Remove the First or Last item from a Dictionary in Python
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Remove the First item from a Dictionary in Python
- Remove the Last element from a Dictionary in Python
- Remove all keys except one from a Dictionary in Python
# Remove the first item from a Dictionary in Python
To remove the first item from a dictionary:
- Use the
next()function to get the first key in the dictionary. - Use the
dict.pop()method to remove the first key from the dictionary.
a_dict = { 'site': 'bobbyhadz.com', 'topic': 'Python', 'id': 100 } first_key = next(iter(a_dict)) print(first_key) # 👉️ site first_value = a_dict.pop(first_key) print(first_value) # 👉️ bobbyhadz.com print(a_dict) # 👉️ {'topic': 'Python', 'id': 100}
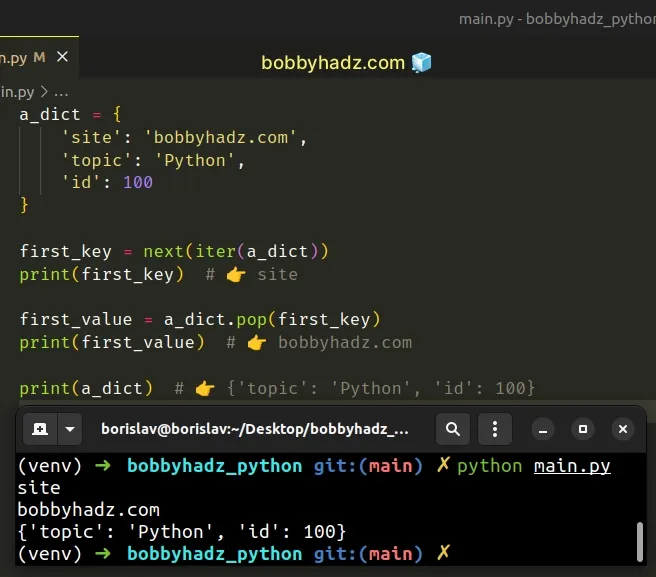
In the first example, we used the iter() function to get an iterator object from the dictionary's keys.
a_dict = { 'site': 'bobbyhadz.com', 'topic': 'Python', 'id': 100 } # 👇️ <dict_keyiterator object at 0x7fc0bbfbdad0> print(iter(a_dict)) first_key = next(iter(a_dict)) print(first_key) # 👉️ site
The next function returns the next item from the iterator.
If the dictionary is empty, the next() function would raise a StopIteration
exception.
# Making sure the dictionary isn't empty before removing the item
You can use an if statement if you need to make sure the dictionary isn't
empty before removing the first item.
a_dict = {} if len(a_dict) != 0: first_key = next(iter(a_dict)) print(first_key) # 👉️ site first_value = a_dict.pop(first_key) print(first_value) # 👉️ bobbyhadz.com
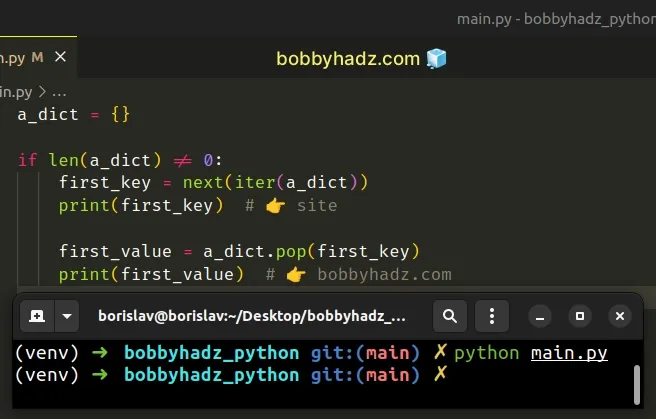
We used the len() function to make sure the dictionary isn't empty before
removing the first key.
# Remove the last element from a Dictionary in Python
Use the dict.popitem() method to remove the last element from a dictionary.
