CORS error: Request header field Authorization is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response
Last updated: Mar 7, 2024
Reading time·12 min

# Table of Contents
- Request header field Authorization is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response
- Request header field Access-Control-Allow-Headers is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response
# Request header field Authorization is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response
The CORS error "Request header field Authorization is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response" occurs when your server doesn't send the necessary CORS headers to the client.
To solve the error, make sure your Access-Control-Allow-Headers header
contains the Authorization header and your Access-Control-Allow-Methods
header contains the OPTIONS method.
Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'https://localhost:5000' from origin 'http://localhost:3000' has been blocked by CORS policy: Request header field authorization is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response. Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'http://localhost:5000/products/5' from origin 'http://localhost:3000' has been blocked by CORS policy: Request header field access-control-allow-headers is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response.
If you've already configured CORS, you have to make sure:
- Your
Access-Control-Allow-Methodsheader contains theOPTIONSmethod. - Your
Access-Control-Allow-Headersheader contains theAuthorizationheader.
# 👇️ your domain below, e.g. http://localhost:3000 Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://example.com Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, PUT, PATCH, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Origin, X-Api-Key, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, Authorization
The error "Request header field X is not allowed by
Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response" occurs when the browser is
sending an HTTP header (X) that is not specified in the server's
Access-Control-Allow-Headers.
The headers the browser sends with the request have to all be specified in the
server's Access-Control-Allow-Headers response header.
You can view the headers your browser and server send in the Network > Headers tab of your browser's developer tools.
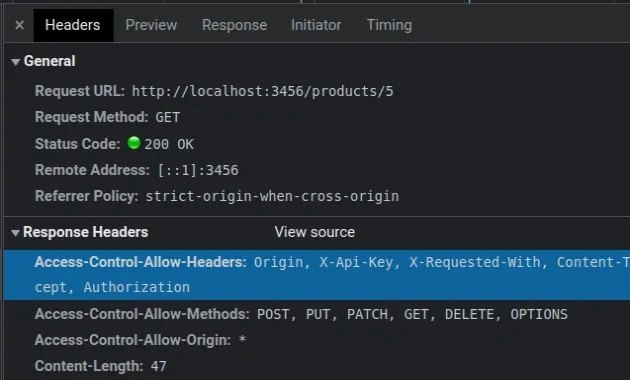
In CORS, a preflight request is sent with the OPTIONS method, so the server
can respond if it is acceptable to send the request.
The error usually occurs when the Authorization header or the OPTIONS method
is missing from the server's response headers.
# How CORS works
CORS is a mechanism that allows a server to use a combination of HTTP headers to indicate from which domains, other than its own, it receives requests.
By default, servers only take requests made from applications hosted on the same domain.
If your server is hosted on http://localhost:5000, for you to be able to make
an HTTP request from http://localhost:3000, your server has to send the
necessary CORS headers in its responses.
To allow other origins to make requests to your server, you have to set the
Access-Control-* headers in your server's responses.
The server should be setting the following CORS headers along with the response:
# 👇️ your domain below, e.g. http://localhost:3000 Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://example.com Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, PUT, PATCH, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Origin, X-Api-Key, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, Authorization
You might have to tweak the values depending on your use case but open the
Network tab in your browser, click on the request and check if your server is
setting these CORS-related headers.
The headers are:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin- which origins are allowed to make requests to the server.Access-Control-Allow-Credentials- whether to expose the server response to the frontend when the request's credentials mode is set toinclude. When credentials mode is set toinclude, our frontend will always send user credentials (i.e. cookies, auth headers) even for CORS calls.Access-Control-Allow-Methods- which HTTP methods the origins are allowed to use when making requests to the serverAccess-Control-Allow-Headers- which HTTP headers the origins are allowed to use when making requests to the server
* (asterisk) symbol as the origin and see if that works.Note that you can't set the Access-Control-Allow-Credentials header to
true if Access-Control-Allow-Origin is set to an asterisk *.
When an asterisk * is set for the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header, any
origin on the internet can access the server.
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: * Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: false Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, PUT, PATCH, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS Access-Control-Allow-Headers: *
You would want to narrow this down in production, but it's a useful tool when debugging.
