Check if a Window or a Browser Tab has Focus in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 5, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
# Check if a Window has Focus using JavaScript
Use the document.hasFocus() method to check if a window has focus.
The method returns a boolean value indicating whether the document or any element in the document has focus.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <title>bobbyhadz.com</title> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div id="box">Box content</div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
// ✅ Check if window has focus if (document.hasFocus()) { console.log('✅ window has focus'); } else { console.log('⛔️ window does NOT have focus'); } // --------------------------------------------- // ✅ Check if window has focus EVERY 1.5 seconds function checkWindowFocused() { if (document.hasFocus()) { console.log('✅ window has focus'); document.body.style.backgroundColor = 'lime'; document.getElementById('box').textContent = 'Window has focus'; } else { console.log('⛔️ window does NOT have focus'); document.body.style.backgroundColor = 'salmon'; document.getElementById('box').textContent = 'Window does NOT have focus'; } } setInterval(checkWindowFocused, 1500); // 👉️ check if focused every 1.5 seconds
We used the document.hasFocus method to check if the document or any of the elements inside it has focus.
The document.hasFocus method returns a boolean value:
trueif the document has focusfalseif it doesn't
The second code snippet in the example uses the setInterval method to check if the window has focus every 1.5 seconds.
The two parameters we passed to the setInterval method are:
- A function that gets invoked every X milliseconds.
- The time, in milliseconds, between invocations of the function.
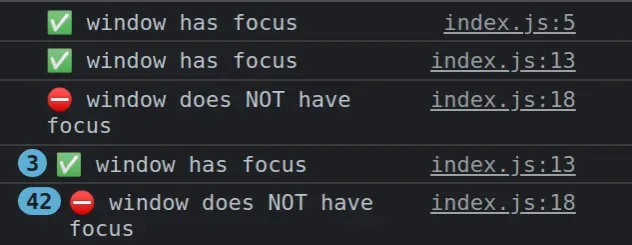
If I open the example in my browser I can see that every time I click off the
document, the document.hasFocus method returns false.
# Checking if the page's content is visible to the user
If you need to check if the page content is visible to the user, e.g. the window
is not minimized and the user has not opened a different tab in the same window,
use the document.visibilityState property.
function checkDocumentVisible() { if (document.visibilityState === 'visible') { console.log('✅ page is in the foreground tab of a non-minimized window'); document.body.style.backgroundColor = 'lime'; document.getElementById('box').textContent = '✅ page is in the foreground tab of a non-minimized window'; } else { console.log( '⛔️ document is in background tab or part of a minimized window', ); document.body.style.backgroundColor = 'salmon'; document.getElementById('box').textContent = '⛔️ document is in background tab or part of a minimized window'; } } setInterval(checkDocumentVisible, 1500);
When using the code snippet above, the
document.visibilityState
property will return visible as long as the page is in the foreground tab of a
non-minimized window
If the page content is not visible to the user, e.g. in a minimized window, or
an inactive tab in the same window, the visibilityState property returns
hidden.
You can also add an event listener to track changes in the visibility.
function checkDocumentVisible() { if (document.visibilityState === 'visible') { console.log('✅ page is in the foreground tab of a non-minimized window'); document.body.style.backgroundColor = 'lime'; document.getElementById('box').textContent = '✅ page is in the foreground tab of a non-minimized window'; } else { console.log( '⛔️ document is in background tab or part of a minimized window', ); document.body.style.backgroundColor = 'salmon'; document.getElementById('box').textContent = '⛔️ document is in background tab or part of a minimized window'; } } // ✅ Add event listener document.addEventListener('visibilitychange', checkDocumentVisible);
We used the visibilitychange event.
If you minimize the window or switch to a different tab, you'll see the
visibilitychange event fire.
# Detect if a Browser tab has Focus using JavaScript
Use the visibilitychange event to detect if a browser tab has focus or
not.
The event is fired at the document when the contents of its tab have become visible or have been hidden.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div id="box">Browser tab has focus</div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
function checkTabFocused() { if (document.visibilityState === 'visible') { console.log('✅ browser tab has focus'); document.body.style.backgroundColor = 'lime'; document.getElementById('box').textContent = '✅ browser tab has focus'; } else { console.log('⛔️ browser tab does NOT have focus'); document.body.style.backgroundColor = 'salmon'; document.getElementById('box').textContent = '⛔️ browser tab does NOT have focus'; } } // ✅ Add event listener document.addEventListener('visibilitychange', checkTabFocused);
We used the visibilitychange event.
