This expression is not callable. Type 'X' no call signatures
Last updated: Feb 27, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# This expression is not callable, Type 'X' no call signatures
The "This expression is not callable. Type 'X' has no call signatures" TypeScript error occurs for 2 reasons:
- Trying to call a type that isn't a function as a function.
- Trying to call a function that is typed as something else as a function.
To solve the error, make sure you're calling a function and it is typed as a function.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
// 👇️ const str: "bobbyhadz.com" const str = 'bobbyhadz.com'; // ⛔️ Error: This expression is not callable. // Type 'String' has no call signatures.ts(2349) str(true);
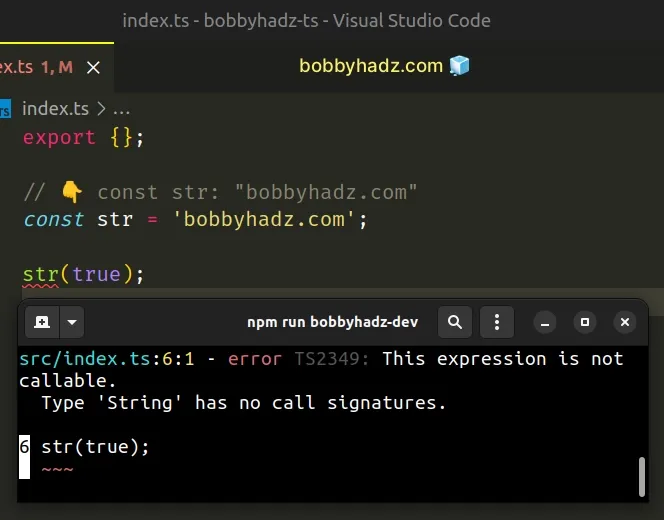
The example shows how trying to call a string as a function causes the error. The same is the case with any other type that is not callable.
Here is another example.
const num = 100; // ⛔️ Error: This expression is not callable. // Type 'Number' has no call signatures.ts(2349) num();
console.log the value you're trying to call.# Accessing a property on an object or class instance
If it isn't a function, then you might be forgetting to access a property on an object or a property on a class instance that points to a method.
function getFunc() { return { sum(a: number, b: number) { return a + b; }, }; } const result = getFunc(); // ⛔️ This expression is not callable. // Type '{ sum(a: number, b: number): number; }' has no call signatures.ts(2349) result();
The example shows that the function returns an object containing a sum method.
However, we try to invoke the object without accessing the sum property.
# Access the property that points to a method
To solve the error, we have to make sure we are accessing the correct property on the object - the one that points to a method.
function getFunc() { return { sum(a: number, b: number) { return a + b; }, }; } const result = getFunc(); console.log(result.sum(10, 50)); // 👉️ 60
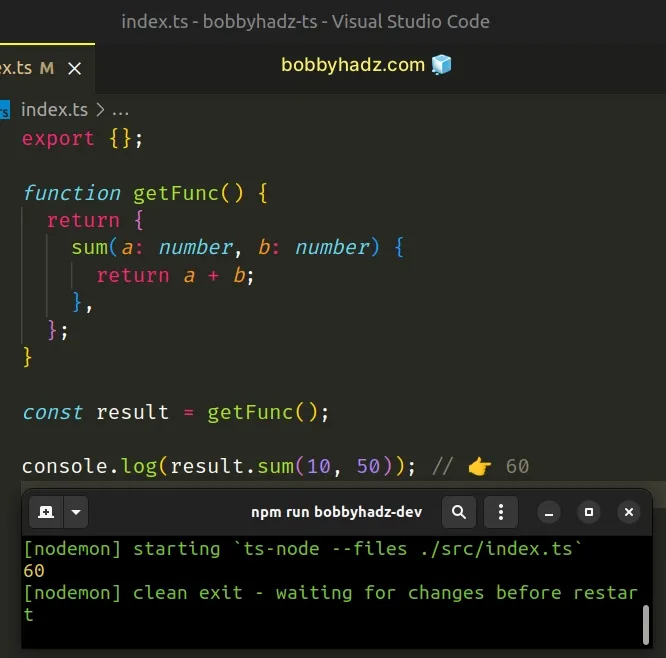
The sum property on the object is a method, so we can safely call it with
parentheses ().
