Check if a Value or a Name exists in an Enum in Python
Last updated: Feb 18, 2023
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
# Check if a value exists in an Enum in Python
To check if a value exists in an enum in Python:
- Use a list comprehension to get a list of all of the enum's values.
- Use the
inoperator to check if the value is present in the list. - The
inoperator will returnTrueif the value is in the list.
from enum import Enum class Sizes(Enum): SMALL = 1 MEDIUM = 2 LARGE = 3 values = [member.value for member in Sizes] print(values) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3] if 2 in values: # 👇️ this runs print('2 is in enum values') else: print('2 is NOT in enum values') print(100 in values) # 👉️ False
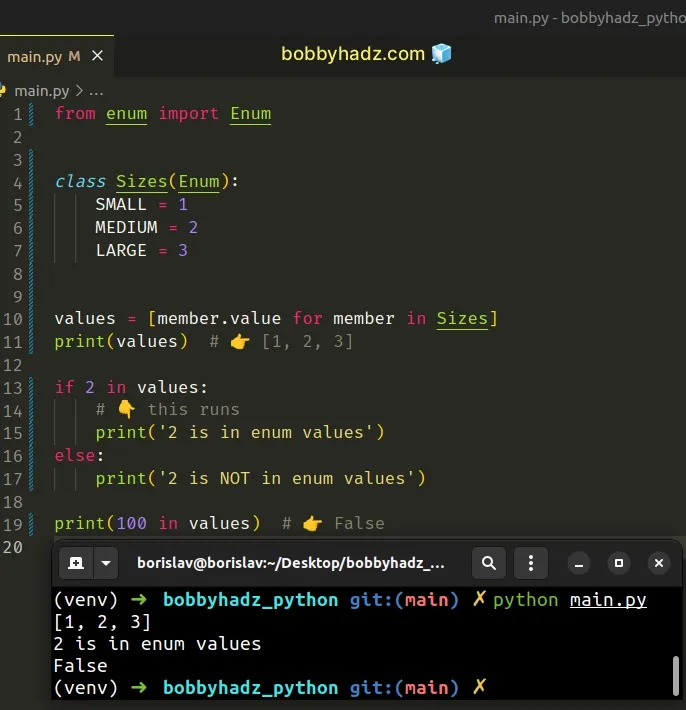
We used a list comprehension to get a list of the enum's values.
The last step is to use the in operator to check if a specific value is in the
list.
The in operator tests
for membership. For example, x in l evaluates to True if x is a member of
l, otherwise it evaluates to False.
# Checking if a value is NOT in an Enum
If you need to check if a value is not in an enum, negate the conditional with
not.
from enum import Enum class Sizes(Enum): SMALL = 1 MEDIUM = 2 LARGE = 3 values = [member.value for member in Sizes] print(values) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3] if 100 not in values: # 👇️ This runs print('100 is NOT in enum values')
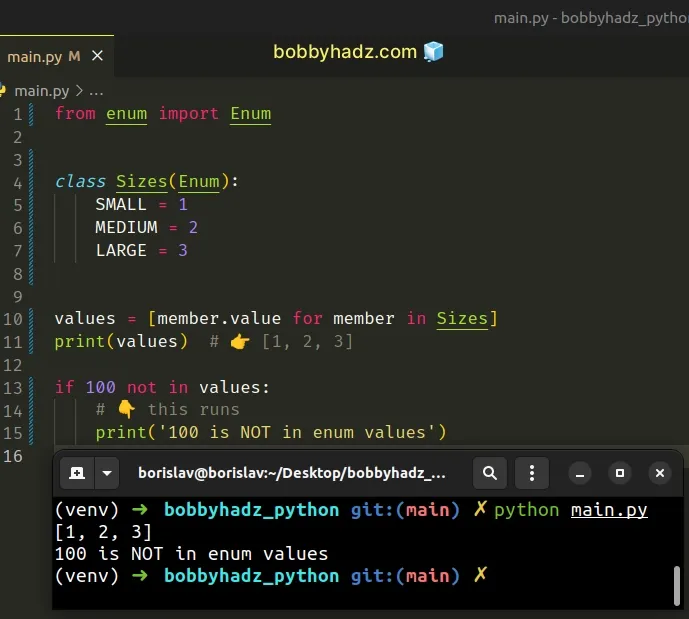
You can use the same approach if you need to check if a specific name is present in an enum.
from enum import Enum class Sizes(Enum): SMALL = 1 MEDIUM = 2 LARGE = 3 names = [member.name for member in Sizes] print(names) # 👉️ ['SMALL', 'MEDIUM', 'LARGE'] if 'SMALL' in names: # 👇️ this runs print('SMALL is in enum names')
Instead of accessing the value attribute, we used the name attribute to get
a list of the enum's names.
