Python binascii.Error: Incorrect padding [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Python binascii.Error: Incorrect padding
- Add padding to your bytes object before decoding
- Make sure the
validatekeyword argument is set toFalse - Creating a reusable function that pads the bytes
- Removing the prefix when decoding base64 image strings
- Try using the
base64.urlsafe_b64decodemethod instead
# Python binascii.Error: Incorrect padding [Solved]
The Python "binascii.Error: Incorrect padding" occurs when you try to base64 decode a bytes object that doesn't have the correct padding.
To solve the error add padding to the bytes object when calling
base64.b64decode().
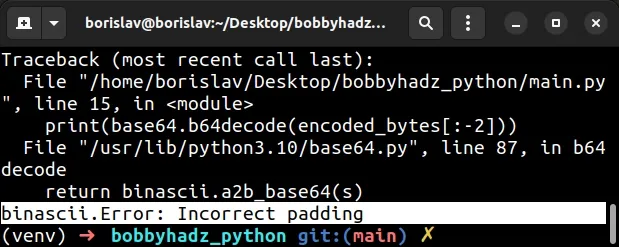
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import base64 data = bytes('{"name": "bobby hadz"}', encoding='utf-8') encoded_bytes = base64.b64encode(data) print(encoded_bytes) # b'eyJuYW1lIjogImJvYmJ5IGhhZHoifQ==' decoded_bytes = base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes) print(decoded_bytes) # 👉️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}' # ⛔️ binascii.Error: Incorrect padding print(base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes[:-2]))
We used the base64.b64encode() method to encode a bytes-like object using Base64.
The method returns the encoded bytes.
We then used the base64.b64decode() method to decode the Base64 encoded bytes-like object.
The last line raises the "binascii.Error: Incorrect padding" error because
we used slicing to remove the last 2 characters ( the padding - ==) from the
bytes object.
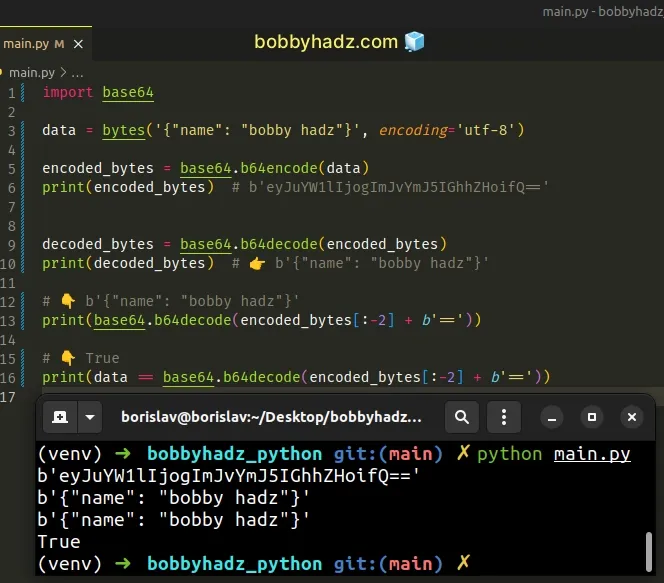
# Add padding to your bytes object before decoding
You can solve the error by adding padding (==) to your bytes object before
decoding.
The base64.b64decode() method will truncate any extra padding, so even if your
bytes object is padded sufficiently, it won't cause any issues.
import base64 data = bytes('{"name": "bobby hadz"}', encoding='utf-8') encoded_bytes = base64.b64encode(data) print(encoded_bytes) # b'eyJuYW1lIjogImJvYmJ5IGhhZHoifQ==' decoded_bytes = base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes) print(decoded_bytes) # 👉️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}' # 👇️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}' print(base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes[:-2] + b'==')) # 👇️ True print(data == base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes[:-2] + b'=='))
You can add padding to your bytes object by using the addition (+) operator.
