IAM Policy Examples in AWS CDK - Complete Guide
Last updated: Jan 26, 2024
Reading time·8 min

# Table of Contents
- Creating IAM Policies in AWS CDK
- Using Managed Policies in AWS CDK
- Policy Statements Example in AWS CDK
- Creating a Managed Policy in AWS CDK
- Attaching Managed Policies on IAM Entities in AWS CDK
- Adding Policy Statements to a Managed Policy in AWS CDK
- Importing Managed Policies in AWS CDK
# Creating IAM Policies in AWS CDK
IAM Policies define specific permissions needed to access AWS resources and can be associated with IAM users, roles or groups.
To create IAM policies in AWS CDK, we use the Policy constructs, for
example:
Let's start by creating a Policy with the PolicyDocument construct, which takes an array of PolicyStatement instances.
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'; import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class CdkStarterStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // 👇 Create a Policy Document (Collection of Policy Statements) const filterLogEvents = new iam.PolicyDocument({ statements: [ new iam.PolicyStatement({ resources: ['arn:aws:logs:*:*:log-group:/aws/lambda/*'], actions: ['logs:FilterLogEvents'], // 👇 Default for `effect` is ALLOW effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, }), ], }); // 👇 Create role, to which we'll attach our Policies const role = new iam.Role(this, 'example-iam-role', { assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal('lambda.amazonaws.com'), description: 'An example IAM role in AWS CDK', inlinePolicies: { // 👇 attach the Policy Document as inline policies FilterLogEvents: filterLogEvents, }, }); } }
Let's go over the code snippet:
We used the
PolicyDocumentclass, which takes astatementsprop. Thestatementsprop is an array of policy statement instances.We passed the following 3 props when instantiating the PolicyStatement class:
resources- a list of ARNs of resources to add to the policy statementactions- a list of actions to add to the policy statementeffect- whether theactionsin the policy statement should be allowed or denied. Note that by defaulteffectis set toALLOWso we could've skipped passingeffectaltogether
We created an IAM role, to which we attached the policy document.
Let's run the deploy command:
npx aws-cdk deploy
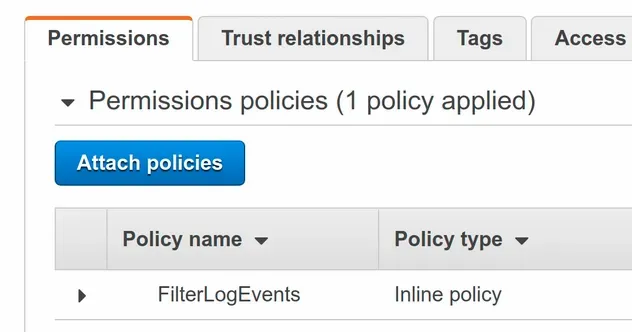
If we take a look at the permission policy of the role we've created, we can see
that the FilterLogEvents policy has been attached to the role.
# Using Managed Policies in AWS CDK
In order to use managed policies in AWS CDK, we have to use the
fromManagedPolicy* methods on the ManagedPolicy construct, for example:
- fromAwsManagedPolicyName - import a policy that is managed by AWS by specifying the name of the policy
- fromManagedPolicyArn - import an external policy by specifying the policy arn
- fromManagedPolicyName - import a customer-managed policy by specifying the name of the policy
Let's use the fromAwsManagedPolicyName method to import a policy that AWS
manages.
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'; import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class CdkStarterStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // ... rest // 👇 Use an AWS-Managed Policy const managedPolicy = iam.ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName( 'service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole', ); // 👇 attach the Managed Policy to the Role role.addManagedPolicy(managedPolicy); } }
Notice that in the call to fromAwsManagedPolicyName method, we prefixed the
policy name with service-role/. Some managed policies have a prefix of
service-role/, others - job-function/ and others have no prefix at all.
Since we always have to include the prefix along with the policy name, the best way to check if a managed policy has a prefix is to look at its ARN.
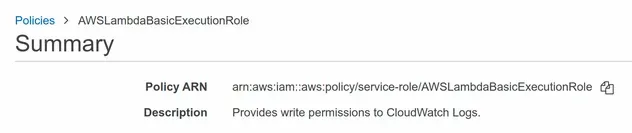
If we take a look at the ARN of the AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole policy, we can
see the service-role/ prefix which we have to include.
# Policy Statements Example in AWS CDK
In order to create a statement in an IAM Policy, we have to use the PolicyStatement class.
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'; import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class CdkStarterStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // ... rest // 👇 Create a Policy using the generic Construct const putLogEventsPolicy = new iam.Policy(this, 'cw-logs', { statements: [ new iam.PolicyStatement({ actions: ['logs:PutLogEvents'], resources: ['*'], }), ], }); // 👇 attach the Policy to the role role.attachInlinePolicy(putLogEventsPolicy); // 👇 Create a Policy Statement const createLogStreams = new iam.PolicyStatement({ actions: ['logs:CreateLogGroup', 'logs:CreateLogStream'], resources: ['*'], }); // 👇 Attach policy to Role role.addToPolicy(createLogStreams); } }
We used the Policy and PolicyStatement classes to create IAM Policies. The
Policy class takes a statements prop, which is an array of PolicyStatement
instances.
