Python: Find range overlap and Check if Ranges overlap
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Python: Find range overlap and Check if Ranges overlap
- Checking if two ranges overlap in Python
- Find the overlap between two ranges using Set intersection
# Python: Find range overlap and Check if Ranges overlap
To find the overlap between two ranges in Python:
- Use the
max()function to find the max starting number of the two ranges. - Use the
min()function to find the min ending number of the two ranges and add1to the result. - Use the
range()class to create a range of overlapping numbers.
def find_range_overlap(a, b): return list(range(max(a[0], b[0]), min(a[-1], b[-1]) + 1)) x = range(1, 7) y = range(5, 10) overlap = find_range_overlap(x, y) print(overlap) # 👉️ [5, 6] if len(overlap) > 0: print('The two ranges overlap') else: print('The two ranges do NOT overlap')
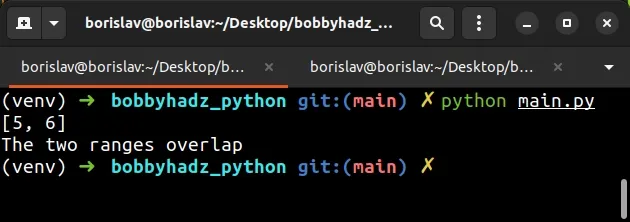
The find_range_overlap() function takes 2 ranges - a and b and returns a
list containing the overlapping numbers.
We used the max() function to get the max starting value of the two ranges.
def find_range_overlap(a, b): return list(range(max(a[0], b[0]), min(a[-1], b[-1]) + 1))
The max() function returns the largest item in an iterable or the largest of
two or more arguments.
print(max(1, 5)) # 👉️ 5
We then used the min() function to get the min number between the stop
values of the ranges.
The min function returns the smallest item in an iterable or the smallest of two or more arguments.
0 and the last item has an index of len(sequence) - 1 or simply -1.Notice that we added 1 to the min value in the call to the range() class.
def find_range_overlap(a, b): return list(range(max(a[0], b[0]), min(a[-1], b[-1]) + 1))
This is necessary because the stop parameter of the range() class is
exclusive (up to, but not including).
The range() class is commonly used for looping a specific number of times in for loops and takes the following arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
start | An integer representing the start of the range (defaults to 0) |
stop | Go up to, but not including the provided integer |
step | Range will consist of every N numbers from start to stop (defaults to 1) |
The last step is to use the list class to
convert the range object to a list.
The list contains the overlapping numbers between the supplied ranges.
def find_range_overlap(a, b): return list(range(max(a[0], b[0]), min(a[-1], b[-1]) + 1)) x = range(1, 7) y = range(5, 10) overlap = find_range_overlap(x, y) print(overlap) # 👉️ [5, 6]
# Checking if two ranges overlap in Python
To check if two ranges overlap:
- Find the overlap between the ranges and store the result in a list.
- Check if the list's length is greater than
0. - If the condition is met, the two ranges overlap.
def find_range_overlap(a, b): return list(range(max(a[0], b[0]), min(a[-1], b[-1]) + 1)) x = range(2, 7) y = range(4, 12) overlap = find_range_overlap(x, y) print(overlap) # 👉️ [4, 5, 6] if len(overlap) > 0: # 👇️ this runs print('The two ranges overlap') else: print('The two ranges do NOT overlap')
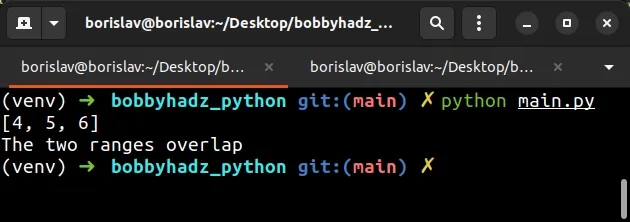
We first find the overlap between the two ranges using the find_range_overlap
function.
The next step is to check if the list's length is greater than 0.
If the condition is met, then the ranges overlap.
If the two ranges don't overlap, the list will be empty.
def find_range_overlap(a, b): return list(range(max(a[0], b[0]), min(a[-1], b[-1]) + 1)) x = range(2, 7) y = range(10, 15) overlap = find_range_overlap(x, y) print(overlap) # 👉️ [] if len(overlap) > 0: print('The two ranges overlap') else: # 👇️ this runs print('The two ranges do NOT overlap')
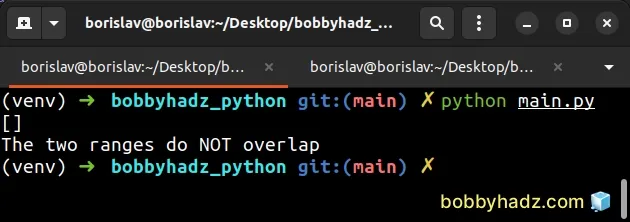
The ranges in the example above don't overlap, so the list is empty and the
else block runs.
# Find the overlap between two ranges using Set intersection
You can also use the intersection method of the Set object to find the
overlap between two ranges.
def find_range_overlap(a, b): return list(set(a).intersection(b)) x = range(2, 10) y = range(7, 15) overlap = find_range_overlap(x, y) print(overlap) # 👉️ [8, 9, 7]
We used the set() class to convert the first range object to a set to be
able to use the intersection() method.
The
intersection
method returns a new set with elements common to both set objects.
The last step is to optionally convert the new set to a list.
intersection() method can be passed any iterable value so we didn't have to convert the second range object to a set.You can also use the ampersand & operator which is an implicit way to call the
intersection() method.
def find_range_overlap(a, b): return list(set(a) & set(b)) x = range(2, 10) y = range(7, 15) overlap = find_range_overlap(x, y) print(overlap) # 👉️ [8, 9, 7]
However, when using the & operator, you have to convert both range object to
sets.
Set objects are an unordered collection of unique elements.
Therefore, this approach shouldn't be used if you need to preserve the order of the overlapping numbers.
It should also be noted that this approach is about 2.5 times slower than the one covered in the first subheading.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

