ImportError: cannot import name 'url' from django.conf.urls
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·11 min
# Table of Contents
- ImportError: cannot import name 'url' from django.conf.urls
- Cannot import name 'force_text' from django.utils.encoding
- Cannot import name 'smart_text' from django.utils.encoding
- Cannot import name 'ugettext_lazy' from django.utils.translation
Make sure to click on the correct subheading depending on your error message.
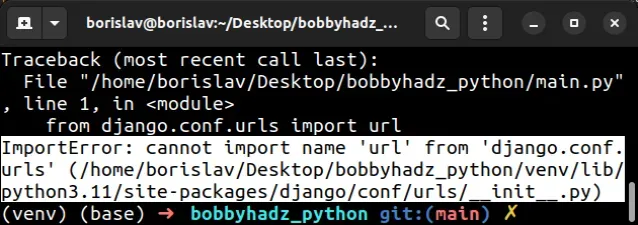
# ImportError: cannot import name 'url' from django.conf.urls
The "ImportError: cannot import name 'url' from 'django.conf.urls'" occurs
because django.conf.urls.url() has been deprecated and removed in version 4 of
Django.
To solve the error, import and use the re_path() method instead.
ImportError: cannot import name 'url' from 'django.conf.urls' (/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/django/conf/urls/__init__.py)
As the
release notes
state, django.conf.urls.url() has been deprecated starting version 3 and has
been removed in version 4 of Django.
# Change your import statements to use re_path
The first thing you should try is to change your import statements to use the
re_path method from django.urls instead.
from django.urls import include, re_path urlpatterns = [ re_path(r'^$', views.home, name='home'), re_path(r'^index/$', views.index, name='index'), re_path(r'^bio/(?P<username>\w+)/$', views.bio, name='bio'), re_path(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls')), # ... ]
You can read more about how the re_path() function works in
this section of the docs.
# Alternatively, use the path() function
Alternatively, you can use the path function.
from django.urls import include, path urlpatterns = [ path('', views.home, name='home'), path('index/', views.index, name='main-view'), path('bio/<username>/', views.bio, name='bio'), path('articles/<slug:title>/', views.article, name='article-detail'), path('articles/<slug:title>/<int:section>/', views.section, name='article-section'), path('blog/', include('blog.urls')), # ... ]
# Aliasing re_path to url in your code
If you're looking for a quick and hacky solution, you can try to alias re_path
to url.
# ✅ New import (alias re_path as url) from django.urls import include, re_path as url
If you decide to use this approach, you have to replace all occurrences of the following import statement with the aliased import statement above.
# ⛔️ Old import (Django older than v4) from django.conf.urls import url
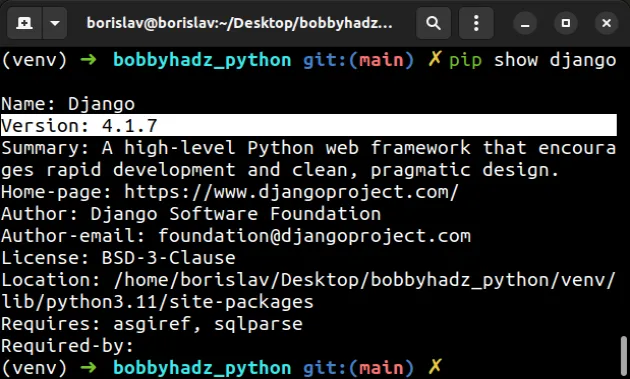
You can check which version of Django your project uses with the
pip show django command.
pip show django pip3 show django python -m pip show django python3 -m pip show django
# Downgrading Django to an older version
If you have other packages in your environment that use the deprecated
django.conf.urls.url() function, you can try downgrading Django to version
3.2.16, or the last version prior to version 4.