When the Access-Control-Allow-Headers is set to an asterisk, all headers are
allowed in a preflight request.
# An example of configuring CORS in Express.js
If you use Express.js, you can use the cors module to configure CORS.
You can install the module with the following command.
npm install cors
And use it to add CORS headers as follows.
const express = require('express'); const cors = require('cors'); const app = express(); // 👇️ specify origins to allow const whitelist = ['http://localhost:3000', 'http://example2.com']; // ✅ Enable pre-flight requests app.options('*', cors()); const corsOptions = { credentials: true, origin: (origin, callback) => { if (whitelist.indexOf(origin) !== -1 || !origin) { callback(null, true); } else { callback(new Error('Not allowed by CORS')); } }, }; app.use(cors(corsOptions)); app.get('/products', function (req, res, next) { res.json({msg: 'This is CORS-enabled for whitelisted domains'}); }); app.listen(3456, function () { console.log('CORS-enabled web server listening on port 3456'); });
The example uses Express.js, but the concepts apply to any other backend technology.
We set credentials to true and specified a list of origins we want to
whitelist.
Origin header defined and to allow the specific origin to make a request.You can do that by dynamically setting the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header
on your server to the origin that made the request.
There is an example of how to do this in the "Configuring CORS Asynchronously" subheading of the Express.js CORS docs.
The example uses the CORS npm package and Express.js, but you could implement
the concept of setting the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to the origin
that made the request using any server technology.
const express = require('express'); const cors = require('cors'); const app = express(); const allowlist = ['http://example1.com', 'http://example2.com']; // ✅ Enable pre-flight requests app.options('*', cors()); const corsOptionsDelegate = function (req, callback) { let corsOptions; if (allowlist.indexOf(req.header('Origin')) !== -1) { // ✅ set `origin` to true to reflect the request origin // as defined by the `Origin` request header // or set `origin` to false to disable CORS corsOptions = {origin: true}; // reflect (enable) the requested origin in the CORS response } else { corsOptions = {origin: false}; // disable CORS for this request } callback(null, corsOptions); // callback expects two parameters: error and options }; app.get('/products/:id', cors(corsOptionsDelegate), function (req, res, next) { res.json({msg: 'This is CORS-enabled for an allowed domain.'}); }); app.listen(3456, function () { console.log('CORS-enabled web server listening on port 3456'); });
The cors package enables us to set origin to a boolean value.
If origin is set to true, then the server sets the
Access-Control-Allow-Origin response header to the value of the Origin
request header and allows the request.
If origin is set to false, CORS is disabled for the specific request.
Most servers also allow you to set the value of the
Access-Control-Allow-Origin header dynamically by using a regular expression
to match the origin.
# Setting the CORS headers on the server
You will most commonly be OK with just setting the Access-Control-Allow-Origin
header to a single origin.
# 👇️ your domain below, e.g. http://localhost:3000 Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://example.com Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, PUT, PATCH, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Origin, X-Api-Key, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, Authorization
The second most common value for the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header when
credentials are included is to specify a list of origins to whitelist.
If a list of whitelisted origins doesn't satisfy your requirements, you can use
a regular expression to dynamically check if the origin should be allowed access
and set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header dynamically on your server.
You can also use a function that dynamically sets the value of the
Access-Control-Allow-Origin header based on some logic that is run on every
request.
To solve the error, make sure:
- Your
Access-Control-Allow-Methodsheader contains theOPTIONSmethod. - Your
Access-Control-Allow-Headersheader contains theAuthorizationheader.
# Request header field Access-Control-Allow-Headers is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response
The CORS error "Request header field Access-Control-Allow-Headers is not
allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response" occurs when your
browser sends a request header that is not included in your server's
Access-Control-Allow-Headers response header.
To solve the error, make sure to include all request headers that your browser
sends in the server's Access-Control-Allow-Headers response header.