# Check if a name exists in an Enum in Python
To check if a name exists in an enum in Python:
- Use a list comprehension to get a list of all of the enum's names.
- Use the
inoperator to check if the name is present in the list. - The
inoperator will returnTrueif the name is in the list.
from enum import Enum class Sizes(Enum): SMALL = 1 MEDIUM = 2 LARGE = 3 names = [member.name for member in Sizes] print(names) # 👉️ ['SMALL', 'MEDIUM', 'LARGE'] if 'SMALL' in names: # 👇️ this runs print('SMALL is in enum names')
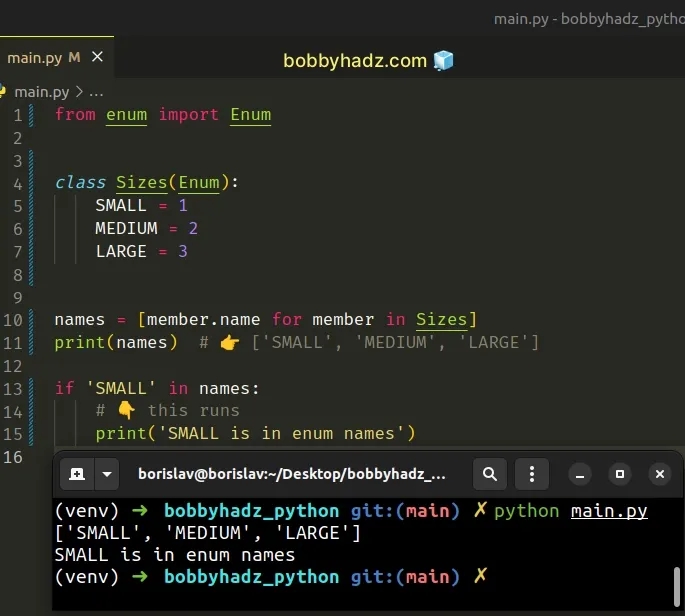
We used a list comprehension to get a list of the enum's names.
The last step is to use the in operator to check if a specific name is in the
list.
The in operator tests
for membership. For example, x in l evaluates to True if x is a member of
l, otherwise it evaluates to False.
# Check if a name exists in an Enum using the __members__ attribute
Alternatively, you could use the __members__ attribute on the class.
from enum import Enum class Sizes(Enum): SMALL = 1 MEDIUM = 2 LARGE = 3 # 👇️ {'SMALL': <Sizes.SMALL: 1>, 'MEDIUM': <Sizes.MEDIUM: 2>, 'LARGE': <Sizes.LARGE: 3>} print(Sizes.__members__) if 'SMALL' in Sizes.__members__: # 👇️ this runs print('SMALL is in enum names')
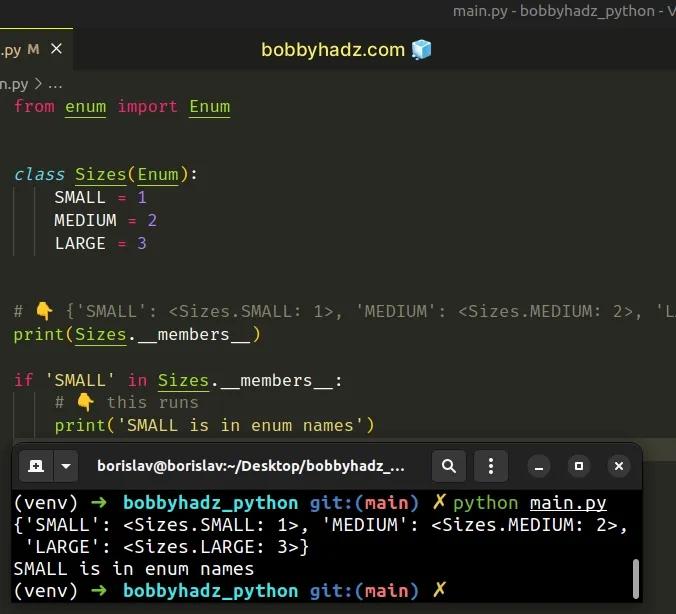
The __members__ attribute is an ordered mapping of names to members.
It contains all names defined in the enum (including the aliases).
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