If you minimize the window or switch to a different tab, you'll see the
visibilitychange event fire.
The document.visibilityState property returns 2 possible values:
visible- the page is in the foreground tab of a non-minimized window.hidden- the page content is not visible because it is in a background tab, part of a minimized window or the operating system's screen lock is active.
If I load the example from the code snippet and switch between tabs in my
browser, I can see that the visibilitychange event fires.
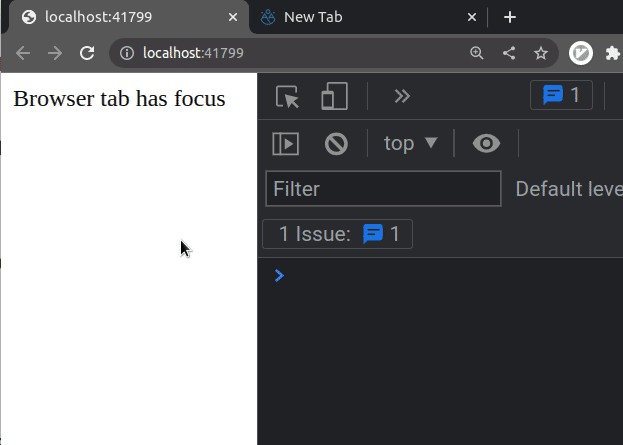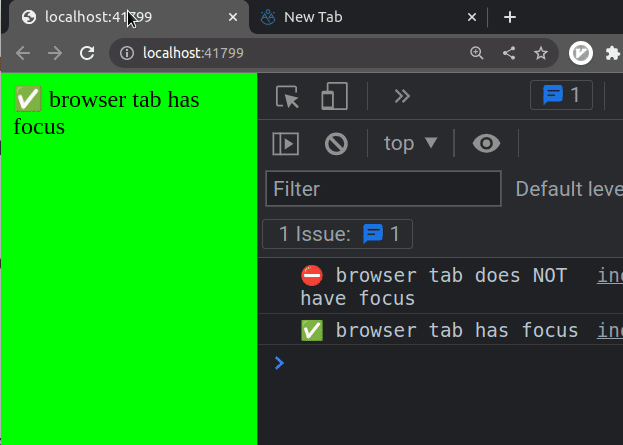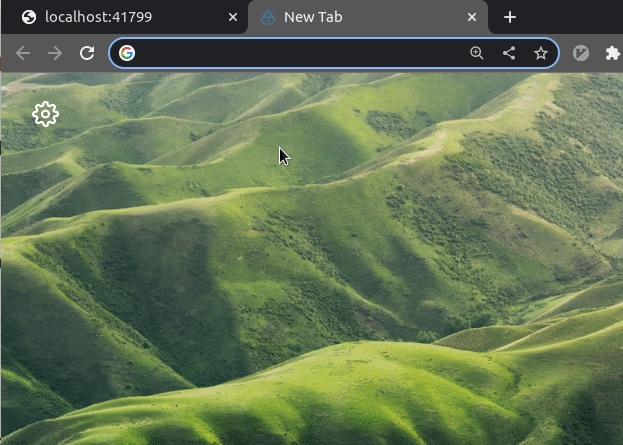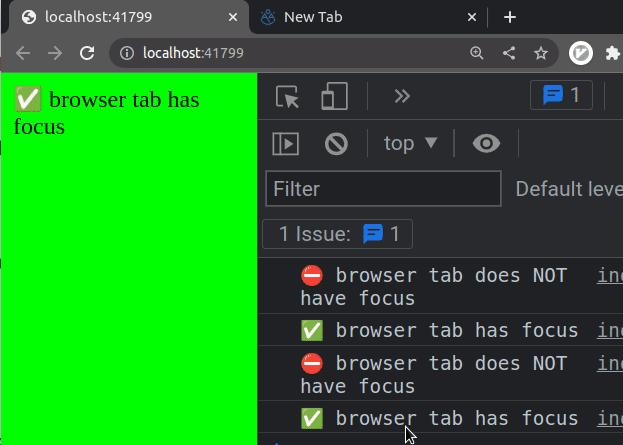
The visibilitychange event also fires if:
- the browser tab has focus, but the browser's window is minimized.
- the user's operating system screen lock gets activated.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