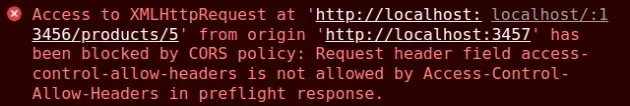
Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'http://localhost:5000/products/5' from origin 'http://localhost:3000' has been blocked by CORS policy: Request header field access-control-allow-headers is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response.
If you've already configured CORS, your server's Access-Control-Allow-*
response headers should look something like this.
# 👇️ your domain below, e.g. http://localhost:3000 Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://example.com # 👇️ only necessary if you send credentials (cookies, or Authorization header with browser requests) Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, PUT, PATCH, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Origin, X-Api-Key, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, Authorization
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials header to true if your frontend sends user credentials (i.e. cookies, auth headers)The error means that your browser sends the Access-Control-Allow-Headers
header when making an HTTP request to your server and your server doesn't
include the Access-Control-Allow-Headers header in its
Access-Control-Allow-Headers response header.
There are 2 common ways to solve this:
- Remove the request header from your browser when making HTTP requests as
Access-Control-Allow-Headersis a header your server should be sending to your browser and not the other way around. - Add the
Access-Control-Allow-Headersheader to your server'sAccess-Control-Allow-Headersresponse header.
Here is an example of adding the header to your server's
Access-Control-Allow-Headers response header.
# 👇️ your domain below, e.g. http://localhost:3000 Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://example.com Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, PUT, PATCH, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Access-Control-Allow-Headers, Origin, X-Api-Key, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, Authorization
The error occurs when the browser is sending an HTTP header (X) that is not
specified in the server's Access-Control-Allow-Headers.
The headers the browser sends with the request have to all be specified in the
server's Access-Control-Allow-Headers response header.
You can view the headers your browser (request headers) and server (response headers) send in the Network > Headers tab of your browser's developer tools.

Access-Control-Request-Headers request header, then the server has to include all of the specified headers in its Access-Control-Allow-Headers response header.In CORS, a preflight request is sent with the OPTIONS method, so the server
can respond if it is acceptable to send the request.
If your browser sends the Authorization header when making HTTP requests, make
sure to add it in your server's Access-Control-Allow-Headers response header
and to add the OPTIONS method in your server's Access-Control-Allow-Methods
header.
By default, servers only take requests made from applications hosted on the same domain.
If your server is hosted on http://localhost:5000, for you to be able to make
an HTTP request from http://localhost:3000, your server has to send the
necessary CORS headers in its responses.
To allow other origins to make requests to your server, you have to set the
Access-Control-* headers in your server's responses.
The server should be setting the following CORS headers along with the response:
# 👇️ your domain below, e.g. http://localhost:3000 Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://example.com # 👇️ only need this if sending credentials (cookies, auth headers) Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, PUT, PATCH, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Origin, X-Api-Key, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, Authorization
You might have to tweak the values depending on your use case but open the
Network tab in your browser, click on the request and check if your server is
setting these CORS-related headers.
The headers are:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin- which origins are allowed to make requests to the server.Access-Control-Allow-Credentials- whether to expose the server response to the frontend when the request's credentials mode is set toinclude. When credentials mode is set toinclude, our frontend will always send user credentials (i.e. cookies, auth headers) even for CORS calls.Access-Control-Allow-Methods- which HTTP methods the origins are allowed to use when making requests to the serverAccess-Control-Allow-Headers- which HTTP headers the origins are allowed to use when making requests to the server
* (asterisk) symbol as the origin and see if that works.Note that you can't set the Access-Control-Allow-Credentials header to
true if Access-Control-Allow-Origin is set to an asterisk *.
When an asterisk * is set for the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header, any
origin on the internet can access the server.
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: * Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: false Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, PUT, PATCH, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS Access-Control-Allow-Headers: *
You would want to narrow this down in production, but it's a useful tool when debugging.
When the Access-Control-Allow-Headers is set to an asterisk, all headers are
allowed in a preflight request.
If you use Express.js, you can use the cors module to configure CORS.