# 👇️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}' print(base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes[:-2] + b'=='))
The base64.b64decode() method truncates the extra padding, so the following
code sample achieves the same result.
import base64 data = bytes('{"name": "bobby hadz"}', encoding='utf-8') encoded_bytes = base64.b64encode(data) print(encoded_bytes) # b'eyJuYW1lIjogImJvYmJ5IGhhZHoifQ==' decoded_bytes = base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes) print(decoded_bytes) # 👉️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}' # 👇️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}' print(base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes[:-2] + b'=======')) # 👇️ True print(data == base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes[:-2] + b'========='))
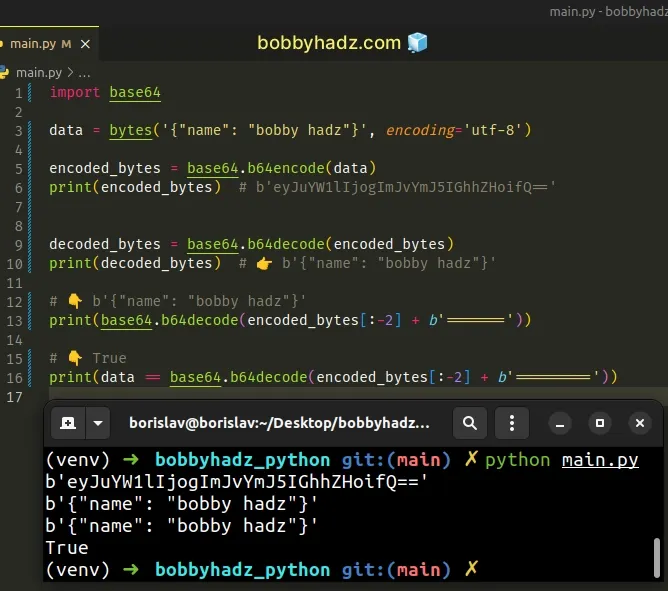
You can simply add the maximum number of pad characters that you need.
# 👇️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}' print(base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes[:-2] + b'======='))
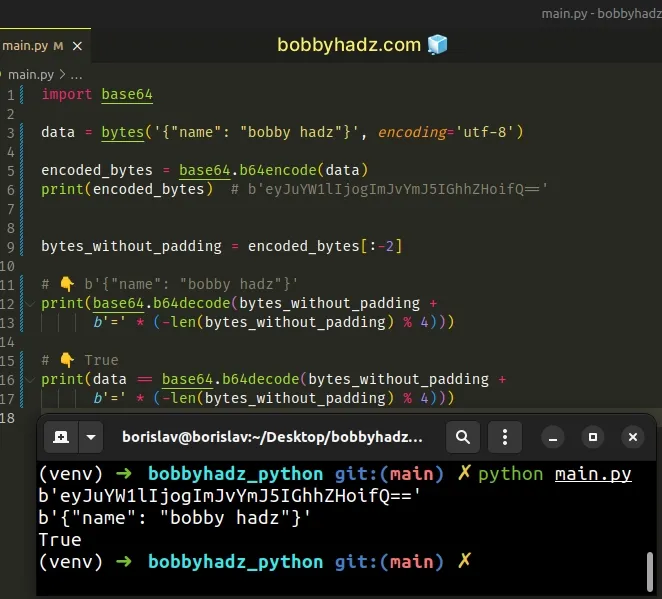
If you don't want to add extra padding, use the following formula.
import base64 data = bytes('{"name": "bobby hadz"}', encoding='utf-8') encoded_bytes = base64.b64encode(data) print(encoded_bytes) # b'eyJuYW1lIjogImJvYmJ5IGhhZHoifQ==' bytes_without_padding = encoded_bytes[:-2] # 👇️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}' print(base64.b64decode(bytes_without_padding + b'=' * (-len(bytes_without_padding) % 4))) # 👇️ True print(data == base64.b64decode(bytes_without_padding + b'=' * (-len(bytes_without_padding) % 4)))
However, using the formula is not necessary and is a bit more difficult to read.
