TypeError: can't compare datetime.datetime to datetime.date
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# TypeError: can't compare datetime.datetime to datetime.date
The Python error "TypeError: can't compare datetime.datetime to datetime.date"
occurs when you try to compare a datetime object with a date.
To solve the error, use the datetime.date() method to convert the datetime
object to a date before the comparison.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
from datetime import datetime, date dt = datetime(2024, 3, 15, 12, 0, 0) print(dt) # 👉️ 2024-03-15 12:00:00 d = date(2024, 2, 10) print(d) # 👉️ 2024-02-10 # ⛔️ TypeError: can't compare datetime.datetime to datetime.date if d < dt: print('d is less than dt') elif d > dt: print('d is greater than dt') else: print('d is equal to dt')
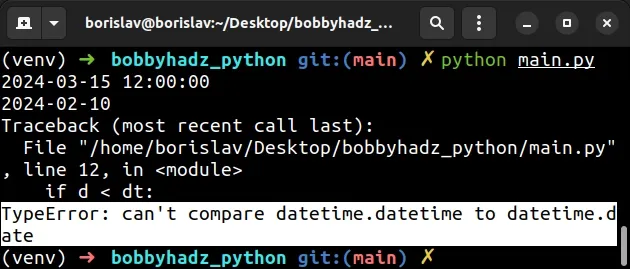
We used the
datetime.datetime()
class to create a datetime object.
Notice that the object contains the date and the time.
We then used the
datetime.date()
class to create a date object.
Notice that the date object only contains the date.
You might have also used the
datetime.now()
method to create a datetime object.
from datetime import datetime, date # 👇️ 2023-06-29 06:45:10.137118 print(datetime.now())
# Convert the datetime object to a date to solve the error
One way to solve the error is to convert the datetime object to a date.
You can use the
datetime.date
method to return a date object with the same year, month and day as the
datetime object.
from datetime import datetime, date dt = datetime(2024, 3, 15, 12, 0, 0) print(dt) # 👉️ 2024-03-15 12:00:00 d = date(2024, 2, 10) print(d) # 👉️ 2024-02-10 # ✅ Convert to date object if d < datetime.date(dt): print('d is less than dt') elif d > dt: print('d is greater than dt') else: print('d is equal to dt')
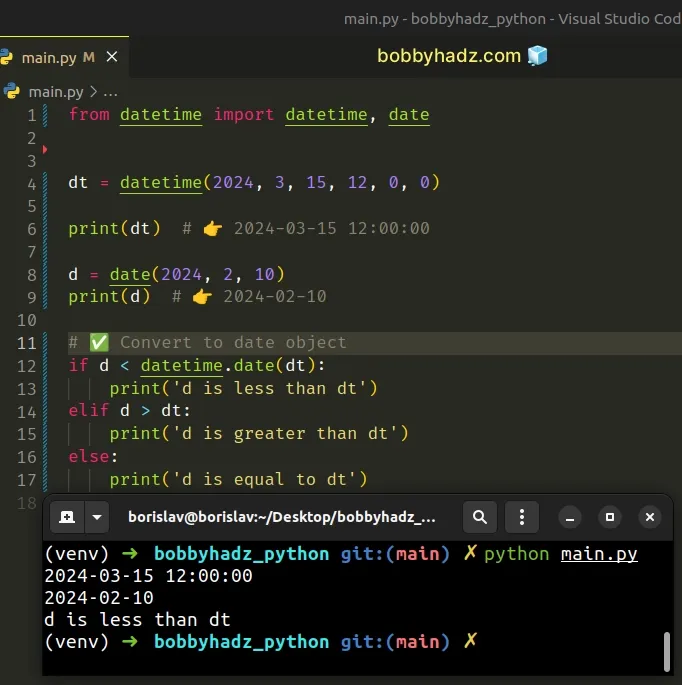
Notice that I passed the datetime object to the datetime.date() class to
convert it to a date object when comparing.
if d < datetime.date(dt):
We could've also converted the datetime object to a date object directly
upon creation.
from datetime import datetime, date # ✅ Convert datetime object to date object dt = datetime.date(datetime(2024, 3, 15, 12, 0, 0)) print(dt) # 👉️ 2024-03-15 d = date(2024, 2, 10) print(d) # 👉️ 2024-02-10 if d < dt: print('d is less than dt') elif d > dt: print('d is greater than dt') else: print('d is equal to dt')
After converting the datetime object to a date object, we have 2 date
objects, so the comparison is allowed.