You can install the module with the following command.
npm install cors
And use it to add CORS headers as follows.
const express = require('express'); const cors = require('cors'); const app = express(); // 👇️ specify origins to allow const whitelist = ['http://localhost:3000', 'http://example2.com']; // ✅ Enable pre-flight requests app.options('*', cors()); const corsOptions = { credentials: true, origin: (origin, callback) => { if (whitelist.indexOf(origin) !== -1 || !origin) { callback(null, true); } else { callback(new Error('Not allowed by CORS')); } }, }; app.use(cors(corsOptions)); app.get('/products', function (req, res, next) { res.json({msg: 'This is CORS-enabled for whitelisted domains'}); }); app.listen(3456, function () { console.log('CORS-enabled web server listening on port 3456'); });
The example uses Express.js, but the concepts apply to any other backend technology.
We set credentials to true and specified a list of origins we want to
whitelist.
Origin header defined and to allow the specific origin to make a request.You can do that by dynamically setting the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header
on your server to the origin that made the request.
Here is how you'd send CORS headers using a more manual approach, without a third-party module.
const express = require('express'); const app = express(); app.use(function (req, res, next) { // 👇️ specify CORS headers to send 👇️ res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*'); res.header( 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'POST, PUT, PATCH, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS', ); res.header( 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Origin, X-Api-Key, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, Authorization', ); next(); }); app.get('/products/:id', function (req, res, next) { res.json({msg: 'This is CORS-enabled for all origins!'}); }); app.listen(3456, function () { console.log('CORS-enabled web server listening on port 3456'); });
Note that you have to set the headers before sending the response over to the browser.
There is an example of how to do this in the "Configuring CORS Asynchronously" subheading of the Express.js CORS docs.
The example uses the CORS npm package and Express.js, but you could implement
the concept of setting the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to the origin
that made the request using any server technology.
const express = require('express'); const cors = require('cors'); const app = express(); const allowlist = ['http://example1.com', 'http://example2.com']; // ✅ Enable pre-flight requests app.options('*', cors()); const corsOptionsDelegate = function (req, callback) { let corsOptions; if (allowlist.indexOf(req.header('Origin')) !== -1) { // ✅ set origin to true to reflect the request origin // as defined by the `Origin` request header // or set origin to false to disable CORS corsOptions = {origin: true}; // reflect (enable) the requested origin in the CORS response } else { corsOptions = {origin: false}; // disable CORS for this request } callback(null, corsOptions); // callback expects two parameters: error and options }; app.get('/products/:id', cors(corsOptionsDelegate), function (req, res, next) { res.json({msg: 'This is CORS-enabled for an allowed domain.'}); }); app.listen(3456, function () { console.log('CORS-enabled web server listening on port 3456'); });
The cors package enables us to set origin to a boolean value.
If origin is set to true, then the server sets the
Access-Control-Allow-Origin response header to the value of the Origin
request header and allows the request.
If origin is set to false, CORS is disabled for the specific request.
Most servers also allow you to set the value of the
Access-Control-Allow-Origin header dynamically by using a regular expression
to match the origin.
You will most commonly be OK with just setting the Access-Control-Allow-Origin
header to a single origin.
# 👇️ your domain below, e.g. http://localhost:3000 Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://example.com Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, PUT, PATCH, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Origin, X-Api-Key, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, Authorization
The second most common value for the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header when
credentials are included is to specify a list of origins to whitelist.
If a list of whitelisted origins doesn't satisfy your requirements, you can use
a regular expression to dynamically check if the origin should be allowed access
and set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header dynamically on your server.
You can also use a function that dynamically sets the value of the
Access-Control-Allow-Origin header based on some logic that is run on every
request.
# Conclusion
To solve the "Request header field Access-Control-Allow-Headers is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response" CORS error, make sure:
- Your server has included all of the headers the browser sends when making the
HTTP request in its
Access-Control-Allow-Headersresponse header. - Your server's
Access-Control-Allow-Methodsheader contains theOPTIONSmethod.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- The value of the 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header in the response must not be the wildcard '*' when the request's credentials mode is 'include'
- Set Cookies when making an Axios request in JS and Node
- TypeError: Failed to fetch and CORS in JavaScript [Solved]
- Clear your Proxy settings in NPM or npm install behind proxy
- Invalid Host header when starting your server [Solved]

