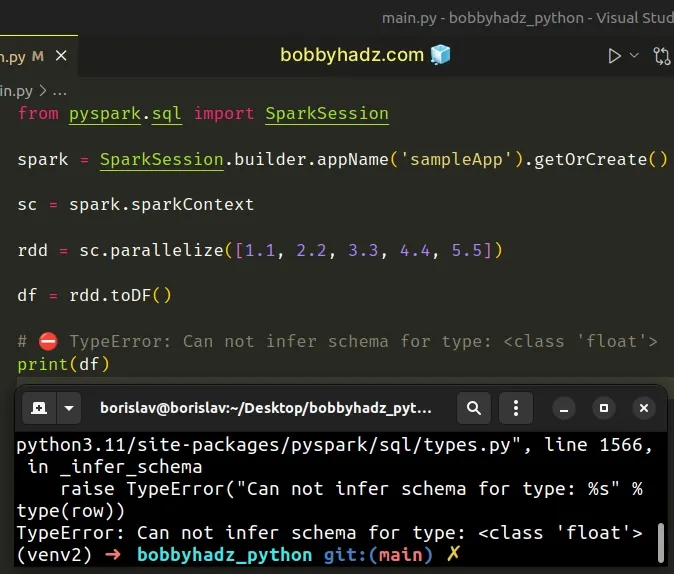
TypeError: Can not infer schema for type: <class 'float'>
Last updated: Apr 13, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# TypeError: Can not infer schema for type: <class 'float'>
The PySpark "TypeError: Can not infer schema for type: <class 'float'>" occurs
when you try to construct a DataFrame from float values.
To solve the error, try to convert the float values to tuples before calling
toDF().
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession spark = SparkSession.builder.appName('sampleApp').getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext rdd = sc.parallelize([1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5]) df = rdd.toDF() # ⛔️ TypeError: Can not infer schema for type: <class 'float'> print(df)
The rdd.toDF() method calls
createDataFrame()
under the hood.
The createDataFrame() method takes a data parameter that is an RDD of any
kind of SQL data representation (e.g. a Row, tuple, int, boolean) or list, or
pandas.DataFrame.
# Converting each float to a tuple containing a float
One way to solve the error is to convert each float to a tuple containing a float.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession spark = SparkSession.builder.appName('sampleApp').getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext rdd = sc.parallelize([1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5]) df = rdd.map(lambda x: (x, )).toDF() print(df)
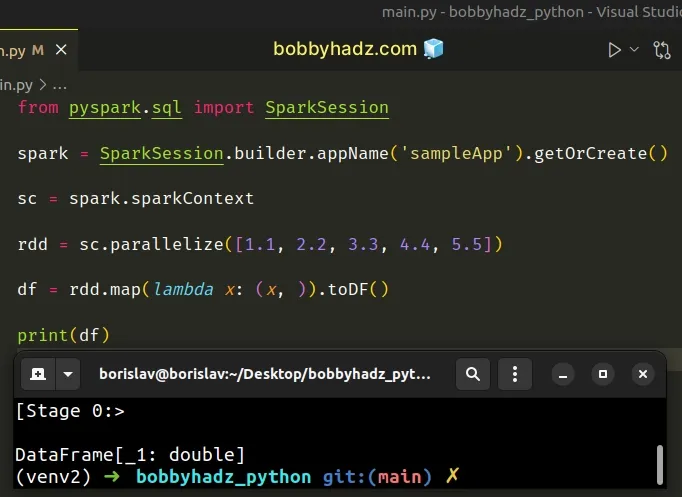
The map() function gets called with each float and returns a tuple containing the float.
You can also supply the column name when calling toDF().
df = rdd.map(lambda x: (x, )).toDF('column_name')
# Converting each float to a Row before calling toDF()
You can also solve the error by converting each float to a Row before calling
toDF().
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession, Row spark = SparkSession.builder.appName('sampleApp').getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext rdd = sc.parallelize([1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5]) row = Row('example') df = rdd.map(row).toDF() print(df) print('-' * 50) print(df.printSchema()) print('-' * 50) df.show()
Running the code sample produces the following output.