You can check all of the available versions of Django in this section of the package's pypi page.
pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall pip3 install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ If you don't have pip in PATH environment variable python -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall python3 -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ py alias (Windows) py -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ For Jupyter Notebook !pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall
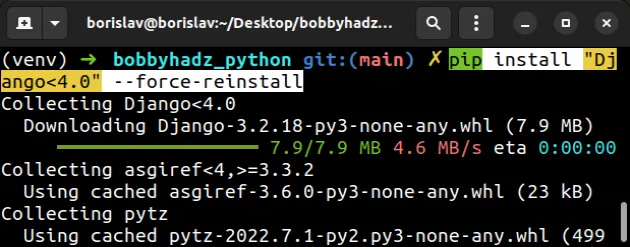
The --force-reinstall option
forces pip to reinstall the package.
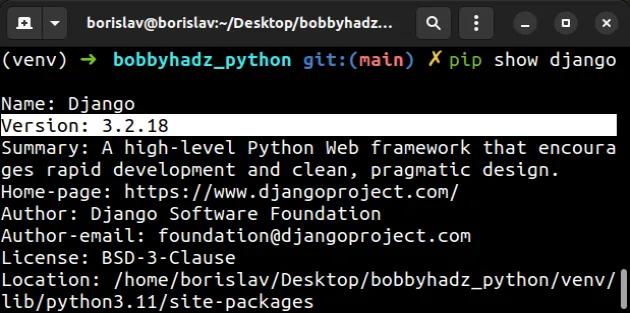
You can check which version of Django your project uses with the
pip show django command.
pip show django pip3 show django python -m pip show django python3 -m pip show django
If you use Django version 3, you can import url from django.conf.urls.
from django.conf.urls import url
If none of the suggestions helped and the error isn't caused in your code by
importing the deprecated django.conf.urls.url() function, try to upgrade all
packages in your environment.
# Upgrade all packages in your environment
The most straightforward way to upgrade all outdated packages is to use a Python script.
import pkg_resources from subprocess import call packages = [dist.project_name for dist in pkg_resources.working_set] call("pip install --upgrade " + ' '.join(packages), shell=True)
main.py and run the file with python main.py to upgrade all of the outdated packages.Here are alternative commands you can use to upgrade all outdated packages.
# 👇️ macOS or Linux pip install -U `pip list --outdated | awk 'NR>2 {print $1}'` # 👇️ Windows for /F "delims= " %i in ('pip list --outdated') do pip install -U %i
If you use a requirements.txt file, you can update it with the following command.
pip freeze > requirements.txt
# Table of Contents
- Cannot import name 'force_text' from django.utils.encoding
- Cannot import name 'smart_text' from django.utils.encoding
- Cannot import name 'ugettext_lazy' from django.utils.translation
# Cannot import name 'force_text' from django.utils.encoding
The "ImportError: cannot import name 'force_text' from
'django.utils.encoding'" occurs because the force_text method has been removed
and replaced by force_str starting Django version 4.
To solve the error, upgrade the package that caused the issue and correct any import statements.
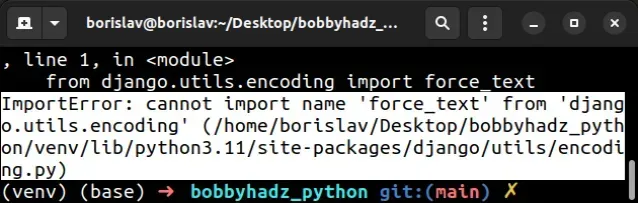
ImportError: cannot import name 'force_text' from 'django.utils.encoding' (/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/django/utils/encoding.py)
# Table of Contents
Make sure to click on the correct subheading depending on your error message.
- Cannot import name 'force_text' from django.utils.encoding
- Cannot import name 'smart_text' from django.utils.encoding
- Cannot import name 'ugettext_lazy' from django.utils.translation
As the
release notes
state, django.utils.encoding.force_text has been removed in version 4 of
Django.

# Having an outdated package that imports force_text
The most common cause of the error is having an outdated package that tries to
import force_text from django.utils.encoding.
The most common packages are:
- graphene-django
- django-elasticsearch-dsl
- djangorestframework-simplejwt
- django-smart-selects
- django-debug-toolbar
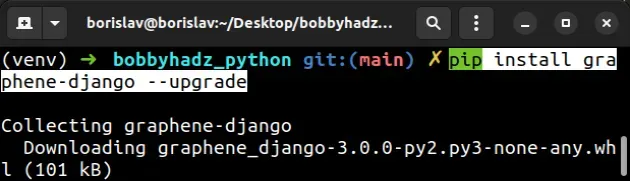
You can upgrade a package by using the --upgrade option at the end of the
pip install command.
