Disable a specific Keyboard key or all keys using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 7, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
# Disable all keyboard keys using JavaScript
To disable all keyboard keys using JavaScript:
- Add a
keydownevent listener on thedocumentor a specific element. - Use the
event.preventDefault()method to prevent the default behavior. - Return
falsefrom the event handler function.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div>bobbyhadz.com</div> <br /> <input id="message" type="text" /> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related index.js file.
// Adding `keydown` event listener on the document document.addEventListener('keydown', event => { console.log(`User pressed: ${event.key}`); event.preventDefault(); return false; }); const inputField = document.getElementById('message'); // or adding `keydown` on the `input` element inputField.addEventListener('keydown', event => { console.log(`User pressed: ${event.key}`); console.log('hi'); event.preventDefault(); return false; });
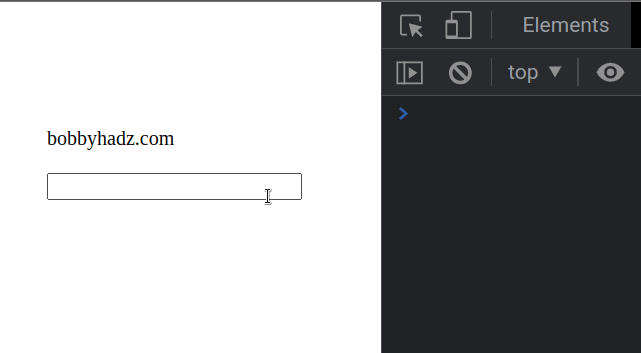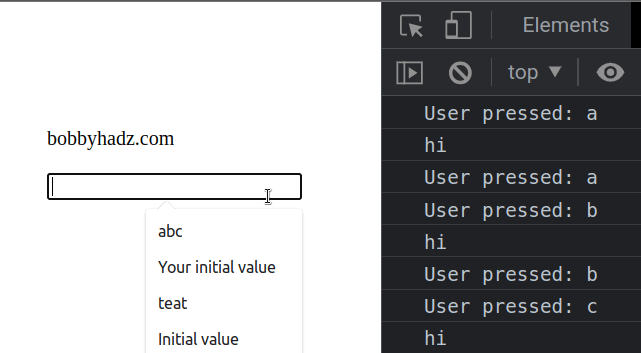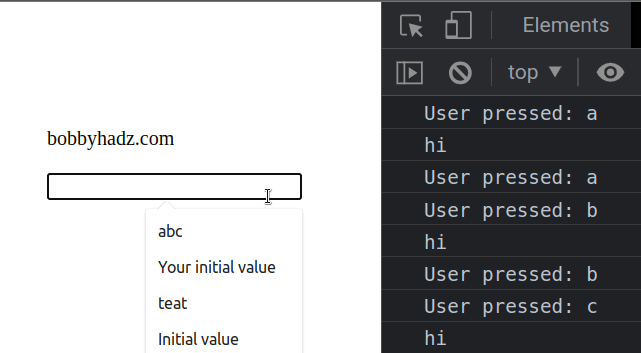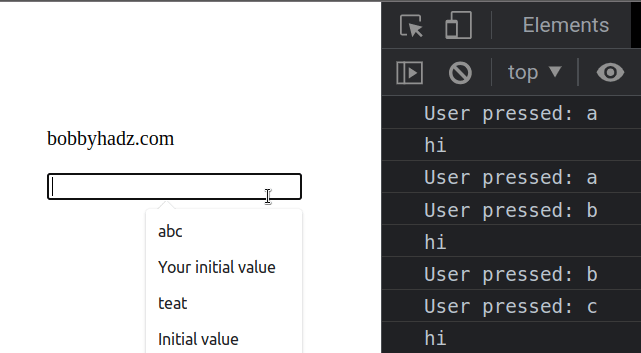
The example shows how to use the
addEventListener()
method to listen for the
keydown
event either on the document or on a specific element.
The keydown event is triggered when the user presses a key.
In the event handler function, we:
console.logthe key the user pressed (event.key).- Use the
event.preventDefault()method to disable the key. - Return
false.
This approach disables all keys (including F5).
If you need to prevent the user from typing in an input field or a text area,
you can set the disabled attribute
instead.
inputField.setAttribute('disabled', '');
You could also set the input field to read-only.
inputField.setAttribute('disabled', '');
# Disable a specific keyboard key or multiple specific keys
If you need to disable a specific keyboard key or multiple specific keys using JavaScript:
- Add a
keydownevent listener on thedocumentor a specific element. - Check if the user pressed the given key(s).
- If they did, call the
event.preventDefault()method and returnfalse.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div>bobbyhadz.com</div> <br /> <input id="message" type="text" /> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related index.js file.
document.addEventListener('keydown', event => { console.log(`User pressed: ${event.key}`); if (event.key === 'a' || event.key === 'b') { event.preventDefault(); return false; } }); const inputField = document.getElementById('message'); inputField.addEventListener('keydown', event => { console.log(`User pressed: ${event.key}`); if (event.key === 'a' || event.key === 'b') { event.preventDefault(); return false; } });
The example shows how to add the keydown event listener on the document or
on a specific element.
