Unknown format code 'f' for object of type 'str' [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# Unknown format code 'f' for object of type 'str' [Solved]
The Python "ValueError: Unknown format code 'f' for object of type 'str' "
occurs when you try to use the f format code with a value that is a string.
To solve the error, use the float() class to convert the string to a
floating-point number.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
my_float = '123.456789' # ⛔️ ValueError: Unknown format code 'f' for object of type 'str' result = f'{my_float:.0f}'
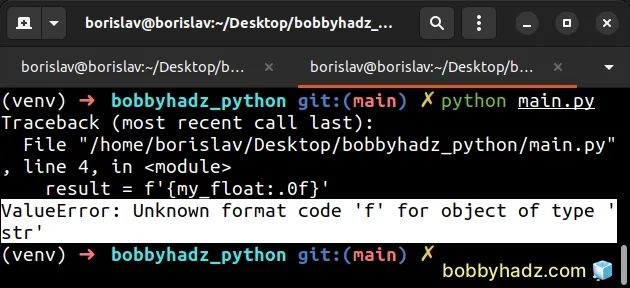
We used a formatted string literal.
Formatted string literals (f-strings) let us include expressions inside of a
string by prefixing the string with f.
The expressions have to be wrapped in curly braces - {expression}.
Formatted string literals also enable us to use the format-specific mini-language in expression blocks.
The f format code stands for fixed-point notation.
The error is caused because the my_float variable stores a string instead of a
floating-point number.
To resolve the issue, use the float() class to convert the value to a floating-point number.
my_float = '123.456789' result = f'{float(my_float):.0f}' print(result) # 👉️ 123 result = f'The number is: {float(my_float):.0f}' print(result) # 👉️ The number is: 123
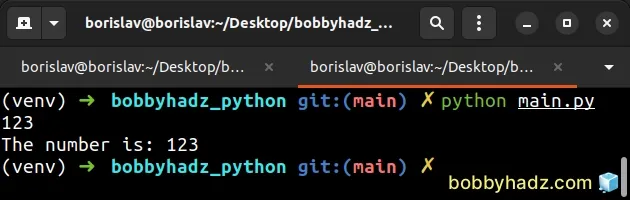
The float class converts the supplied value to a floating-point number.
As shown in this section of the docs, the digit after the period is the number of decimal places the number should have.
my_float = '123.456789' result = f'{float(my_float):.3f}' print(result) # 👉️ 123.457 result = f'The number is: {float(my_float):.3f}' print(result) # 👉️ The number is: 123.457
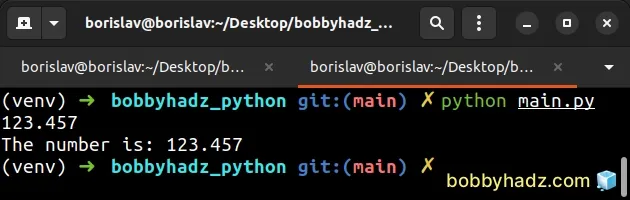
The f character in the expression stands for fixed-point notation.
It is used to format the number as a decimal with exactly N digits following the decimal point.
# Solving the error when using str.format()
You might also get the error when using the str.format() method.
my_float = '123.456789123' # ⛔️ ValueError: Unknown format code 'f' for object of type 'str' result = '{:.0f}'.format(my_float)
The solution to the error is the same - you have to convert the string to a floating-point number when passing it to str.format().
my_float = '123.456789123' result = '{:.0f}'.format(float(my_float)) print(result) # 👉️ 123 result = 'The number is: {:.0f}'.format(float(my_float)) print(result) # 👉️ The number is: 123
The digit after the period is the number of decimal places the number should have.
my_float = '123.456789' result = '{:.3f}'.format(float(my_float)) print(result) # 👉️ 123.457 result = 'The number is: {:.3f}'.format(float(my_float)) print(result) # 👉️ The number is: 123.457
The example converts the string to a float and formats it to 3 decimal places.
The str.format() method performs string formatting operations.
The string the method is called on can contain replacement fields specified
using curly braces {}.
I've also written articles on:
- How to remove the decimal part from a float in Python.
- Round a Float to 1, 2 or 3 Decimal places in Python
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