# 👇️ Upgrade graphene-django pip install graphene-django --upgrade pip3 install graphene-django --upgrade # --------------------------------------- # 👇️ Upgrade django-elasticsearch-dsl pip install django-elasticsearch-dsl --upgrade pip3 install django-elasticsearch-dsl --upgrade # --------------------------------------- # 👇️ Upgrade djangorestframework-simplejwt pip install djangorestframework-simplejwt --upgrade pip3 install djangorestframework-simplejwt --upgrade # --------------------------------------- # 👇️ Upgrade django-smart-selects pip install django-smart-selects --upgrade pip3 install django-smart-selects --upgrade # --------------------------------------- # 👇️ Upgrade django-debug-toolbar pip install django-debug-toolbar --upgrade pip3 install django-debug-toolbar --upgrade
# Update your import statements to use force_str
If the error occurred in your code, you have to replace any occurrences of the following import.
# ⛔️ Old import (Django < v4) from django.utils.encoding import force_text
With the following import.
# ✅ Correct import statement (Django v4+) from django.utils.encoding import force_str
Starting Django v4, you should be using
force_str
instead of the deprecated and removed force_text.
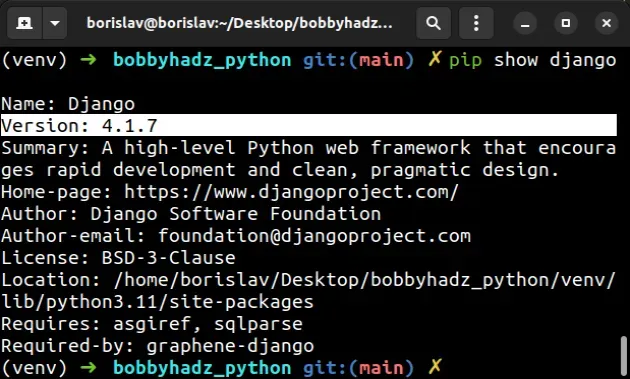
You can check which version of Django
your project uses with the pip show django command.
pip show django pip3 show django python -m pip show django python3 -m pip show django
# Patching the error in your settings.py file
If none of the solutions helped, you can add the following code sample at the
top of your settings.py file.
import django from django.utils.encoding import force_str django.utils.encoding.force_text = force_str
force_str method and sets the force_text attribute to force_str, so that if any modules try to access force_text, they'd access force_str instead.# Downgrading your version of Django
Another approach, which I don't recommend, is to:
- remove the 3 lines above from your
settings.pyfile. - downgrade Django to the last version that contains the
force_textmethod and keep the old import statements.
pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall pip3 install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ If you don't have pip in PATH environment variable python -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall python3 -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ py alias (Windows) py -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ For Jupyter Notebook !pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall

The --force-reinstall option
forces pip to reinstall the package.
When you run the command, you might get an error that states "ERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed.".
If you use Django version 3, you can use the following import statement in your code.
# 👇️ Code for Django version 3.X from django.utils.encoding import force_text print(force_text)
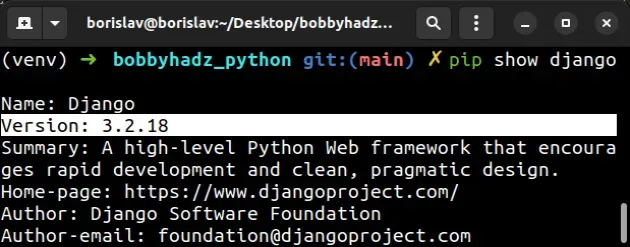
You can check which version of Django your project uses with the
pip show django command.
pip show django pip3 show django python -m pip show django python3 -m pip show django
If none of the suggestions helped and the error isn't caused in your code by
importing the deprecated force_text function, try to upgrade all packages in
your environment.
