Declare a Function with variable Number of Arguments in TS
Last updated: Feb 27, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Declare a Function with variable Number of Arguments in TS
Use rest parameters to declare a function with a variable number of arguments in TypeScript.
Rest parameters are used when a function takes an indefinite number of
arguments. They appear after all other parameters and use the ... syntax.
function getArgsAsArray(...args: string[]) { console.log(args); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c'] return args; } console.log(getArgsAsArray('a', 'b', 'c'));
Here is another example.
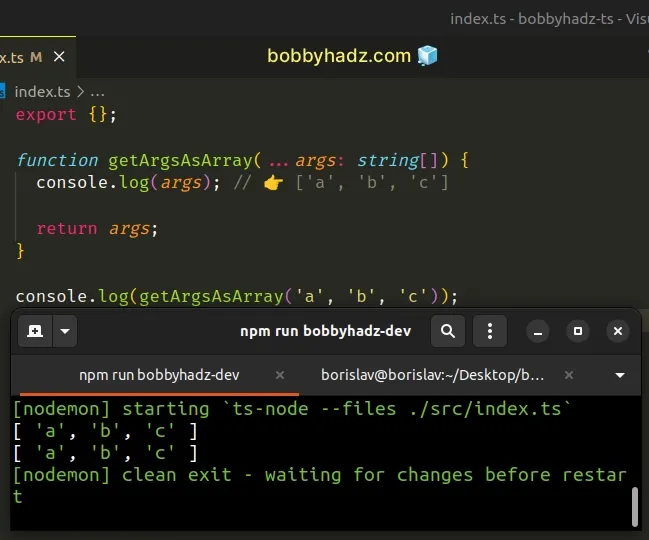
const multiply = (...numbers: number[]) => { console.log(numbers); return numbers.reduce((acc, curr) => acc * curr, 1); }; console.log(multiply(1, 2, 3, 4)); // 👉️ 24
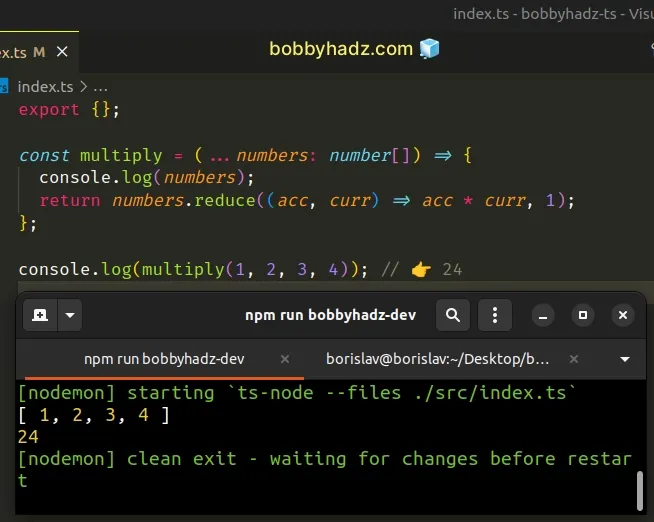
We used the rest parameters syntax to declare functions that take a variable number of arguments.
... syntax gathers the passed-in arguments into an array.Notice that we typed the rest parameters as Type[] and not Type. This is
because the ... syntax gathers all the passed-in parameters into an array.
When using rest parameters, make sure to explicitly type them because otherwise
they will be implicitly typed as any[].
# Rest parameters must come last
When using rest parameters, make sure they come last.
// 👇️ rest parameter must come last function getArgsAsArray(str: string, ...args: string[]) { console.log(str); // 👉️ 'a' console.log(args); // 👉️ ['b', 'c'] return args; } console.log(getArgsAsArray('a', 'b', 'c'));
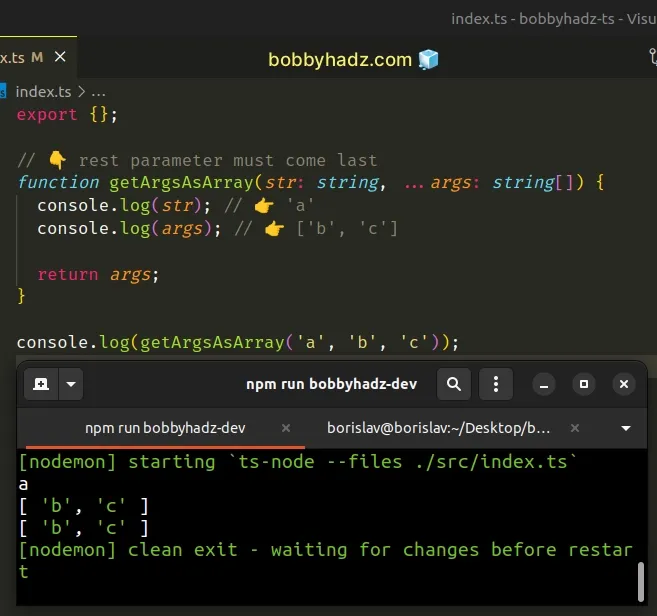
When using rest parameters, make sure to:
- Type the rest parameter as an array.
- Only use rest parameters at the end of the function's parameter list.
# Using a type alias or an interface
You can also use a type alias if your function declaration gets too busy.
type Multiply = (...numbers: number[]) => number; const multiply: Multiply = (...numbers) => { console.log(numbers); return numbers.reduce((acc, curr) => acc * curr, 1); }; console.log(multiply(1, 2, 3, 4)); // 👉️ 24
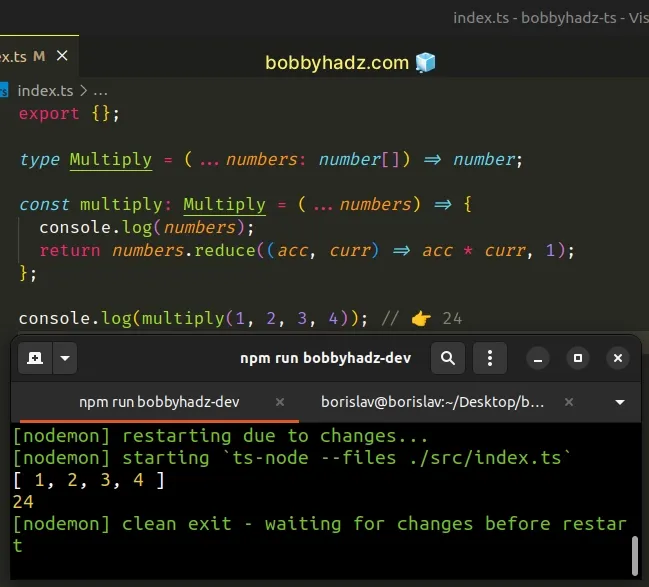
An easy way to think about the rest parameters syntax is:
- All of the passed-in values for the rest parameters are gathered into an array.
- Only the last parameter in a function definition can be a rest parameter.
Note that rest parameters are often confused with rest arguments.
Here is an example of using rest arguments.
// 👇️ this is rest parameters function logger(...args: string[]) { console.log(args); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c'] } const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c']; // 👇️ this is rest arguments logger(...arr);
Rest arguments use the ... syntax as well but are used when calling a function
and not when defining one.
The arr variable is an
array of strings, but the
logger() function takes multiple, comma-separated strings, so we can't pass it
an array of strings directly.
This is why we used rest arguments - to unpack the values of the array in the
call to the logger() function.
If you need to pass a function as a parameter, check out the following article.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

