How to bind the Enter key to a function in Tkinter
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
- How to bind the Enter key to a function in Tkinter
- Binding the
Enterkey and a Button to a function in Tkinter
# How to bind the Enter key to a function in Tkinter
You can use the root.bind() method to bind the Enter key to a function.
The method takes the key sequence and the function as parameters and binds the specified key to the function.
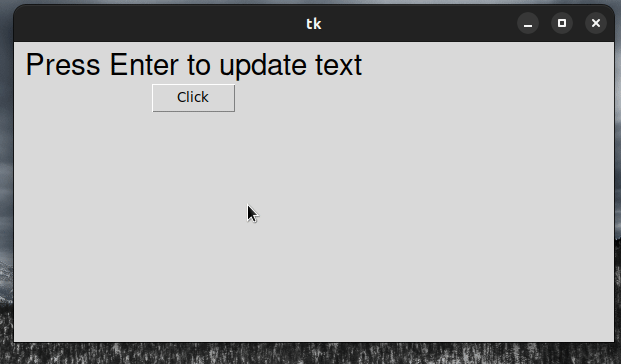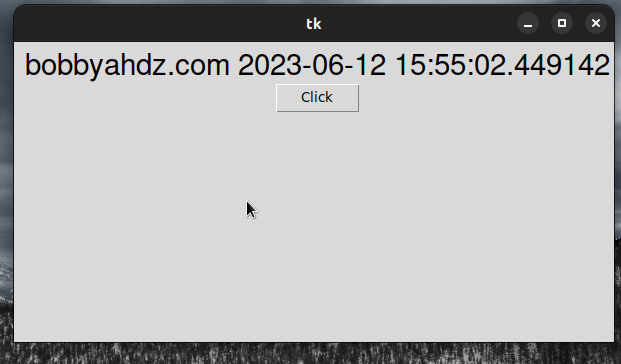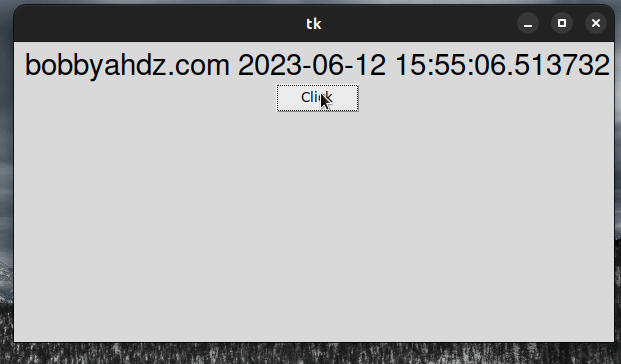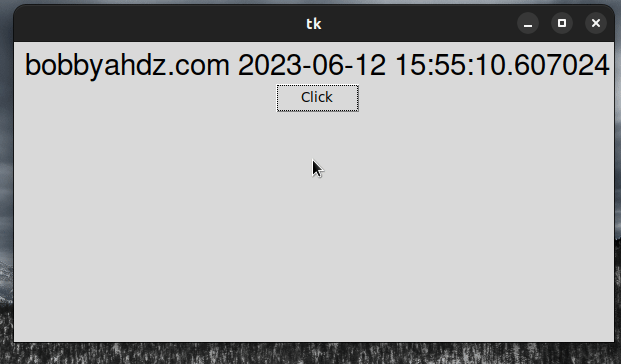
from tkinter import Tk, ttk root = Tk() root.geometry('400x400') frm = ttk.Frame(root, padding=10) frm.grid() label = ttk.Label(frm, text="Press Enter to update text", font=('Helvetica', 22)) label.grid(column=0, row=0) def example_func(event): print(event) print('User pressed Enter') label.config(text="bobbyahdz.com") root.bind('<Return>', example_func) root.mainloop()
We used the ttk.Label class to create a Label widget that has its text
initially set to "Press Enter to update text".
label = ttk.Label(frm, text="Press Enter to update text", font=('Helvetica', 22)) label.grid(column=0, row=0)
Then, we defined the function we want to run when the Enter key is pressed.
def example_func(event): print(event) print('User pressed Enter') label.config(text="bobbyahdz.com")
The function prints the event object and a message to the terminal and updates
the text of the Label widget.
The root.bind() method is used to bind the Enter key to the function.
root.bind('<Return>', example_func)
When the <Return> (Enter) key is pressed, the example_func function is
invoked.
Note that the function is invoked every time the Enter key is pressed, not
just the first time.
The event handler function must take an event parameter even if it isn't used.
# Binding the Enter key and a Button to a function in Tkinter
In some cases, you might want to run a function when the Enter key is pressed
or when a button is clicked.
You can use the bind() method to set up an Enter key press event listener
and a button click event listener.
from tkinter import Tk, ttk from datetime import datetime root = Tk() root.geometry('600x300') frm = ttk.Frame(root, padding=10) frm.grid() label = ttk.Label(frm, text="Press Enter or click to update text", font=('Helvetica', 22)) label.grid(column=0, row=0) def example_func(event): print(event) print('User pressed Enter or clicked Button') label.config(text=f"bobbyahdz.com {datetime.now()}") button = ttk.Button(frm, text='Click') button.bind('<Button-1>', example_func) button.grid(column=0, row=2) root.bind('<Return>', example_func) root.mainloop()
The example_func() function is invoked when the user presses Enter or clicks
on the button.
The root.bind() method binds the <Return> (Enter) key to the example_func
just like in the previous subheading.
We also created a Button widget using the ttk.Button class.
button = ttk.Button(frm, text='Click')
The last step is to bind the button click to example_func as well.
button.bind('<Button-1>', example_func)
Every time the user presses Enter or clicks on the button, the function is
invoked.
You could also use the command keyword argument of the ttk.Button() class,
however, you would have to set a default value of None for the event
argument in example_func.
from tkinter import Tk, ttk from datetime import datetime root = Tk() root.geometry('600x300') frm = ttk.Frame(root, padding=10) frm.grid() label = ttk.Label(frm, text="Press Enter to update text", font=('Helvetica', 22)) label.grid(column=0, row=0) # 1) 👇️ Event has a default value of None def example_func(event=None): print(event) print('User pressed Enter or clicked Button') label.config(text=f"bobbyahdz.com {datetime.now()}") # 2) 👇️ Using command keyword argument button = ttk.Button(frm, text='Click', command=example_func) button.grid(column=0, row=2) # 3) 👇️ Only bind the Enter key to the function root.bind('<Return>', example_func) root.mainloop()
Notice that we set a default value of None for the event argument.
# 1) 👇️ Event has a default value of None def example_func(event=None): print(event) print('User pressed Enter or clicked Button') label.config(text=f"bobbyahdz.com {datetime.now()}")
This is necessary because when the button is clicked, the event argument won't
get passed to the function.
The event argument will only get passed to the function when the Enter key
is pressed.
We set the command keyword argument of the ttk.Button() class to the
function.
# 2) 👇️ Using command keyword argument button = ttk.Button(frm, text='Click', command=example_func)
Every time the button is clicked, example_func is invoked.
We didn't have to use the following line because we used the command keyword
argument.
button.bind('<Button-1>', example_func)
When using button.bind(), an event object is still passed to the bound
function, so we didn't have to default the event keyword argument to None in
the previous example.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