# Upgrade all packages in your environment
The most straightforward way to upgrade all outdated packages is to use a Python script.
import pkg_resources from subprocess import call packages = [dist.project_name for dist in pkg_resources.working_set] call("pip install --upgrade " + ' '.join(packages), shell=True)
main.py and run the file with python main.py to upgrade all of the outdated packages.Here are alternative commands you can use to upgrade all outdated packages.
# 👇️ macOS or Linux pip install -U `pip list --outdated | awk 'NR>2 {print $1}'` # 👇️ Windows for /F "delims= " %i in ('pip list --outdated') do pip install -U %i
If you use a requirements.txt file, you can update it with the following command.
pip freeze > requirements.txt
After upgrading Django to the latest version, make sure to use the following import.
# 👇️ Correct import statement (Django v4+) from django.utils.encoding import force_str
# Table of Contents
- Cannot import name 'smart_text' from django.utils.encoding
- Cannot import name 'ugettext_lazy' from django.utils.translation
# Cannot import name 'smart_text' from django.utils.encoding
The "ImportError: cannot import name 'smart_text' from
'django.utils.encoding'" occurs because the smart_text method has been removed
and replaced by smart_str starting Django version 4.
To solve the error, upgrade the package that caused the issue and correct any import statements.
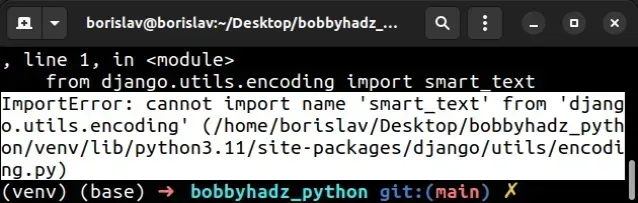
ImportError: cannot import name 'smart_text' from 'django.utils.encoding' (/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/django/utils/encoding.py)
As the
release notes
state, django.utils.encoding.smart_text has been removed in version 4 of
Django.
# Having an outdated package with an incorrect import
The most common cause of the error is having an outdated package that tries to
import smart_text from django.utils.encoding.
The most common packages are:
You can upgrade a package by using the --upgrade option at the end of the
pip install command.
# 👇️ Upgrade django-admin-charts pip install django-admin-charts --upgrade # 👇️ Upgrade graphene-django pip install graphene-django --upgrade # 👇️ Upgrade django-elasticsearch-dsl pip install django-elasticsearch-dsl --upgrade
# Update the import statements in your code
If the error occurred in your code, you have to replace any occurrences of the following import.
# 👇️ Old import (Django < v4) from django.utils.encoding import smart_text
With the following import.
# 👇️ Correct import statement (Django v4+) from django.utils.encoding import smart_str
Starting Django v4, you should be using
smart_str
instead of the deprecated and removed smart_text.
You can check which version of Django your project uses with the
pip show django command.
pip show django pip3 show django python -m pip show django python3 -m pip show django
# Patching the error in your settings.py file
If none of the solutions helped, you can add the following code sample at the
top of your settings.py file.
import django from django.utils.encoding import smart_str django.utils.encoding.smart_text = smart_str
smart_str method and sets the smart_text attribute to smart_str, so that if any modules try to access smart_text, they'd access smart_str instead.# Downgrading your version of Django
Another approach, which I don't recommend, is to:
- remove the 3 lines above from your
settings.pyfile. - downgrade Django to the last version that contains the
smart_textmethod and keep the old import statements.
pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall pip3 install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ If you don't have pip in PATH environment variable python -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall python3 -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ py alias (Windows) py -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ For Jupyter Notebook !pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall
When you run the command, you might get an error that states "ERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed.".
If you use Django version 3, you can use the following import statement in your code.
from django.utils.encoding import smart_text print(smart_text)
If none of the suggestions helped and the error isn't caused in your code by
importing the deprecated smart_text function, try to upgrade all packages in
your environment.
# Upgrade all packages in your environment
The most straightforward way to upgrade all outdated packages is to use a Python script.
import pkg_resources from subprocess import call packages = [dist.project_name for dist in pkg_resources.working_set] call("pip install --upgrade " + ' '.join(packages), shell=True)
main.py and run the file with python main.py to upgrade all of the outdated packages.Here are alternative commands you can use to upgrade all outdated packages.
