A class member cannot have the 'const' keyword in TS [Fixed]
Last updated: Jan 23, 2023
Reading time·3 min

# A class member cannot have the 'const' keyword in TS
The error "A class member cannot have the 'const' keyword" occurs when we use
the const keyword to declare a property in a class.
To solve the error, remove the const keyword and use the readonly modifier
to indicate that a class property shouldn't be changed.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
class Employee { // ⛔️ A class member cannot have the 'const' keyword.ts(1248) const name = 'Bobby Hadz'; }
We can't use the const keyword when declaring a class property.
# Use the readonly modifier to solve the error
Instead, use the readonly modifier.
class Employee { readonly name = 'Bobby Hadz'; readonly age = 30; logName() { console.log(this.name); } } const emp = new Employee(); emp.logName(); // 👉️ "Bobby Hadz" console.log(emp.name); // 👉️ "Bobby Hadz"
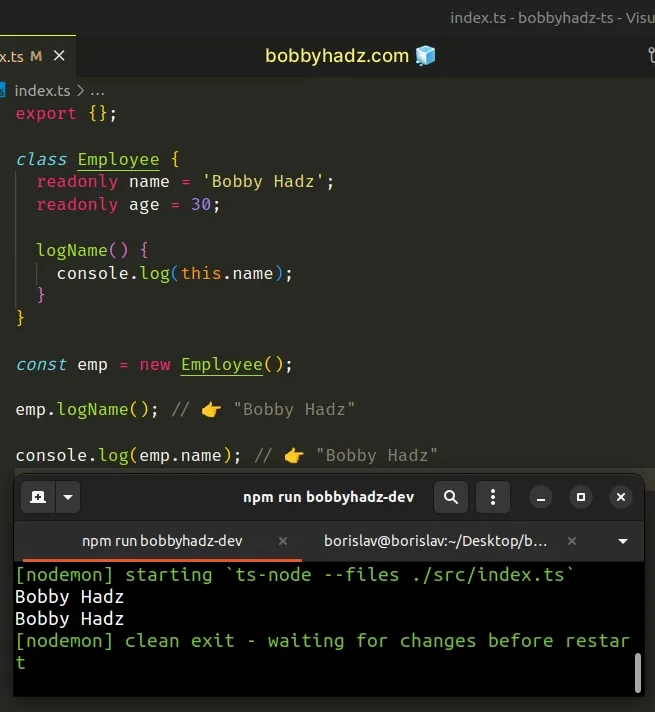
We used readonly modifiers to prevent assignment to class properties outside of the constructor.
When using this approach, we are still able to change the value of the properties inside of the constructor function.
class Employee { readonly name: string = 'Bobby Hadz'; readonly age: number = 30; constructor() { this.name = 'Freddy'; this.age = 29; } logName() { console.log(this.name); } } const emp = new Employee(); console.log(emp.name); // 👉️ "Freddy"
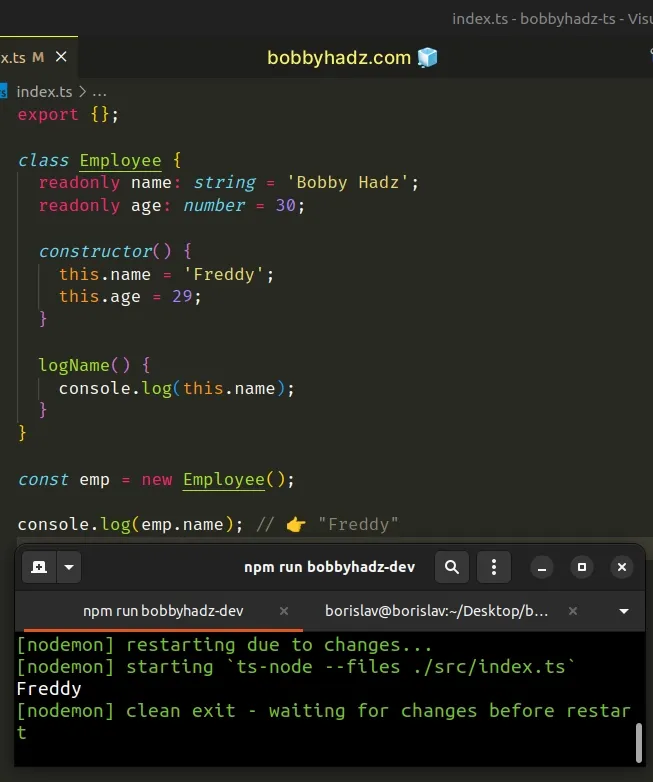
Assignment outside of the constructor would cause the type checker to issue an error.
