Swap the Keys and Values in an Object using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Swap the Keys and Values in an Object in JavaScript
To swap the keys and values in an object:
- Use the
Object.entries()method to get an array of key-value pairs. - Use the
map()method to switch the places of each key and value. - Use the
Object.fromEntries()method to get an object with swapped keys and values.
function swapKeysAndValues(obj) { // 👇️ [['color', 'blue'], ['fruit', 'apple']] const swapped = Object.entries(obj).map( ([key, value]) => [value, key] ); return Object.fromEntries(swapped); } // 👇️ {color: 'blue', fruit: 'apple'} console.log( swapKeysAndValues({blue: 'color', apple: 'fruit'}) );
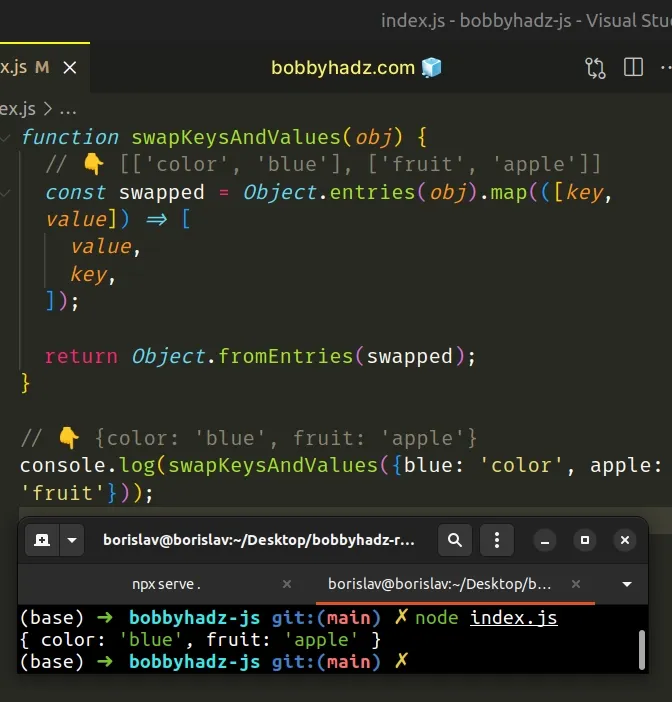
The Object.entries() method returns an array of the given object's key-value pairs.
// 👇️ [['blue', 'color'], ['apple', 'fruit']] console.log(Object.entries({blue: 'color', apple: 'fruit'}))
The function we passed to the Array.map() method gets called with each element in the array.
function swapKeysAndValues(obj) { // 👇️ [['color', 'blue'], ['fruit', 'apple']] const swapped = Object.entries(obj).map( ([key, value]) => [value, key] ); return Object.fromEntries(swapped); }
The map() method returns a new array containing the values returned from the
callback function.
We used destructuring assignment to get the first and second elements of each nested array.
const [key, value] = ['color', 'blue']; console.log(key); // 👉️ "color" console.log(value); // 👉️ "blue"
We simply switch the order of the key and value and return a new array containing the result.
swapped variable contains is an array of arrays, where the values are at index 0 and the keys are at index 1.The last step is to pass the array to the Object.fromEntries() method.
The Object.fromEntries() transforms a list of key-value pairs into an object.
// 👇️ {blue: 'color', apple: 'fruit'} console.log( Object.fromEntries([ ['blue', 'color'], ['apple', 'fruit'], ]), );
Swapping the keys and values of an object is a 3-step process:
- Get an array of key-value pairs using the
Object.entries()method. - Use the
map()method to swap the place of each key and value. - Use the
Object.fromEntries()method to transform the key-value pair arrays into an object.
# Swap the keys and values in an object using Object.assign()
An alternative approach is to return an array of objects from the map()
method.
function swapKeysAndValues(obj) { // 👇️ [{color: 'blue'}, {fruit: 'apple'}] const swapped = Object.entries(obj).map( ([key, value]) => ({[value]: key}) ); return Object.assign({}, ...swapped); } // 👇️ {color: 'blue', fruit: 'apple'} console.log(swapKeysAndValues({blue: 'color', apple: 'fruit'}));
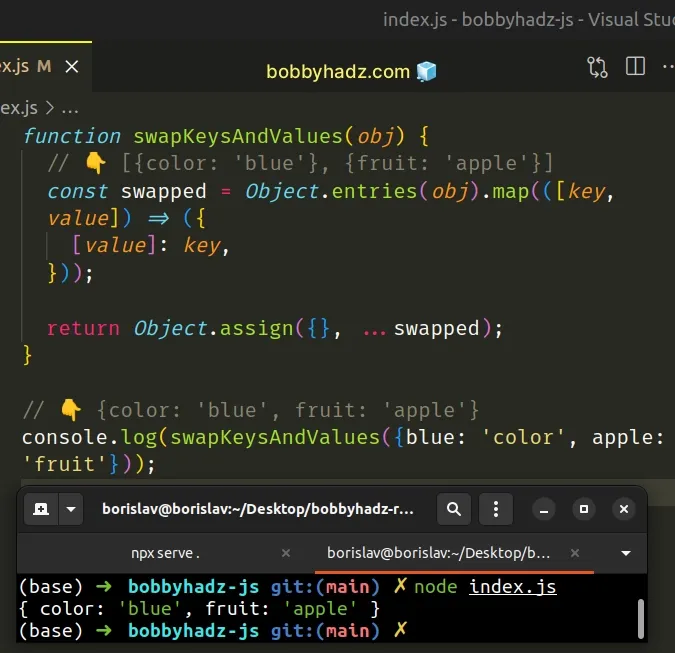
The callback function we passed to map() returns an array of objects with
switched keys and values.