# Make sure the validate keyword argument is set to False
Make sure the validate keyword argument is set to False when calling the
base64.b64decode() method.
import base64 data = bytes('{"name": "bobby hadz"}', encoding='utf-8') encoded_bytes = base64.b64encode(data) print(encoded_bytes) # b'eyJuYW1lIjogImJvYmJ5IGhhZHoifQ==' decoded_bytes = base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes) print(decoded_bytes) # 👉️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}' # 👇️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}' print( base64.b64decode( encoded_bytes[:-2] + b'=======', validate=False ) ) # 👇️ True print(data == base64.b64decode( encoded_bytes[:-2] + b'=========', validate=False ) )
If your bytes-like object already has some padding, you have to set the
validate keyword argument to False.
If validate is set to True, a binascii.Error error is raised if the
padding is longer than 2 characters.
validate argument is set to False, the b64decode method truncates any extra padding automatically.The default value for the validate keyword argument is False, so not passing
it and setting it to False explicitly is equivalent.
# Creating a reusable function that pads the bytes
You can also create a reusable function that pads the bytes and base64 decodes them.
import re import base64 data = bytes('{"name": "bobby hadz"}', encoding='utf-8') encoded_bytes = base64.b64encode(data) print(encoded_bytes) # b'eyJuYW1lIjogImJvYmJ5IGhhZHoifQ==' def decode_base64(encoded_bytes, altchars=b'+/'): encoded_bytes = re.sub( rb'[^a-zA-Z0-9%s]+' % altchars, b'', encoded_bytes) missing_padding_length = len(encoded_bytes) % 4 if missing_padding_length: encoded_bytes += b'=' * (4 - missing_padding_length) return base64.b64decode(encoded_bytes, altchars) bytes_without_padding = encoded_bytes[:-2] # 👇️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}' print(decode_base64(bytes_without_padding))
The decode_base64 function:
- Takes an encoded bytes object as a parameter.
- Pads the bytes object sufficiently, so there is no missing padding.
- Base64 decodes the bytes object.
The re.sub() method is used to normalize the bytes object.
The method removes any non-Base64 characters and returns the result.
# Removing the prefix when decoding base64 image strings
If your string starts with a prefix of data:image/png;base64,, you have to
remove it before base64 decoding it
from io import BytesIO import base64 from PIL import Image data = 'data:image/png;base64, iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAUAAAAFCAYAAACNbyblAAAAHElEQVQI12P4//8/w38GIAXDIBKE0DHxgljNBAAO9TXL0Y4OHwAAAABJRU5ErkJggg==' im = Image.open(BytesIO(base64.b64decode(data.split(',')[1]))) im.save("my-image.png")
We used the str.split
method to split the string on the comma and then accessed the element at index
1 (the second list element).
This effectively removes the data:image/png:base64 prefix from the string.
We can then pass the result to the base64.b64decode() method.
Make sure you have the Pillow module installed to be able to run the code sample.
pip install Pillow # 👇️ or with pip3 pip3 install Pillow
# Try using the base64.urlsafe_b64decode method instead
If the error persists, try to use the base64.urlsafe_b64decode method instead.
import base64 data = bytes('{"name": "bobby hadz"}', encoding='utf-8') encoded_bytes = base64.b64encode(data) print(encoded_bytes) # b'eyJuYW1lIjogImJvYmJ5IGhhZHoifQ==' decoded_bytes = base64.urlsafe_b64decode(encoded_bytes) print(decoded_bytes) # 👉️ b'{"name": "bobby hadz"}'
The base64.urlsafe_b64decode() method decodes the supplied bytes-like object or ASCII string using the URL and filesystem-safe alphabet.
The method substitutes + with - and / with _ in the standard Base64
alphabet.
The method returns the decoded bytes.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- ValueError: I/O operation on closed file in Python [Solved]
- Print the binary representation of a Number in Python
- How to Print a Variable in Hexadecimal in Python
- Generate random bytes of length N in Python
- How to convert Bytes to Dictionary in Python
- Cannot use a string pattern on a bytes-like object in Python
- AttributeError: 'bytes' object has no attribute 'encode'
- The JSON object must be str, bytes or bytearray, not dict
- How to convert from HEX to ASCII in Python [5 Ways]

