Check if a Date is during the Weekend using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 6, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Check if a Date is during the Weekend using JavaScript
- Check if a Date is during the Weekend using modulo % operator
- Check if a Date is a Monday using JavaScript
- Check if a Date is the Monday of the Current Week
# Check if a Date is during the Weekend using JavaScript
Use the getDay() method to check if a date is during the weekend.
The method returns a number between 0 and 6 for the day of the week, where
Sunday is 0 and Saturday is 6.
function isWeekend(date = new Date()) { return date.getDay() === 6 || date.getDay() === 0; } const d1 = new Date('2022-09-24'); console.log(d1); // 👉️ Saturday Sep 24 2022 console.log(d1.getDay()); // 👉️ 6 console.log(isWeekend(d1)); // 👉️ true const d2 = new Date('2022-09-23'); console.log(d2); // 👉️ Friday Sep 23 2022 console.log(isWeekend(d2)); // 👉️ false
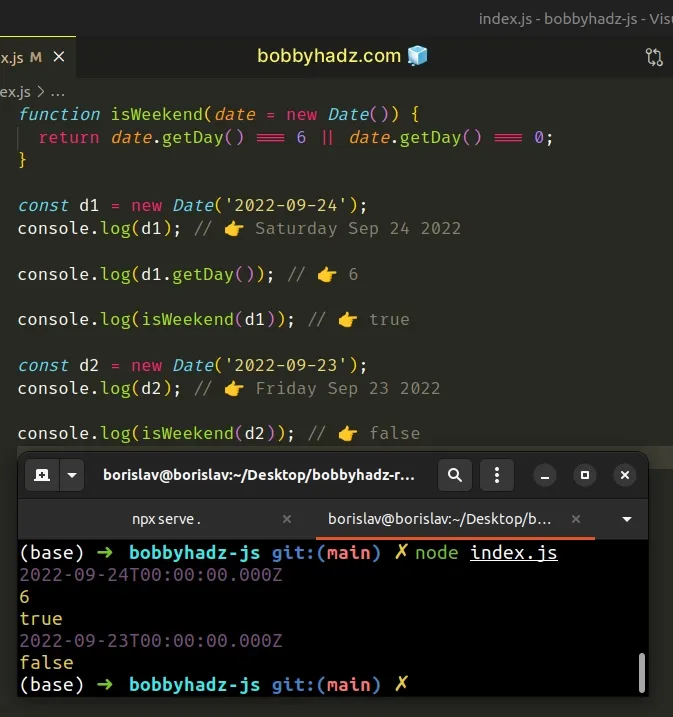
Date object as a parameter and checks if the date is during the weekend.If you don't pass a Date object to the function, it uses the current date.
The Date.getDay() method returns a number
between 0 and 6 that represents the day of the week for the given date.
The method returns 0 for Sunday, 1 for Monday, 2 for Tuesday, etc.
0 and 6, all we have to do is check if calling the getDay method on the date returns either of the two values.The logical OR (||) operator returns
the value to the right if the value to the left is falsy, so if either condition
is met, the function returns true.
# Check if a Date is during the Weekend using modulo % operator
An alternative approach is to check if dividing the result of calling the
getDay() method by 6 has a remainder.
function isWeekend(date = new Date()) { return date.getDay() % 6 === 0; } const d1 = new Date('2022-09-24'); console.log(d1); // 👉️ Saturday Sep 24 2022 console.log(isWeekend(d1)); // 👉️ true const d2 = new Date('2022-09-23'); console.log(d2); // 👉️ Friday Sep 23 2022 console.log(isWeekend(d2)); // 👉️ false
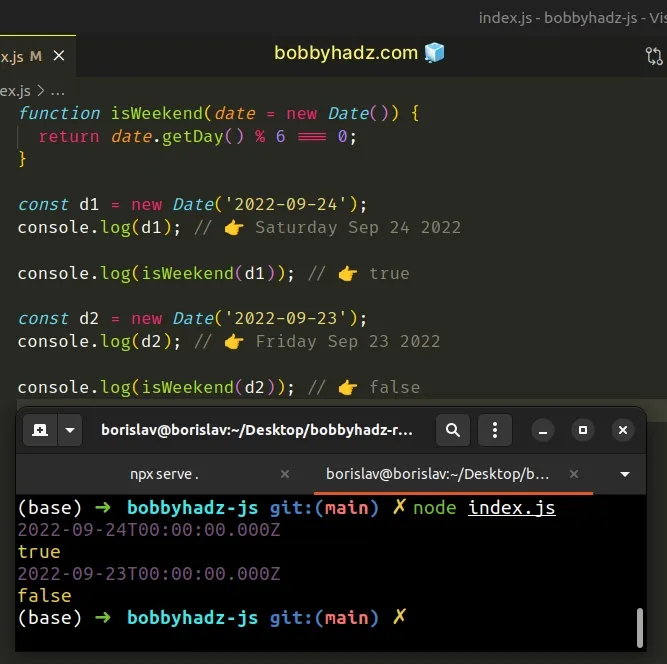
The modulo (%) operator returns the remainder of the division.
console.log(6 % 6); // 👉️ 0 console.log(0 % 6); // 👉️ 0
Dividing 6 and 0 by 6 gives us a remainder of 0, so the condition will
only be met if the date is Saturday or Sunday.
# Check if a Date is a Monday using JavaScript
You can also use the getDay() method to check if a day is Monday.