This allows us to use the Object.assign() method to copy the properties of all
objects into a single object.
Object.assign method.The Object.assign() method copies all of the properties from a source object
to a target object.
const target = {a: 1, b: 3}; const source = {a: 2, c: 5}; const obj = Object.assign(target, source); console.log(obj); // 👉️ { a: 2, b: 3, c: 5 }
The Object.assign() method takes 2 parameters:
- the target object - the object to which the sources' properties are applied
- the sources - the source objects that contain the properties to be applied to the target object.
The method returns the target object with the provided properties applied.
# Swap the keys and values in an object using Array.forEach()
You can also use the Array.forEach() method to swap the keys and values in an
object.
function swapKeysAndValues(obj) { const newObj = {}; Object.entries(obj).forEach(([key, value]) => { newObj[value] = key; }); return newObj; } // 👇️ {color: 'blue', fruit: 'apple'} console.log(swapKeysAndValues({blue: 'color', apple: 'fruit'}));
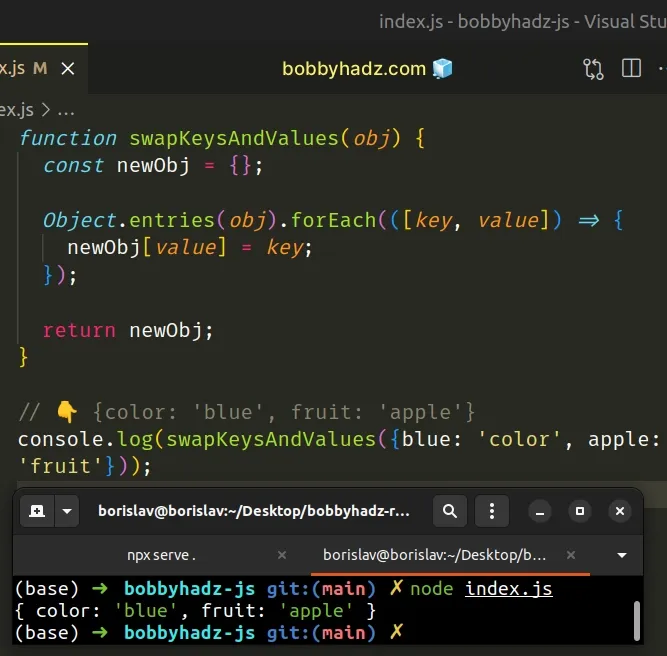
We first used the Object.entries() method to get an array of key-value pairs.
// 👇️ [ [ 'blue', 'color' ], [ 'apple', 'fruit' ] ] console.log(Object.entries({blue: 'color', apple: 'fruit'}));
The function we passed to the Array.forEach() method gets called with each element in the array.
On each iteration, we swap the key and value of the object.
# Swap the keys and values in an object using Array.reduce()
You can also use the Array.reduce() method to swap the keys and values in an
object.
function swapKeysAndValues(obj) { return Object.entries(obj).reduce((accumulator, entry) => { const [key, value] = entry; accumulator[value] = key; return accumulator; }, {}); } // 👇️ {color: 'blue', fruit: 'apple'} console.log(swapKeysAndValues({blue: 'color', apple: 'fruit'}));
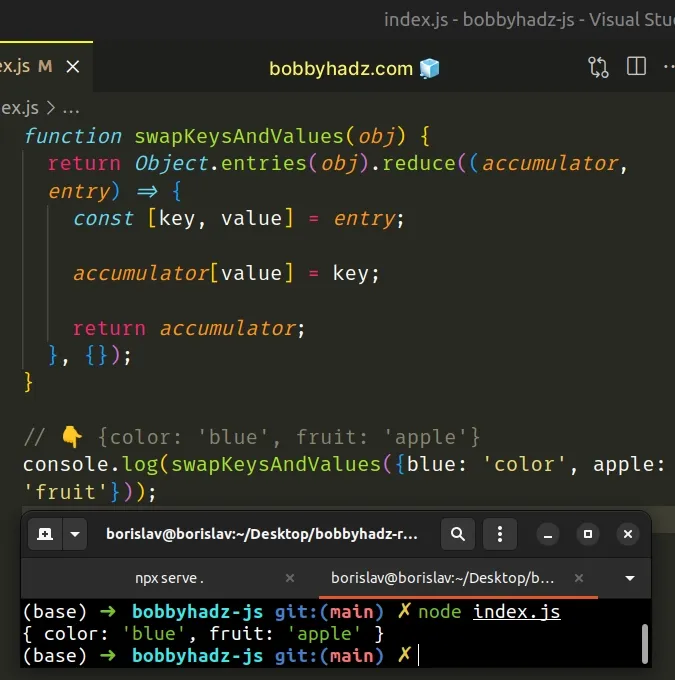
We used the Object.entries() method to get an array of key-value pairs and
used the reduce() method to iterate over the array.
The function we passed to the Array.reduce() method gets called for each element in the array.
We initialized the accumulator variable to an empty object because that's what
we passed as the second argument to the reduce() method.
The value we return from the callback function gets passed as the accumulator
on the next iteration.
On each iteration, we swap the current key-value pair and return the
accumulator object.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

