Property does not exist on type void in TypeScript
Last updated: Feb 27, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Property does not exist on type void in TypeScript
The "Property does not exist on type void" error occurs when we try to access a property on the return value of a function that doesn't return anything.
To solve the error, make sure to return the correct value from all of the function's code paths.
Here is an example of how the error occurs:
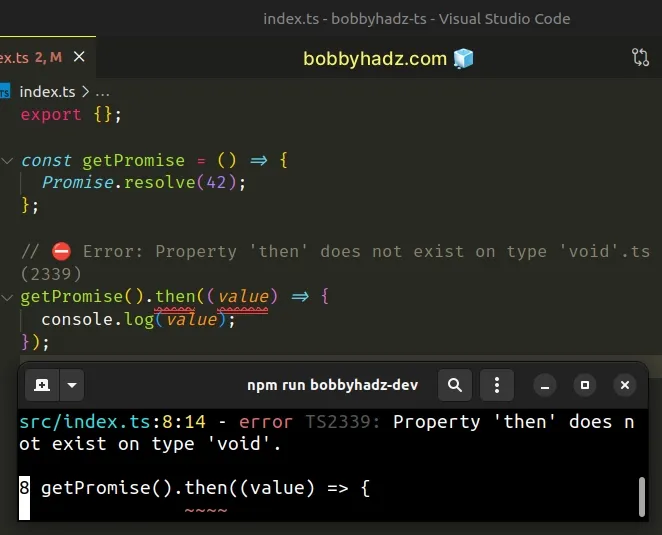
const getPromise = () => { Promise.resolve(42); }; // ⛔️ Error: Property 'then' does not exist on type 'void'.ts(2339) getPromise().then((value) => { console.log(value); });
# Functions that don't return anything return void
The getPromise() function doesn't return a value so TypeScript sets its return
type to be
void.
// 👇️ const getPromise: () => void const getPromise = () => { Promise.resolve(42); };
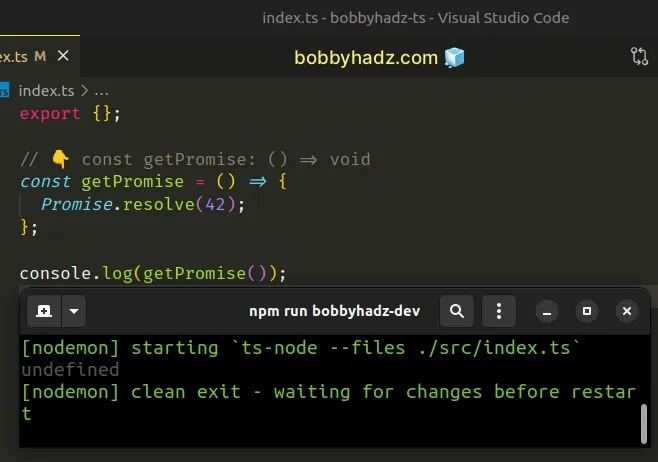
The function implicitly returns undefined, so we can't access a property on an
undefined value.
# Make sure to return a value from the function
To solve the error, make sure to correct the return value of your function before accessing a specific property.
// 👇️ const getPromise: () => Promise<number> const getPromise = () => { return Promise.resolve('bobbyhadz.com'); }; // ✅ Works getPromise().then((value) => { console.log(value); // 👉️ "bobbyhadz.com" });
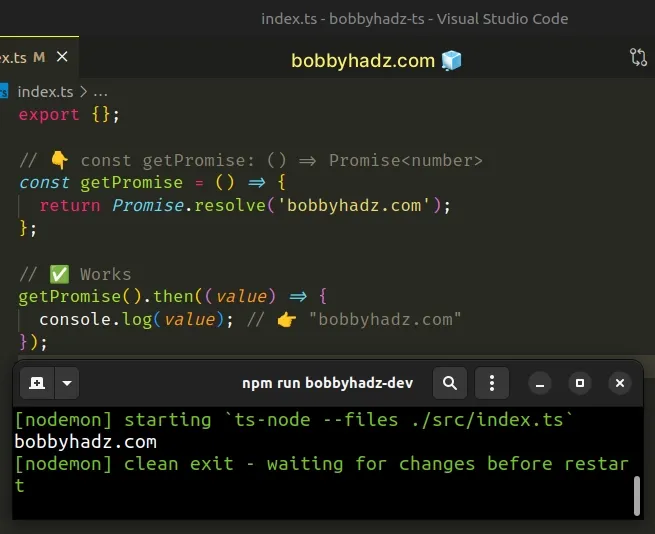
We used the return keyword to explicitly return a value from the function.
Notice that TypeScript types the function's return type as Promise<number> and
not void.
Now we can access the then() method on the function because it returns a valid
promise.
# Forgetting to return an object from a function
You might also get this error if you forget to return an object from a function.
const getObj = () => { const obj = { name: 'Bobby Hadz' }; }; // ⛔️ Error: Property 'name' does not exist on type 'void'.ts(2339) getObj().name;
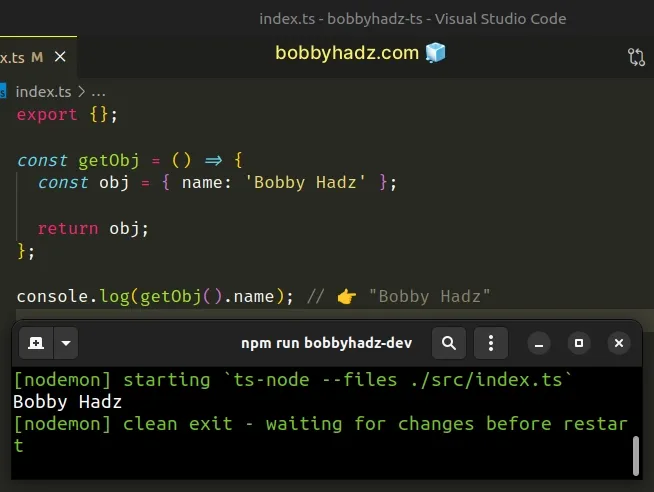
The solution is the same - you have to return the value from the function.
const getObj = () => { const obj = { name: 'Bobby Hadz' }; return obj; }; console.log(getObj().name); // 👉️ "Bobby Hadz"
Sometimes it's hard to see where exactly the missing return statement is.
In some cases, you have many code paths (nested conditions, etc), but the error
means that your function returns undefined, so you know what to look for.
# Explicitly set the function's return type
A good solution when debugging is to explicitly set the function's return type.
// ⛔️ Error: A function whose declared type // is neither 'void' nor 'any' must return a value.ts(2355) const getPromise = (): Promise<number> => { Promise.resolve(42); };
We explicitly typed the return value of the function to be Promise<number>, so
TypeScript tells us that we aren't returning a value from the function.
This is an easy way to spot that you have a bug in your application.
# All code paths of the function should return a value
All code paths of the function should return a value.
// ⛔️ Function lacks ending return statement and // return type does not include 'undefined'.ts(2366) const getPromise = (): Promise<number> => { if (Math.random()) { return Promise.resolve(42); } Promise.resolve(33); };
We've explicitly typed the return type of the function to be Promise<number>,
but we only return a promise in our if statement.
If the condition isn't met, the if block won't run and the function will
implicitly return undefined.
To resolve this, make sure to explicitly return a value from all of the function's code paths.
const getPromise = (): Promise<number> => { if (Math.random()) { return Promise.resolve(42); } return Promise.resolve(33); };
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