The method removes and returns the last key-value pair from the dictionary.
a_dict = { 'site': 'bobbyhadz.com', 'topic': 'Python', 'id': 100 } last = a_dict.popitem() print(last) # 👉️ ('id', 100) print(last[0]) # 👉️ id print(last[1]) # 👉️ 100
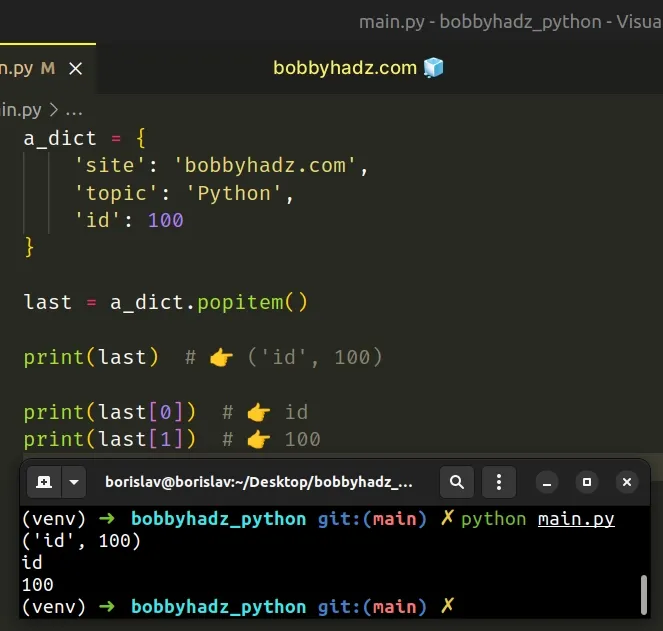
The dict.popitem() method removes and returns a (key, value) pair from the dictionary.
The key-value pair that was last added to the dictionary is returned first.
# Remove the first item from a Dictionary using del
You can also use the del if you need to just remove the key without retrieving
the value.
a_dict = { 'site': 'bobbyhadz.com', 'topic': 'Python', 'id': 100 } first_key = next(iter(a_dict)) print(first_key) # 👉️ site del a_dict[first_key] print(a_dict) # 👉️ {'topic': 'Python', 'id': 100}
The del statement removes an item from a dictionary by key.
# Remove the last element from a Dictionary using dict.pop()
To remove the last element from a dictionary:
- Use the
dict.keys()method to get a view of the dictionary's keys. - Convert the view object to a list.
- Get the last key from the list.
- Use the
dict.pop()method to remove the last element from the dictionary.
a_dict = { 'id': 1, 'site': 'bobbyhadz.com', 'topic': 'Python' } last_key = list(a_dict.keys())[-1] print(last_key) # 👉️ topic last_value = a_dict.pop(last_key) print(last_value) # 👉️ Python
The dict.keys() method returns a new view of the dictionary's keys.
a_dict = { 'id': 1, 'site': 'bobbyhadz.com', 'topic': 'Python' } keys = a_dict.keys() print(keys) # 👉️ dict_keys(['id', 'site', 'topic'])
View objects cannot be accessed at a specific index, so we had to convert the view object to a list.
We then accessed the list at index -1 to get the last key.
The last step is to use the dict.pop() method to remove the last element from
the dictionary.
dict.pop() method removes the specified key and returns the corresponding value.You can also use the reversed() function to
get the last key in a dictionary.
a_dict = { 'id': 1, 'site': 'bobbyhadz.com', 'topic': 'Python' } last_key = next(reversed(a_dict.keys())) print(last_key) # 👉️ topic last_value = a_dict.pop(last_key, 'default value') print(last_value) # 👉️ Python
The reversed function takes an iterator, reverses it and returns the result.
The next() function returns the next item from the provided iterator.
# Remove all keys except one from a Dictionary in Python
To remove all keys except one from a dictionary:
- Declare a new variable and initialize it to a dictionary.
- Assign the key you want to keep and its value to the new dictionary.
a_dict = { 'id': 1, 'first': 'bobby', 'last': 'hadz', 'site': 'bobbyhadz.com', 'topic': 'Python' } key_to_keep = 'site' new_dict = {key_to_keep: a_dict[key_to_keep]} print(new_dict) # 👉️ {'site': 'bobbyhadz.com'}
The first code sample removes all dictionary keys except one.
We basically create a new dictionary that only contains the key we want to keep.
This approach is much faster than iterating over the entire dictionary and checking if each key is the one to be kept.
# Remove all dictionary keys except multiple, specific keys
If you need to remove all dictionary keys except multiple, specific keys, use a dict comprehension.
a_dict = { 'id': 1, 'first': 'bobby', 'last': 'hadz', 'site': 'bobbyhadz.com', 'topic': 'Python' } keys_to_keep = ['first', 'site', 'topic'] new_dict = { key: a_dict[key] for key in keys_to_keep } # 👇️ {'first': 'bobby', 'site': 'bobbyhadz.com', 'topic': 'Python'} print(new_dict)
We stored the keys we wanted to keep in a list and used a dict comprehension to iterate over the list of keys.
Dict comprehensions are very similar to list comprehensions.
On each iteration, we return the current key and the corresponding value.
The new dictionary only contains the key-value pairs we want to keep.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