# Importing an object instead of a function
This error often occurs when we import an object, instead of a function and try to directly call the object without accessing a property.
If you console.log the value and it is a function, then maybe your typings are
incorrect.
# Your function could have an incorrect type
Hover over the function you're trying to invoke and make sure it has a type of function.
function getFunc(): any { return (a: number, b: number) => { return a + b; }; } // 👇️ const result: Record<string, string> const result = getFunc() as Record<string, string>; // ⛔️ This expression is not callable. // Type 'Record<string, string>' has no call signatures.ts(2349) result(50, 40);
The example shows how somehow the function got assigned a different type somewhere in the codebase (most commonly caused by using type assertions).
result variable stores a function, we have told TypeScript that the type of the stored value is something else - something that has no call signatures.# Typing a function in TypeScript
Here are some examples of how to type a function using a type alias or an interface.
// 👇️ using Type Alias (for only function) 👇️ type FunctionA = (a: number, b: number) => number; const funcA: FunctionA = (a, b) => a + b; console.log(funcA(100, 100)); // ------------------------------------------------ // 👇️ Using interface (for only function) 👇️ interface FunctionB { (a: number, b: number): number; } const funcB: FunctionB = (a, b) => a + b; console.log(funcB(100, 200));
Here are 2 more examples.
// 👇️ Type Alias with other members 👇️ type DateThings = { date: string; getTimestamp: (str: string) => number; }; const d: DateThings = { date: '2023-09-24', getTimestamp(str) { return new Date(str).getTime(); }, }; console.log(d.getTimestamp('2024-04-16')); // ------------------------------------------------ // 👇️ Interface with other members 👇️ interface MathThings { sum: (a: number, b: number) => number; num: number; } const obj: MathThings = { num: 100, sum(a, b) { return a + b; }, }; console.log(obj.sum(50, 50));
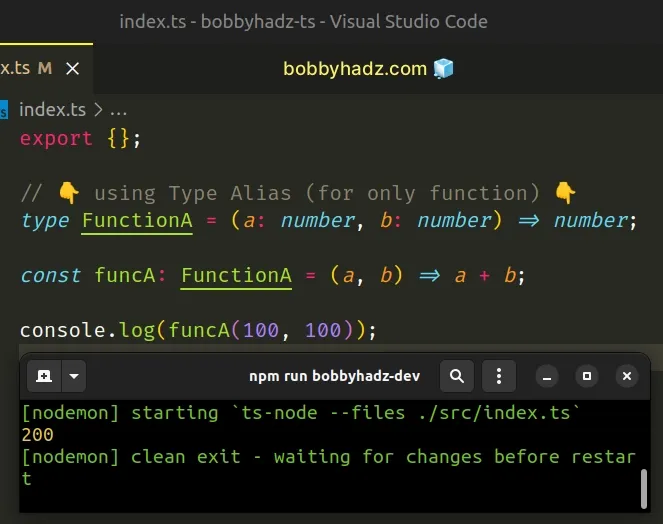
The first two examples show how to correctly type a function using a type alias or an interface that only represents a single function.
# Conclusion
To solve the "This expression is not callable. Type 'X' has no call signatures" TypeScript error:
- Make sure the value you are calling as a function is an actual function.
- Make sure the function is typed correctly.
- TypeScript won't let you call a function that is typed as something else.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to pass a Function as a Parameter in TypeScript
- Declare functions returning Object or Array in TypeScript
- Declare a function with a Promise return type in TypeScript
- How to Declare a Function that throws an Error in TypeScript
- How to Check the Type of a Variable in TypeScript
- Get the return Type of a Function in TypeScript
- Get Argument types for Function/Constructor in TypeScript

