Access the First Property of an Object in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 1, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Access the First Property of an Object in JavaScript
- Access the First Property of an Object using Object.entries()
- Access the First Property of an Object using for...in
- Access the First Property of an Object using Object.keys()
- Access the First Property of an Object using lodash.find()
# Access the First Property of an Object in JavaScript
To access the first property on an object in JavaScript:
- Use the
Object.values()method to get an array of the object's values. - Access the element at index
0, e.g.Object.values(obj)[0].
const obj = {one: '1', two: '2', three: '3'}; const firstValue = Object.values(obj)[0]; console.log(firstValue); // 👉️ '1'
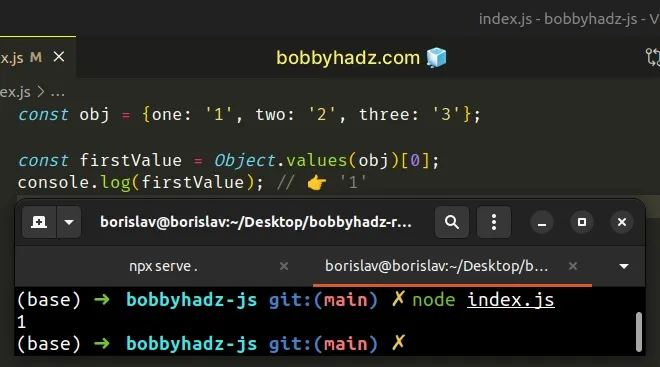
The Object.values() method returns an array containing all of the object's values.
const obj = {one: '1', two: '2', three: '3'}; // 👇️ [ '1', '2', '3' ] console.log(Object.values(obj));
0 to get the value of the first key in the object.You can also use destructuring assignment to not have to access the array at an index.
const obj = {one: '1', two: '2', three: '3'}; const [firstValue] = Object.values(obj); console.log(firstValue); // 👉️ '1'
We used destructuring assignment to assign the first value of the object to a variable.
# Access the First Property of an Object using Object.entries()
You can also use the Object.entries() method to get the
first key or value of an
object.
const obj = {one: '1', two: '2', three: '3'}; const entries = Object.entries(obj); // 👇️ [ [ 'one', '1' ], [ 'two', '2' ], [ 'three', '3' ] ] console.log(entries); const [firstKey, firstValue] = entries[0]; console.log(firstKey); // 👉️ one console.log(firstValue); // 👉️ 1
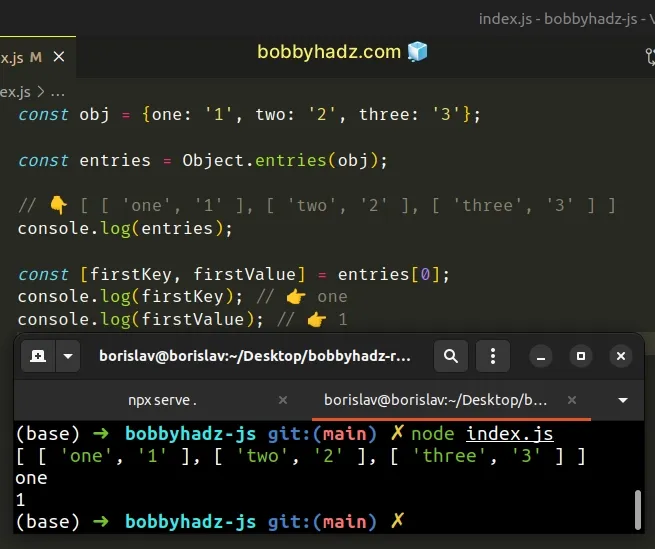
The Object.entries() method returns an array of the given object's key-value pairs.
const obj = {one: '1', two: '2', three: '3'}; const entries = Object.entries(obj); // 👇️ [ [ 'one', '1' ], [ 'two', '2' ], [ 'three', '3' ] ] console.log(entries);
We had to access the array of key-value pairs at index 0 to get the first
key-value pair.
JavaScript indexes are zero-based, so the first element in an array has an index
of 0 and the last element has an index of array.length - 1.
The last step is to use the destructuring assignment to assign the key and value to variables.
Alternatively, you can use the Object.keys() method.
# Access the First Property of an Object using for...in
You can also use a simple for...in loop to get the first property of an
object.
const obj = {one: '1', two: '2', three: '3'}; let firstKey; for (const key in obj) { firstKey = key; break; } console.log(firstKey); // 👉️ one console.log(obj[firstKey]); // 👉️ 1
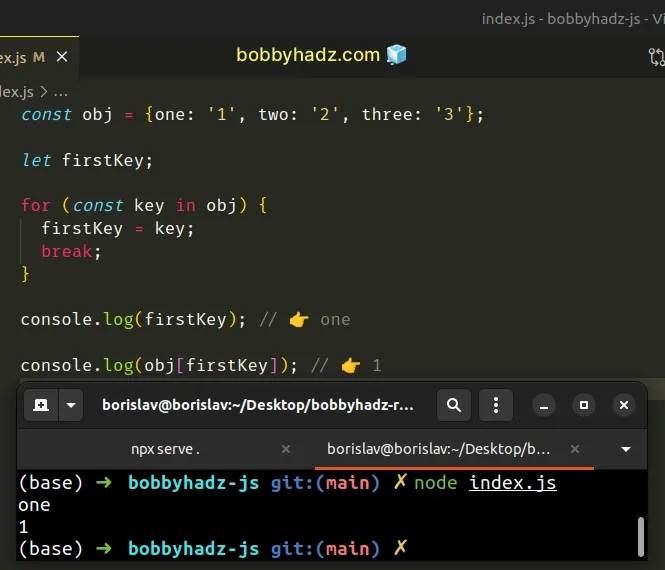
We declared the firstKey variable using the let keyword.
Using let is important because variables declared using const cannot be
reassigned.
We used the for...in loop to iterate for a single iteration.
Once we assign the first key to a variable, we use the break statement to exit
the loop.
The
break
statement terminates the current loop or switch statement.
Alternatively, you can use the Object.keys() method.
# Access the First Property of an Object using Object.keys()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Object.keys()method to get an array of the object's keys. - Access the array at index
0to get the first key. - Access the object using the first key to get the corresponding value.
const obj = {one: '1', two: '2', three: '3'}; const firstValue = obj[Object.keys(obj)[0]]; // 👉️ '1' console.log(firstValue);
We used the Object.keys method to get an array of the object's keys.
const obj = {one: '1', two: '2', three: '3'}; const keys = Object.keys(obj) // 👉️ ['one', 'two', 'three'] console.log(keys)
To get the first key of the object, we access the array at index 0.
The last step is to access the object at the first property to get the corresponding value.
const obj = {one: '1', two: '2', three: '3'}; const keys = Object.keys(obj); // 👉️ ['one', 'two', 'three'] const value = obj[keys[0]]; // 👉️ '1' console.log(value);
# Access the First Property of an Object using lodash.find()
If you use the lodash library, you can also use the lodash.find() method to
access the first property of an object.
import _ from 'lodash'; const obj = {one: '1', two: '2', three: '3'}; const firstKey = _.find(obj); console.log(firstKey); // 👉️ '1'
If you need to install lodash, run the following command.
# 👇️ initialize a package.json file npm init -y npm install lodash
The lodash.find() method returns the first element that matches the specified
condition.
When no condition is supplied, the first value of the object is returned.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference.
I'd use the Object.values() or Object.entries() methods because they are
quite direct and easy to read.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

