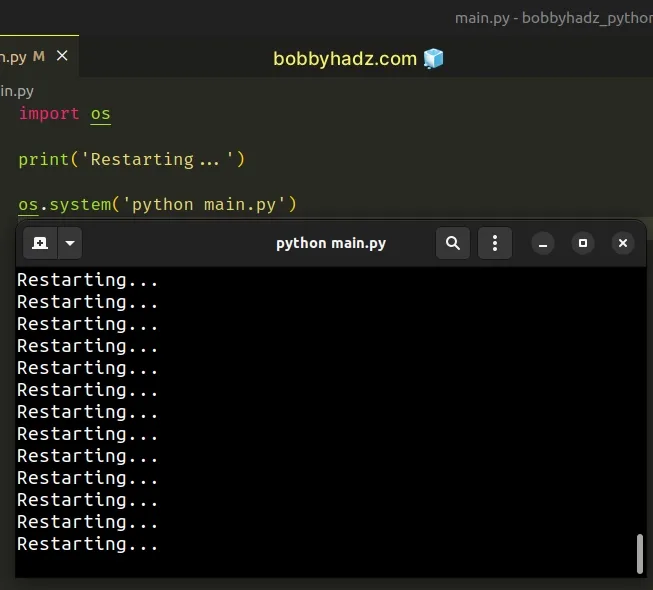
The os.system() method takes a string command and executes it in a subshell.
Depending on your Python installation, you might have to use python3 or py
instead of python.
# python3 (macOS and Linux) os.system('python3 main.py') # py alias (Windows) os.system('py main.py')
# Only restarting a Python script once
You can also use the os.system() method if you only want to restart a Python
script once.
Suppose we have the following another.py file.
print('bobbyhadz.com')
And the following main.py file.
import os # Restart 1 time os.system('python another.py') # Restart 2 times os.system('python another.py') # Restart 3 times os.system('python another.py')
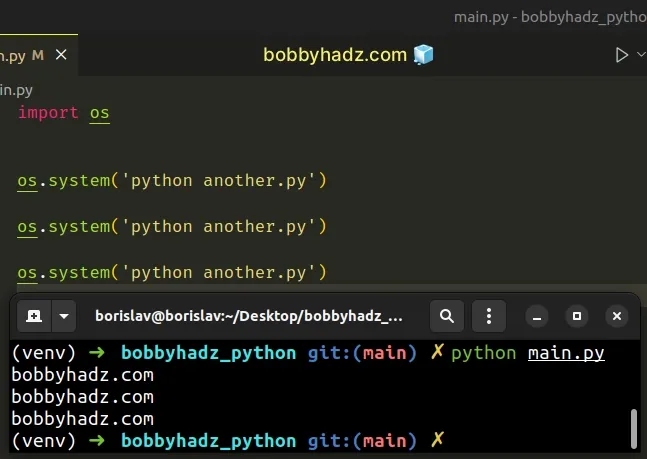
You can add the os.system('python another.py') lines as many times as
necessary to rerun the code in the another.py script.
The same approach can be used if you need to restart a script indefinitely.
You just have to wrap the line in a while True loop.
import os import time while True: time.sleep(1) os.system('python another.py')
The time.sleep() line is optional. Remove it if you don't want to add a delay
between script restarts.
# Restarting a Python script with psutil
You can also use the psutil module to restart a Python script.
First, make sure you
have the psutil module installed.
pip install psutil pip3 install psutil
Now import the module and use it as follows.
import sys import os import psutil print('bobbyhadz.com') def restart_script(): try: process = psutil.Process(os.getpid()) for handler in process.open_files() + process.connections(): os.close(handler.fd) except Exception as e: print(e) python = sys.executable os.execl(python, python, *sys.argv) restart_script()
The psutil (process and system utilities) module is a cross-platform library
for retrieving information on running processes.
You can read more about the package on its Pypi page.
# Restart a Python Script with a bash script
You can also restart a Python script using a bash script.
Create the following restart-script.sh file in the same directory as your
Python script.
#!/bin/bash pkill -f main.py python main.py
Add the following code to your main.py file.
import os print('bobbyhadz.com') os.execl('restart-script.sh', '&')
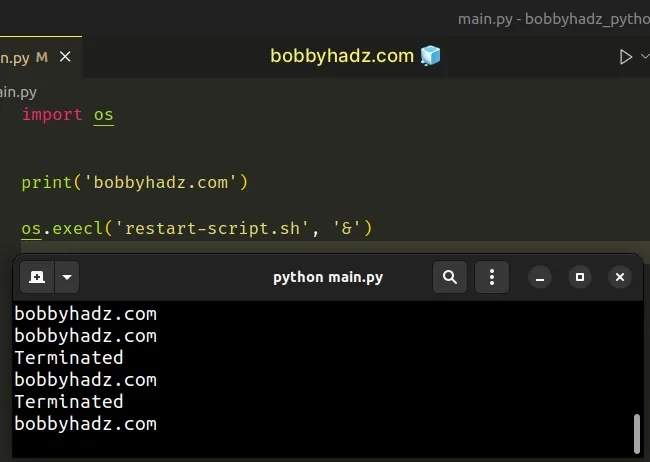
The script terminates the process and returns the main.py file.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'psutil' in Python
- OSError: [Errno 8] Exec format error in Python [Solved]
- Write a List of Tuples to a File in Python
- Write a String to a File on a New Line every time in Python
- How to check if a File is Empty in Python
- Count number of unique Words in a String or File in Python
- Create a file name using Variables in Python