# Using the datetime.combine() method to solve the error
Alternatively, you can solve the error by converting the date object to a
datetime object and comparing the two datetime objects.
from datetime import datetime, date, time dt = datetime(2024, 3, 15, 12, 0, 0) print(dt) # 👉️ 2024-03-15 12:00:00 # ✅ Convert to datetime object d = datetime.combine(date(2024, 2, 10), time(0, 0)) print(d) # 👉️ 2024-02-10 00:00:00 if d < dt: print('d is less than dt') elif d > dt: print('d is greater than dt') else: print('d is equal to dt')
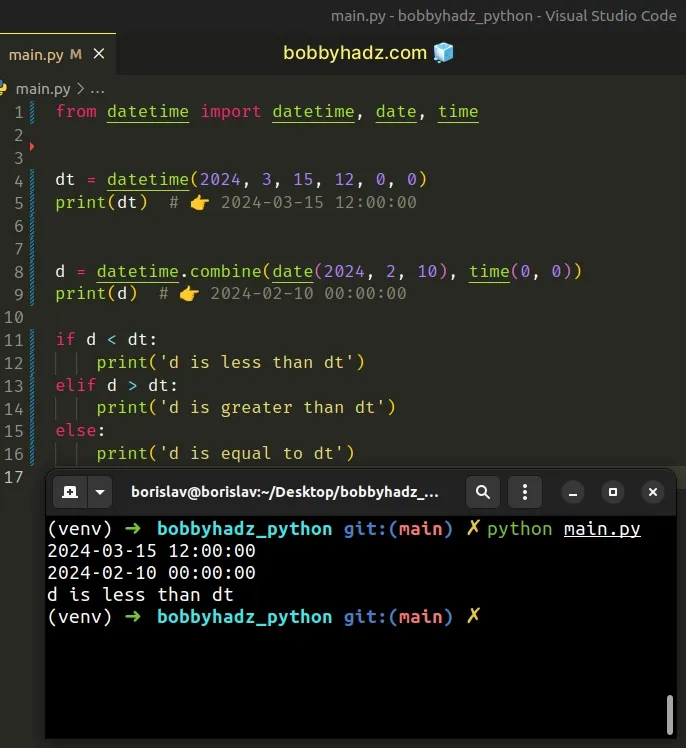
The
datetime.combine()
method returns a new datetime object whose date components are equal to the
given date object's components and whose time components are equal to the given
time object's components.
Once we convert the date object to a datetime object, we can compare the two
datetime objects without any issues.
You can also convert the date object to a datetime object when comparing
instead of upon instantiation.
from datetime import datetime, date, time dt = datetime(2024, 3, 15, 12, 0, 0) print(dt) # 👉️ 2024-03-15 12:00:00 d = date(2024, 2, 10) print(d) # 👉️ 2024-02-10 # ✅ Convert date object to datetime object here if datetime.combine(d, time(0, 0)) < dt: print('d is less than dt') elif d > dt: print('d is greater than dt') else: print('d is equal to dt')
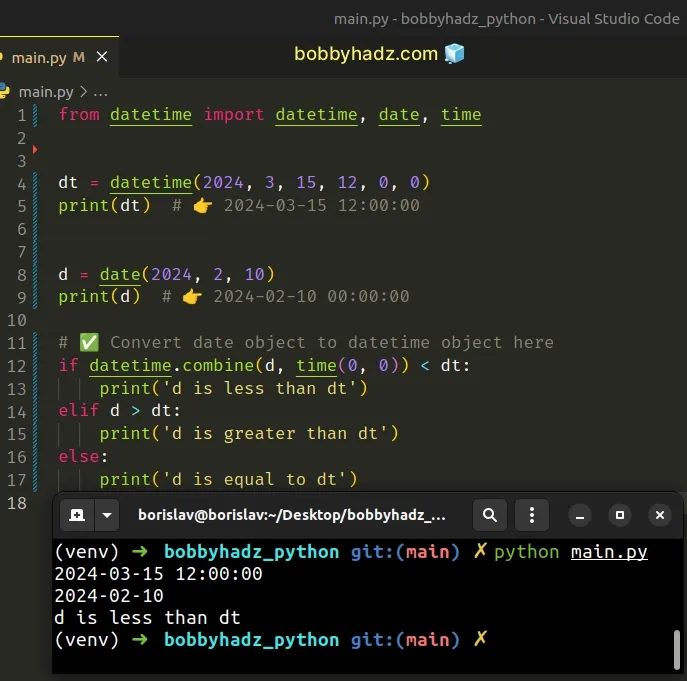
The first argument the datetime.combine() method takes is a date object and
the second is a time object.