Notice how we didn't pass the effect prop when instantiating the
PolicyStatement class. The default value for effect is Effect.ALLOW. If
you want to override this behavior you should set effect to Effect.DENY.
Let's deploy the updated resources.
npx aws-cdk deploy
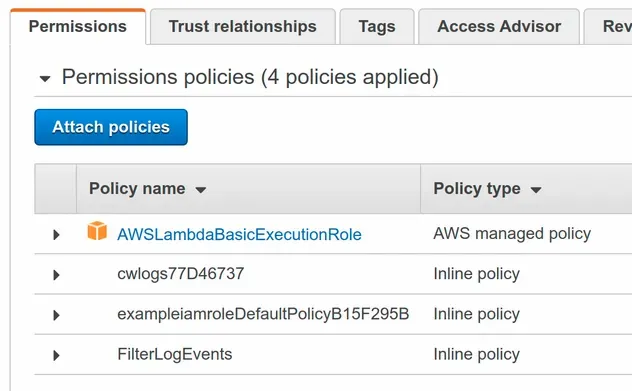
If we take a look at the IAM role we've provisioned, we can see that it has 4 permission policies attached to it:
# Clean up
To delete the resources we've provisioned, run the destroy command.
npx aws-cdk destroy
# Managed Policies in AWS CDK
Policies in AWS define the permissions that allow or deny access to resources.
Managed policies can be reused on multiple IAM entities, as opposed to inline Policies, which are only applied to a single entity.
We are going to go over examples of AWS-managed and Customer-managed policies.
# Creating a Managed Policy in AWS CDK
To create a managed policy in CDK, we have to instantiate the ManagedPolicy class and pass it one or more policy statements.
Let's look at a simple example where we create a managed policy and attach it to an IAM role:
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'; import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class CdkStarterStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // 👇 Create a Role const role = new iam.Role(this, 'iam-role-id', { assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal('lambda.amazonaws.com'), description: 'An example IAM role in AWS CDK', }); // 👇 Create a Managed Policy and associate it with the role const managedPolicy = new iam.ManagedPolicy(this, 'managed-policy-id', { description: 'Allows ec2 describe action', statements: [ new iam.PolicyStatement({ effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, actions: ['ec2:Describe'], resources: ['*'], }), ], roles: [role], }); } }
Let's go over what we did in the code sample:
We created an IAM role by instantiating the Role construct. We set the
lambdaservice as the principal of the role.We created a managed policy by instantiating the ManagedPolicy class. The props we passed to it are:
description- a short description of the managed policystatements- a list of PolicyStatement instances. Note that theeffectfor policy statements is set toALLOWby default, so we could have omitted the property.roles- a list of roles to attach the managed policy to
Let's run the deploy command.
npx aws-cdk deploy
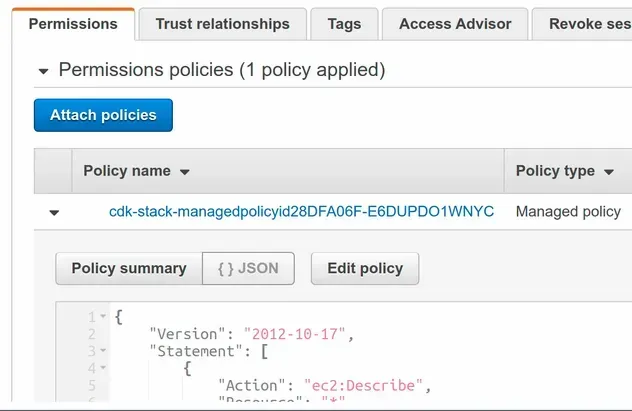
After a successful deployment, we can see that the managed policy has been attached to the role.
# Attaching Managed Policies on IAM Entities in AWS CDK
To attach a managed policy to an IAM entity, after the entity has been created,
we have to use the addManagedPolicy method.
This method is available on instances of the Role, User and Group classes.
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'; import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class CdkStarterStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // ... rest // 👇 Create group and pass it an AWS-Managed Policy const group = new iam.Group(this, 'group-id', { managedPolicies: [ iam.ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName('AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess'), ], }); // 👇 add a managed policy to a group after creation group.addManagedPolicy(managedPolicy); } }
Let's go over what we did in the code sample.
- We created a group, by instantiating the Group construct. We also imported an AWS-managed policy and set it on the group.
- We used the
addManagedPolicymethod on the group instance to attach the managed policy to the group.
