How to Remove \ufeff from a String in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Remove \ufeff from a string in Python
Use the str.replace() method to remove \ufeff BOM character from a string.
The replace() method will remove the \ufeff character from the string by
replacing it with an empty string.
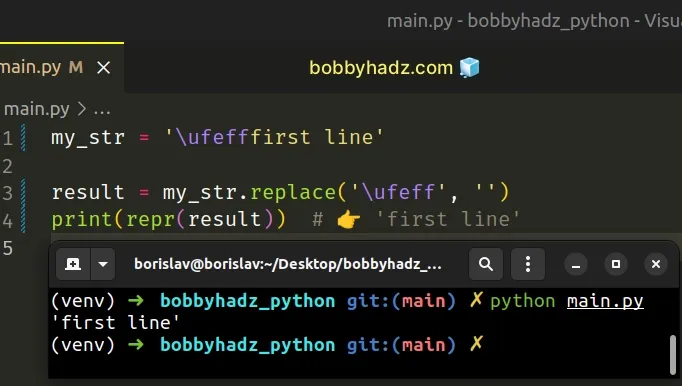
my_str = '\ufefffirst line' result = my_str.replace('\ufeff', '') print(repr(result)) # 👉️ 'first line'
The \ufeff character is a byte order mark (BOM) and is interpreted as a
zero-width non-breaking space.
If you have a string that contains a BOM character, use the str.replace()
method to remove it.
my_str = '\ufefffirst line' result = my_str.replace('\ufeff', '') print(repr(result)) # 👉️ 'first line'
The str.replace method returns a copy of the string with all occurrences of a substring replaced by the provided replacement.
The method takes the following parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| old | The substring we want to replace in the string |
| new | The replacement for each occurrence of old |
| count | Only the first count occurrences are replaced (optional) |
The method doesn't change the original string. Strings are immutable in Python.
# Set the encoding to utf-8-sig when opening a file
If you got the error "UnicodeEncodeError: 'ascii' codec can't encode character
u'\ufeff'" when trying to read from a file, explicitly set the
encoding keyword argument
to utf-8-sig.
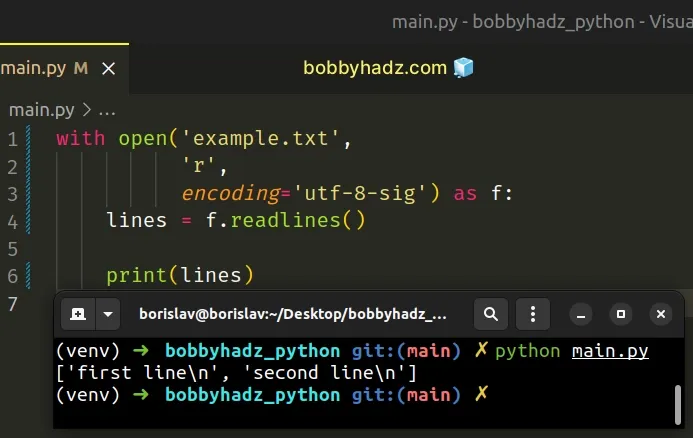
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8-sig') as f: lines = f.readlines() print(lines)
The
open() function
takes an encoding keyword argument, which can be set to utf-8-sig to treat
the byte order mark as metadata instead of a string.
When decoding, the utf-8-sig codec skips the BOM byte if it appears as the
first byte in the file.
When using the utf-8 encoding, the use of the byte order mark (BOM) is
discouraged and should be avoided.
# The \ufeff character should automatically get removed
The \ufeff Unicode character should automatically get removed if you decode
the bytes using the correct encoding.
For example, the utf-8-sig encoding is used to encode with BOM.
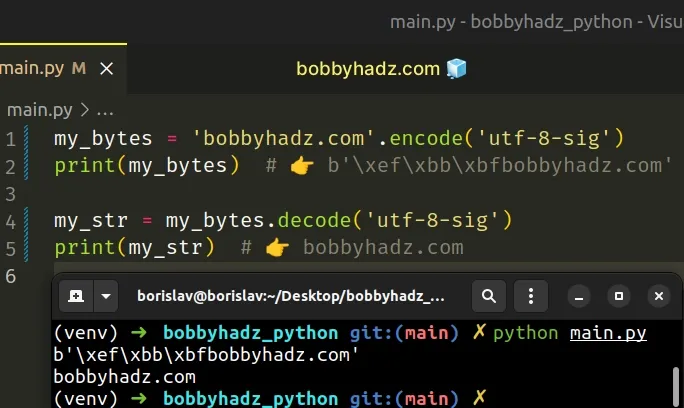
my_bytes = 'bobbyhadz.com'.encode('utf-8-sig') print(my_bytes) # 👉️ b'\xef\xbb\xbfbobbyhadz.com' my_str = my_bytes.decode('utf-8-sig') print(my_str) # 👉️ bobbyhadz.com
If you decode the bytes with the same encoding, the \ufeff character gets
automatically removed.
The utf-16 encoding also encodes with BOM.
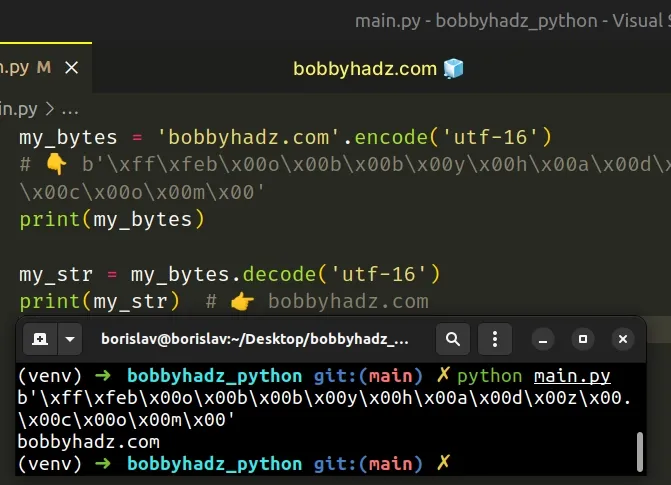
my_bytes = 'bobbyhadz.com'.encode('utf-16') # 👇️ b'\xff\xfeb\x00o\x00b\x00b\x00y\x00h\x00a\x00d\x00z\x00.\x00c\x00o\x00m\x00' print(my_bytes) my_str = my_bytes.decode('utf-16') print(my_str) # 👉️ bobbyhadz.com
On the other hand, the utf-8 encoding encodes without BOM.
my_bytes = 'bobbyhadz.com'.encode('utf-8') print(my_bytes) # 👉️ b'bobbyhadz.com' my_str = my_bytes.decode('utf-8') print(my_str) # 👉️ bobbyhadz.com
The Byte Order Mark should only appear at the start of a document and should automatically get removed when the correct encoding is used.
If you don't know the correct encoding, use the str.replace() method to remove
the character from the string.
my_str = '\ufeffbobbyhadz.com' result = my_str.replace('\ufeff', '') print(repr(result)) # 👉️ 'bobbyhadz.com'
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to Remove \xa0 from a String in Python
- Remove punctuation from a List of strings in Python
- How to remove Quotes from a List of Strings in Python
- Remove characters matching Regex from a String in Python
- Remove special characters except Space from String in Python
- Remove square brackets from a List or a String in Python
- How to Remove the Tabs from a String in Python
- ValueError: pattern contains no capture groups [Solved]
- Pandas: How to efficiently Read a Large CSV File