class Employee { readonly name: string = 'Bobby Hadz'; readonly age: number = 30; constructor() { this.name = 'Freddy'; this.age = 29; } logName() { console.log(this.name); // ⛔️ Cannot assign to 'name' because it is a read-only property.ts(2540) this.name = 'Bobby'; } }
# Using the static keyword with readonly
If you don't want to be able to change the value in the constructor, use the
static
keyword with readonly.
export class Employee { // 👇️ public if you need to access from outside the class public static readonly department = 'Accounting'; // 👇️ private if you need to access only from inside this class private static readonly salary = 100; // 👇️ protected if you need to access only from this class // and its subclasses protected static readonly age = 30; logSalary() { console.log(Employee.salary); console.log(Employee.age); } } // 👇️ Access on class (NOT on instances) console.log(Employee.department);
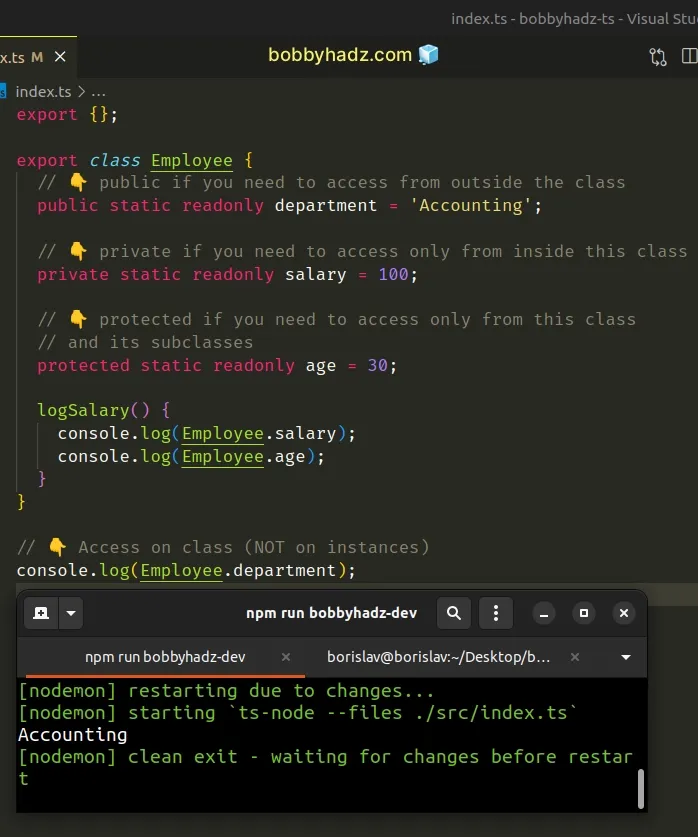
static keyword, we define static methods or properties. Static methods and properties aren't accessed on instances of the class, they are accessed on the class itself.The department property in the example is declared as
public.
Properties declared as public can be accessed anywhere.
public when you need to access the property from outside the class.Private visibility only allows access from inside the class.
Members marked as protected are only visible to the class itself and its subclasses.
Make sure you are accessing static properties and methods on the class, e.g.
Employee.myProperty, and not on instances of the class.
# Declaring a constant outside the class
If you don't like any of the approaches covered in this article, declare a constant outside of the class and use it in the class.
const name = 'Bobby Hadz'; export class Employee { logName() { console.log(name); } } const employee = new Employee(); employee.logName(); // 👉️ "Bobby Hadz"
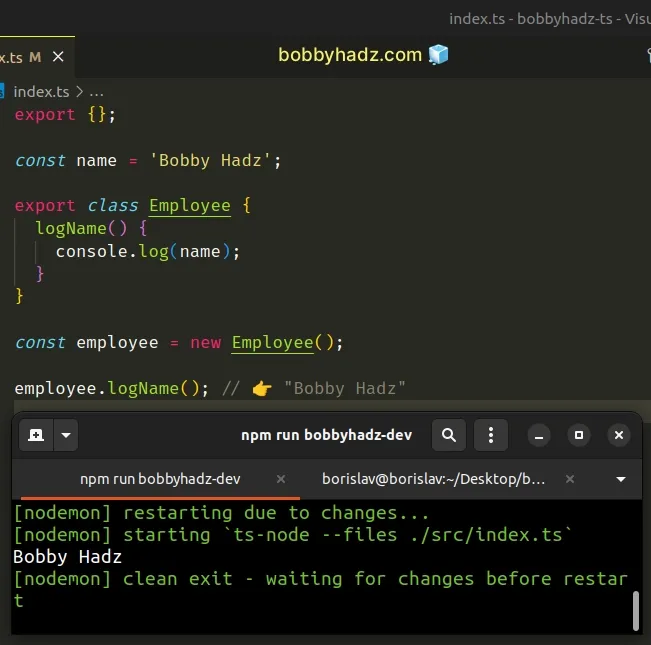
I've also written an article on how to change a read-only property to mutable.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