Every time the user presses a key, the keydown event is triggered and the
handler function is invoked.
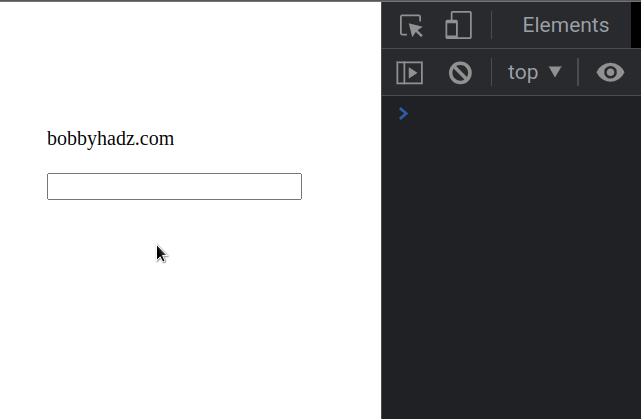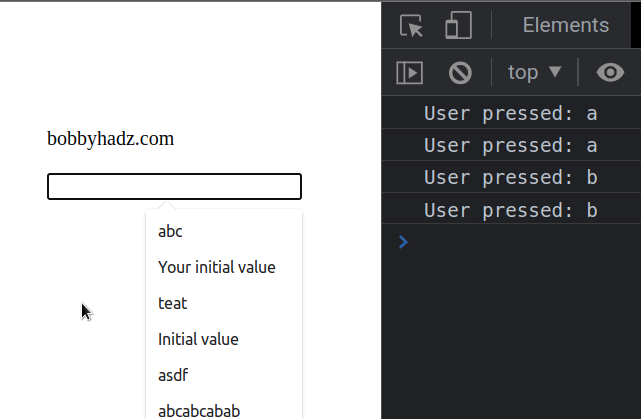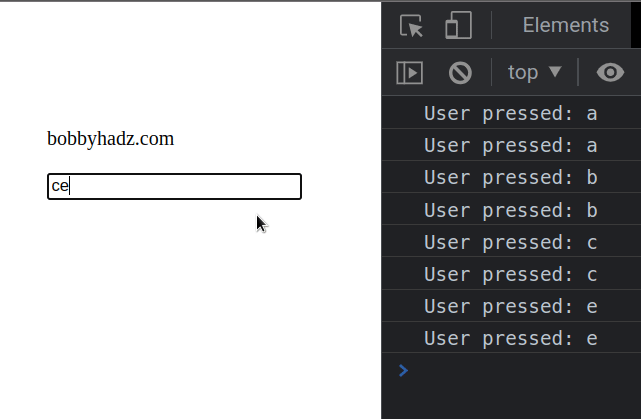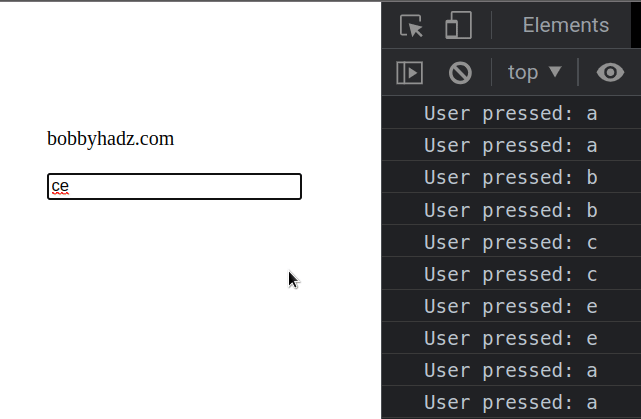
The if statement takes care of disabling the a and b keys.
The KeyboardEvent.key property stores the key that the user pressed.
You can console.log the event.key property to get the value of the key you
want to check for in the if statement.
if (event.key === 'a' || event.key === 'b') { event.preventDefault(); return false; }
The if statement uses the
logical OR (||) operator to check for
multiple conditions.
The if block runs if either condition is met.
If the user presses a or b, we disable the keys.
You can achieve the same result by using a switch statement.
document.addEventListener('keydown', event => { console.log(`User pressed: ${event.key}`); switch (event.key) { case 'a': case 'b': event.preventDefault(); return false; } }); const inputField = document.getElementById('message'); inputField.addEventListener('keydown', event => { console.log(`User pressed: ${event.key}`); switch (event.key) { case 'a': case 'b': event.preventDefault(); return false; } });
The switch statement checks for the value of the event.key property.
If the value is a or b, we call the event.preventDefault() method to
disable the key and return false.
Otherwise, the event handler function does nothing.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