The method returns a number between 0 and 6 for the day of the week, where
Monday is 1.
function isMonday(date = new Date()) { return date.getDay() === 1; } const d1 = new Date('2022-09-19'); console.log(d1); // 👉️ Mon Sep 19 2022 console.log(d1.getDay()); // 👉️ 1 console.log(isMonday(d1)); // 👉️ true const d2 = new Date('2022-09-20'); console.log(d2); // 👉️ Tue Sep 20 2022 console.log(d2.getDay()); // 👉️ 2 console.log(isMonday(d2)); // 👉️ false
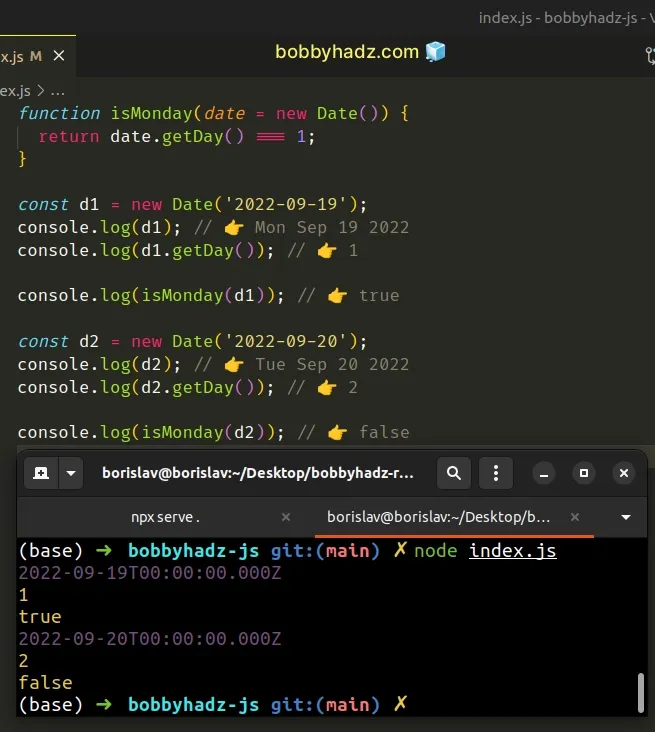
We created a reusable function that takes a Date object as a parameter and
checks if the date is a Monday.
If you don't pass a Date object to the function, it uses the current date.
The Date.getDay() method returns a number
between 0 and 6 that represents the day of the week for the given date.
1, all we have to do is check if calling the getDay method on the date returns 1.# Check if a Date is the Monday of the Current Week
To check if a date is the Monday of the current week:
- Get the date for the Monday of the current week.
- Use the
toDateString()method to compare Monday to the passed-in date. - If the method returns
2equal strings, then the passed-in date is the Monday of the current week.
function isMondayOfCurrentWeek(date = new Date()) { const today = new Date(); const first = today.getDate() - today.getDay() + 1; const monday = new Date(today.setDate(first)); return monday.toDateString() === date.toDateString(); } const today = new Date(); const first = today.getDate() - today.getDay() + 1; const currentMonday = new Date(today.setDate(first)); console.log(isMondayOfCurrentWeek(currentMonday)); // 👉️ true const date = new Date('2022-09-24'); console.log(date); // 👉️ Sat Sep 24 2022 console.log(isMondayOfCurrentWeek(date)); // 👉️ false
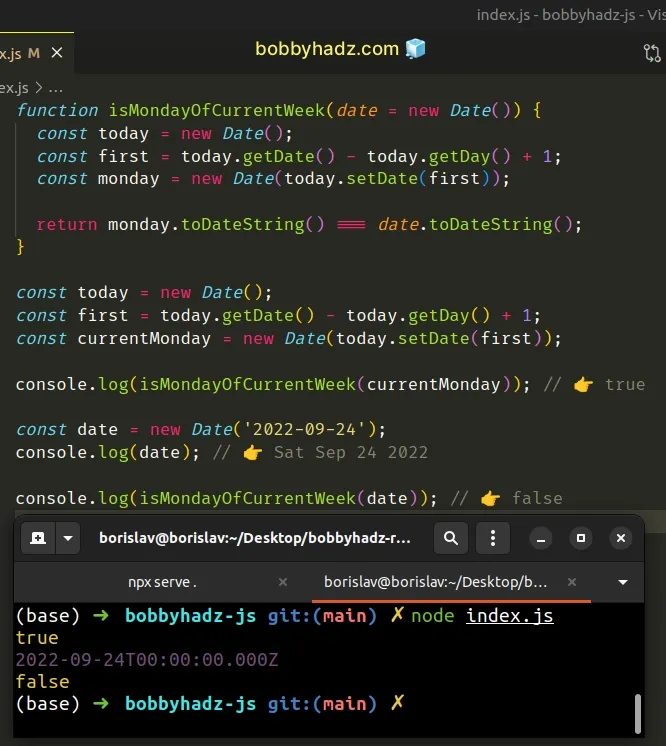
To get the Monday of the current week, we had to calculate the day of the month for Monday.
We basically subtracted the value for the day of the week from the day of the
month and added 1 to get the Monday.
The
toDateString()
returns a string representing the date portion of the given Date instance in
human-readable form.
// 👇️ Tue Jan 25 2022 console.log(new Date().toDateString());
If the output from calling toDateString() for the two dates is the same, then
the date is the Monday of the current week.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