The method combines the date and time objects to produce a datetime
object.
# Using the date() attribute to solve the error
You can also solve the error by calling the date() method on the datetime
object.
from datetime import datetime, date dt = datetime(2024, 3, 15, 12, 0, 0) print(dt) # 👉️ 2024-03-15 12:00:00 d = date(2024, 2, 10) print(d) # 👉️ 2024-02-10 # ✅ Call date() on datetime object if d < dt.date(): print('d is less than dt') elif d > dt: print('d is greater than dt') else: print('d is equal to dt')
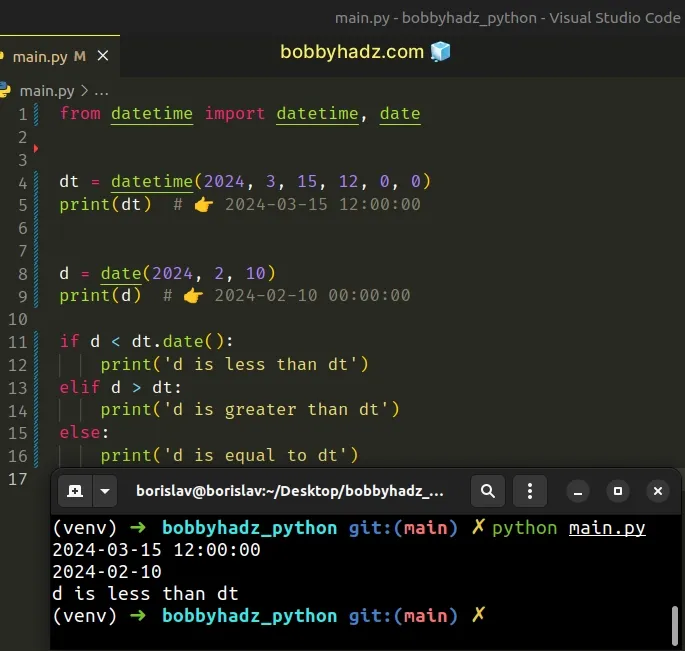
We called the date() method on the datetime object to convert the datetime
object to a date object.
Comparing the two date objects is allowed, so the error is resolved.
You can also call the date() method on the datetime object upon
instantiation.
from datetime import datetime, date # ✅ calling date() method here instead dt = datetime(2024, 3, 15, 12, 0, 0).date() print(dt) # 👉️ 2024-03-15 d = date(2024, 2, 10) print(d) # 👉️ 2024-02-10 if d < dt: print('d is less than dt') elif d > dt: print('d is greater than dt') else: print('d is equal to dt')
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Descriptor 'date' for 'datetime.datetime' objects doesn't apply to a 'int' object
- How to Create a Date from user Input in Python
- How to add Days or Weeks to a Date in Python
- How to add Hours to Datetime in Python
- How to add Milliseconds to Datetime in Python
- How to add Minutes to Datetime in Python
- How to add Months to a Date in Python
- How to add Seconds to Datetime in Python
- How to Add year(s) to a date in Python