root |-- example: double (nullable = true) -------------------------------------------------- +-------+ |example| +-------+ | 1.1| | 2.2| | 3.3| | 4.4| | 5.5| +-------+
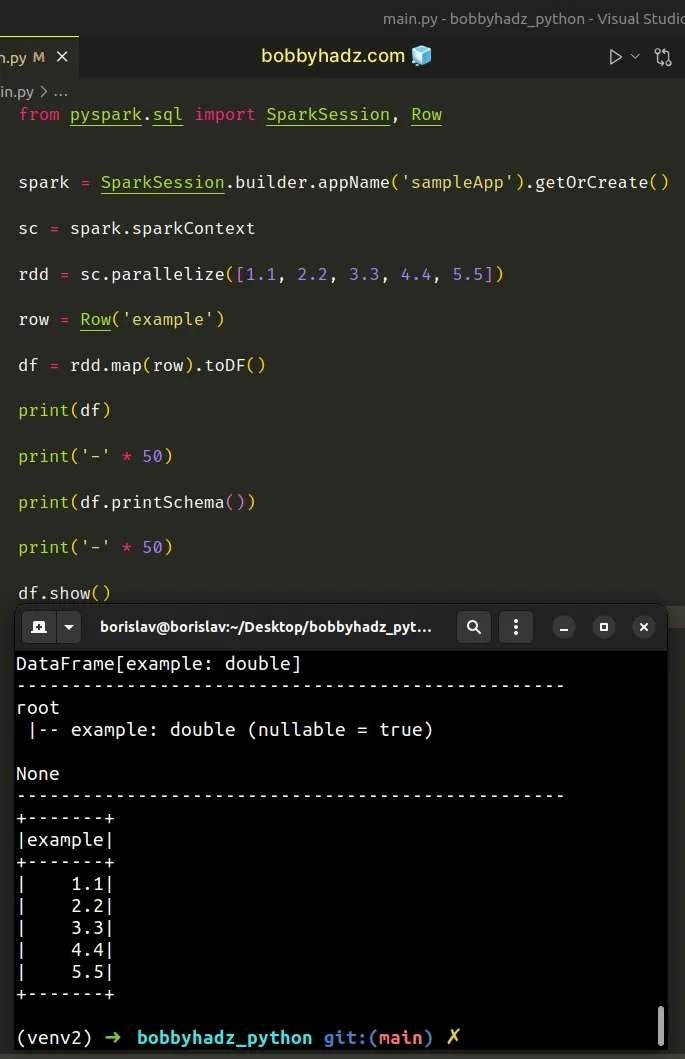
You can pass a different value to the Row class to give the column a different
name.
# Creating a DataFrame from a list of floats
If you need to create a DataFrame from a list of floats, pass the list and
instantiate the FloatType() class in the call to spark.createDataFrame().
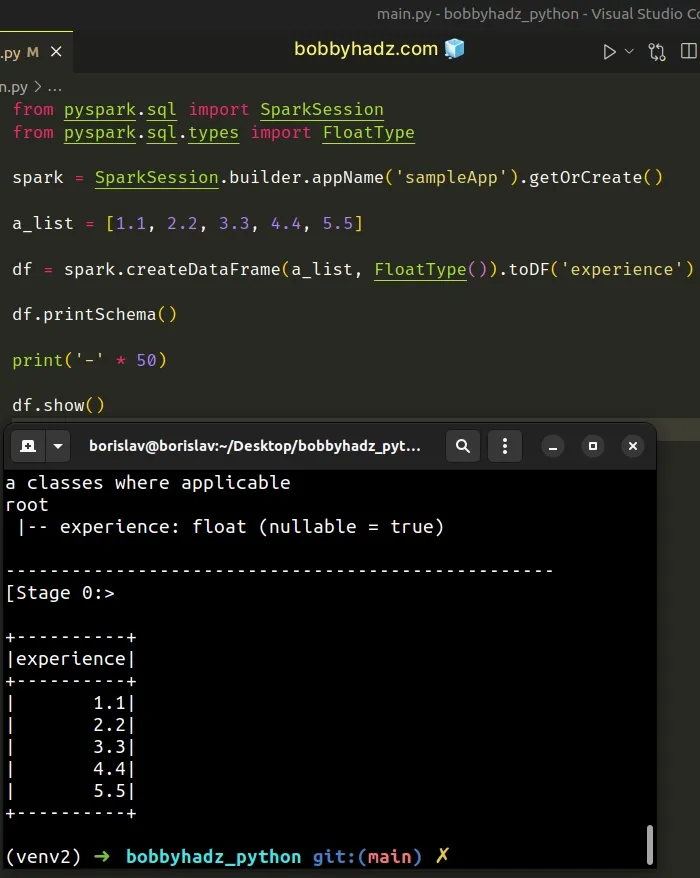
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession from pyspark.sql.types import FloatType spark = SparkSession.builder.appName('sampleApp').getOrCreate() a_list = [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5] df = spark.createDataFrame(a_list, FloatType()) df.printSchema() print('-' * 50) df.show()
Running the code sample produces the following output.
root |-- value: float (nullable = true) -------------------------------------------------- [Stage 0:> +-----+ |value| +-----+ | 1.1| | 2.2| | 3.3| | 4.4| | 5.5| +-----+
If you want to give a name to the column, use the toDF() method.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession from pyspark.sql.types import FloatType spark = SparkSession.builder.appName('sampleApp').getOrCreate() a_list = [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5] df = spark.createDataFrame(a_list, FloatType()).toDF('experience') df.printSchema() print('-' * 50) df.show()
Running the code sample produces the following output.
root |-- experience: float (nullable = true) -------------------------------------------------- [Stage 0:> +----------+ |experience| +----------+ | 1.1| | 2.2| | 3.3| | 4.4| | 5.5| +----------+
Alternatively, you can use a list comprehension.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession spark = SparkSession.builder.appName('sampleApp').getOrCreate() a_list = [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5] df = spark.createDataFrame([(float(x), ) for x in a_list]).toDF('experience') df.printSchema() print('-' * 50) df.show()
Running the code sample produces the following output.
root |-- experience: double (nullable = true) -------------------------------------------------- [Stage 0:> +----------+ |experience| +----------+ | 1.1| | 2.2| | 3.3| | 4.4| | 5.5| +----------+
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element, or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
df = spark.createDataFrame([(float(x), ) for x in a_list]).toDF('experience')
On each iteration, we return a tuple containing each float.