Let's run the deploy command:
npx aws-cdk deploy
If we take a look at the group we created, we can see that both of our managed policies are attached:
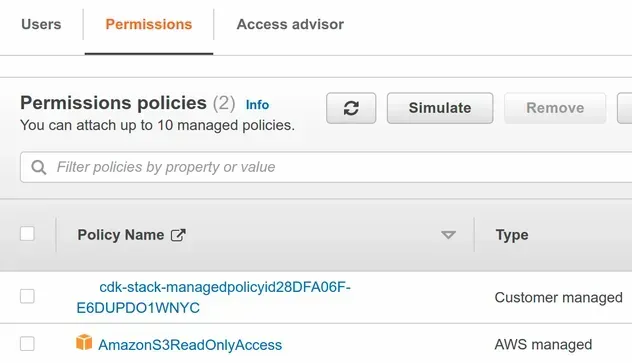
An alternative way to attach a managed policy to an IAM entity is to use the
attachTo* methods on instances of the
ManagedPolicy
class.
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'; import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class CdkStarterStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // ... rest // 👇 Create User const user = new iam.User(this, 'example-user', { userName: 'example-user', }); // 👇 attach the managed policy to a User managedPolicy.attachToUser(user) } }
We created an IAM user and used the
attachToUser method to attach a managed policy to it.
# Adding Policy Statements to a Managed Policy in AWS CDK
In order to add policy statements to a managed policy in CDK, we have to use the addStatements method on a managed policy instance.
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'; import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class CdkStarterStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // ... rest // 👇 add policy statements to a managed policy managedPolicy.addStatements( new iam.PolicyStatement({ actions: ['sqs:GetQueueUrl'], resources: ['*'], }), ); } }
We used the addStatements method on a managed policy instance. The method
takes
PolicyStatement
instances.
Let's run the deploy command:
npx aws-cdk deploy
If we look at the managed policy we provisioned, we can see that the
sqs:GetQueueUrl action is also permitted on all resources:
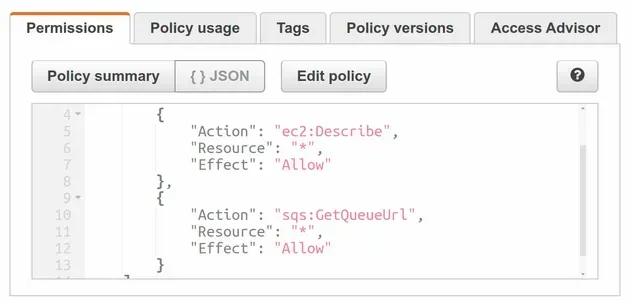
# Importing Managed Policies in AWS CDK
In order to import managed policies in AWS CDK, we have to use the from*
static methods on the
ManagedPolicy
construct:
- fromAwsManagedPolicyName - import an AWS-managed policy by the policy name
- fromManagedPolicyName - import a customer-managed policy by the policy name
- fromManagedPolicyArn - import a customer-managed policy by the ARN
Let's start with an example where we import an AWS-managed policy:
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'; import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class CdkStarterStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // ... rest // 👇 Import an AWS-Managed policy const lambdaManagedPolicy = iam.ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName( 'service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole', ); console.log('managed policy arn 👉', lambdaManagedPolicy.managedPolicyArn); } }
We used the fromAwsManagedPolicyName static method on the ManagedPolicy
class.
Note that we prefixed the policy name with service-role/. Some managed policy
names have to be prefixed with service-role/, others with job-function/ and
others don't have a prefix. The prefix should always be included for the
managed policies that have one, otherwise, we'd get an error.
The easiest way to see if a managed policy has a prefix is to look at the ARN of the policy, for example:
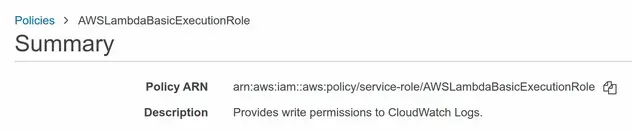
In the screenshot, we can see that the managed policy ARN includes a
service-role/ prefix, which we should specify in the parameter passed to
fromAwsManagedPolicyName.
In order to import external customer-managed policies, we have to use the
fromManagedPolicyName or fromManagedPolicyArn static methods:
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'; import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'; export class CdkStarterStack extends cdk.Stack { constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) { super(scope, id, props); // ... rest // 👇 Import a Customer-Managed Policy by Name const customerManagedPolicyByName = iam.ManagedPolicy.fromManagedPolicyName( this, 'external-policy-by-name', 'YOUR_MANAGED_POLICY_NAME', ); // 👇 Import a Customer-Managed Policy by ARN const customerManagedPolicyByArn = iam.ManagedPolicy.fromManagedPolicyArn( this, 'external-policy-by-arn', 'YOUR_MANAGED_POLICY_ARN', ); } }
The third parameter we pass to the fromManagedPolicyName static method is the
name of the externally managed policy we want to import.
The third parameter of the fromManagedPolicyArn static method is the ARN of
the externally managed policy we want to import.
# Clean up
To delete the provisioned resources, execute the destroy command:
npx aws-cdk destroy
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- AWS CDK IAM Role Example - Complete Guide
- IAM Principal Examples in AWS CDK - Complete Guide
- IAM Condition Examples in AWS CDK - Complete Guide
- Managed Policy Examples in AWS CDK - Complete Guide
- AWS CDK Tutorial for Beginners - Step-by-Step Guide
- How to use Context in AWS CDK
- How to use Parameters in AWS CDK
- What is a Token in AWS CDK