# 👇️ macOS or Linux pip install -U `pip list --outdated | awk 'NR>2 {print $1}'` # 👇️ Windows for /F "delims= " %i in ('pip list --outdated') do pip install -U %i
If you use a requirements.txt file, you can update it with the following
command.
pip freeze > requirements.txt
After upgrading Django to the latest version, make sure to use the following import.
# 👇️ Correct import statement (Django v4+) from django.utils.encoding import smart_str
# Cannot import name 'ugettext_lazy' from django.utils.translation
The "ImportError: cannot import name 'ugettext_lazy' from
'django.utils.translation'" occurs because ugettext_lazy function has been
deprecated and removed starting Django version 4.
To solve the error, update your import statements to import the gettext_lazy
instead.
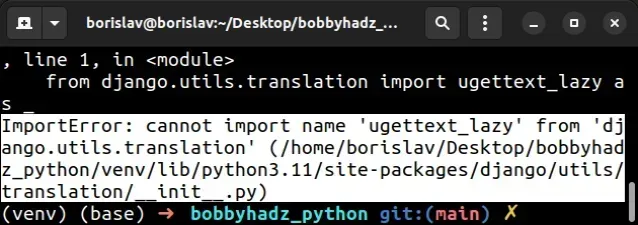
ImportError: cannot import name 'ugettext_lazy' from 'django.utils.translation' (/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/django/utils/translation/__init__.py)
As the release notes
state, django.utils.translation import ugettext_lazy has been deprecated
starting version 3 and has been removed in version 4 of Django.
# Update your imports to use the gettext_lazy function
The first thing you should try is to upgrade your import statements to use the
gettext_lazy function instead.
from django.db import models from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _ class MyThing(models.Model): name = models.CharField(help_text=_('This is the help text'))
You can read more about how lazy translation works in this section of the docs.
Here are the two import statements, the new one and the old one.
# 👇️ New import statement (Django 4) from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _ # 👇️ Old import statement (Django older than version 4) from django.utils.translation import ugettext_lazy as _
You can check which version of Django your project uses with the
pip show django command.
pip show django pip3 show django python -m pip show django python3 -m pip show django
# Downgrading your version of Django
If you have other packages in your environment that use the deprecated
ugettext_lazy function, you can try downgrading Django to version 3.2.16, or
the last version prior to version 4.
You can check all of the available versions of Django in this section of the package's pypi page.
pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall pip3 install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ If you don't have pip in PATH environment variable python -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall python3 -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ py alias (Windows) py -m pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall # 👇️ For Jupyter Notebook !pip install "Django<4.0" --force-reinstall
When you run the command, you might get an error that states "ERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed.".
If you use Django version 3, you and the packages you use should be able to use both of the following import statements.
# 👇️ New import statement (Django 4) from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _ # 👇️ Old import statement (Django older than version 4) from django.utils.translation import ugettext_lazy as _
If none of the suggestions helped and the error isn't caused in your code by
importing the deprecated ugettext_lazy function, try to upgrade all packages
in your environment.
# Upgrade all packages in your environment
The most straightforward way to upgrade all outdated packages is to use a Python script.
import pkg_resources from subprocess import call packages = [dist.project_name for dist in pkg_resources.working_set] call("pip install --upgrade " + ' '.join(packages), shell=True)
main.py and run the file with python main.py to upgrade all of the outdated packages.Here are alternative commands you can use to upgrade all outdated packages.
# 👇️ macOS or Linux pip install -U `pip list --outdated | awk 'NR>2 {print $1}'` # 👇️ Windows for /F "delims= " %i in ('pip list --outdated') do pip install -U %i
If you use a requirements.txt file, you can update it with the following
command.
pip freeze > requirements.txt
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'django' in Python
- Cannot import name 'force_text' from django.utils.encoding
- OperationalError: database is locked Python SQLite [Solved]
- You must either define the environment variable DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE or call settings.configure() before accessing settings
- Python: Not all parameters were used in the SQL statement
- How to restart a Python Script