# TypeError: Can not infer schema for type: <class 'str'>
You might also get the "TypeError: Can not infer schema for type: <class 'str'>"
error if you pass a row object to the spark.createDataFrame() method.
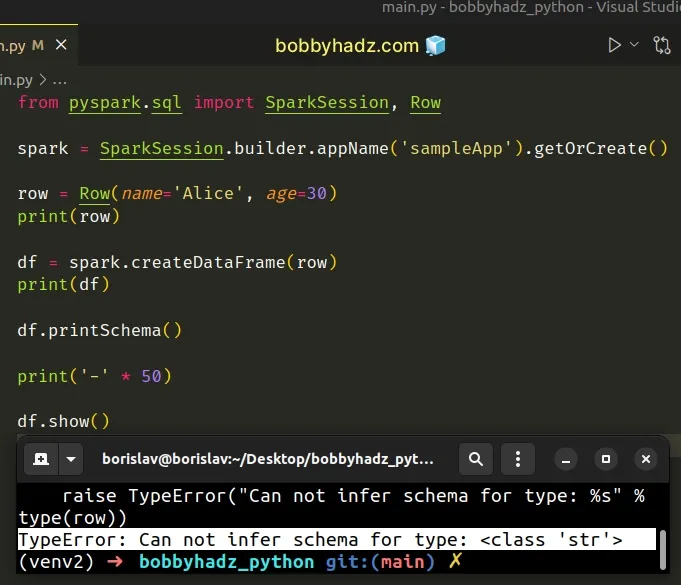
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession, Row spark = SparkSession.builder.appName('sampleApp').getOrCreate() row = Row(name='Alice', age=30) print(row) # ⛔️ TypeError: Can not infer schema for type: <class 'str'> df = spark.createDataFrame(row) print(df) df.printSchema() print('-' * 50) df.show()
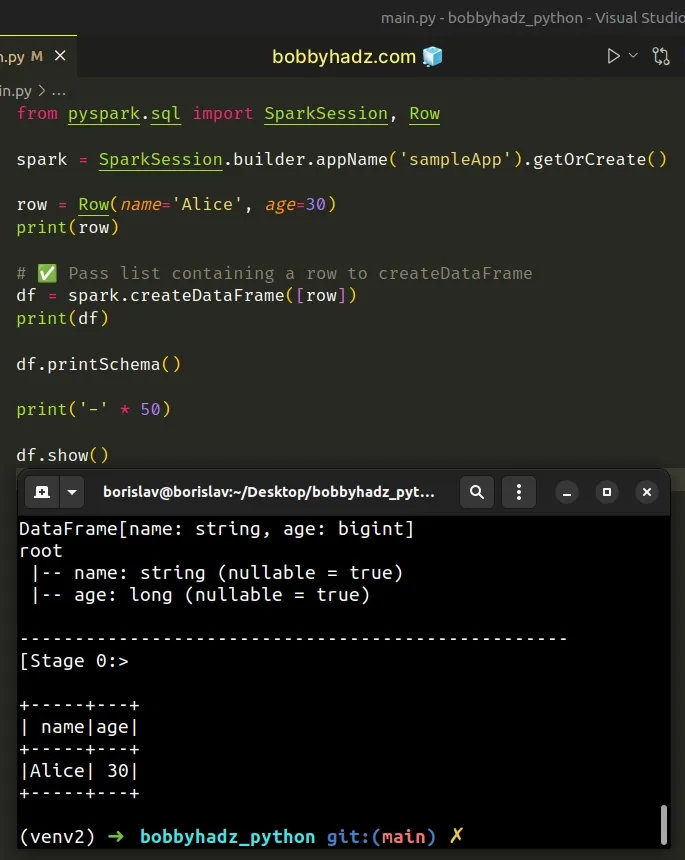
You can solve the error by passing a list containing a row object to
createDataFrame().
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession, Row spark = SparkSession.builder.appName('sampleApp').getOrCreate() row = Row(name='Alice', age=30) print(row) # ✅ Pass list containing a row to createDataFrame df = spark.createDataFrame([row]) print(df) df.printSchema() print('-' * 50) df.show()
Running the code sample produces the following output.
DataFrame[name: string, age: bigint] root |-- name: string (nullable = true) |-- age: long (nullable = true) -------------------------------------------------- [Stage 0:> +-----+---+ | name|age| +-----+---+ |Alice| 30| +-----+---+
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Multiply each element in a List by a Number in Python
- Remove the Max and Min numbers from a List in Python
- Subtract a Value from every Number in a List in Python
- OpenCV TypeError: Expected cv::UMat for argument [Solved]
- OSError: [E050] Can't find model 'en_core_web_sm'
- ssl.SSLError: [SSL: WRONG_VERSION_NUMBER] wrong version number (_ssl.c:1002)

