You provided 'value' prop to a form field without onChange handler
Last updated: Apr 6, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- You provided 'value' prop to a form field without onChange handler
- You provided 'checked' prop to a form field without onChange handler
If you got the error "You provided 'checked' prop to a form field without onChange handler", click on the second subheading.
# You provided 'value' prop to a form field without onChange handler
The error "You provided a value prop to a form field without an onChange
handler" occurs when we set a value prop on a field that has no onChange
handler.
To solve the error, use the defaultValue prop or set an onChange prop on
the field.
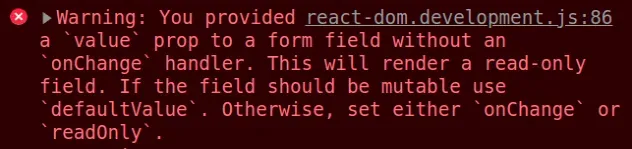
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
export default function App() { // ⛔️ You provided a `value` prop to a form field // without an `onChange` handler. This will render // a read-only field. If the field should be mutable // use `defaultValue`. Otherwise, set either `onChange` or `readOnly`. return ( <div> <input type="text" id="message" value="Initial value" /> </div> ); }
The issue is that we've set the value prop on the input field without
providing an onChange event handler. This makes the input's value static.
# Using the defaultValue prop to solve the error
One way to solve the error is to use the defaultValue prop instead.
export default function App() { return ( <div> <input type="text" id="message" defaultValue="Initial value" /> </div> ); }
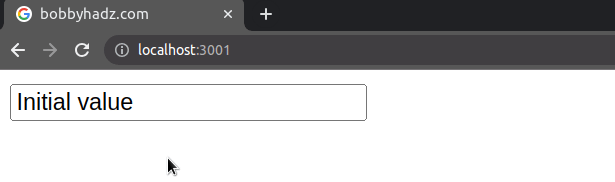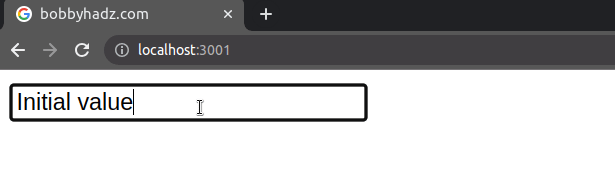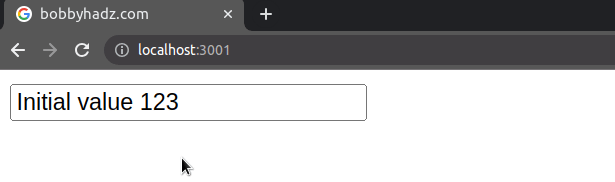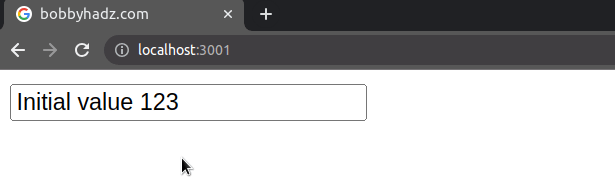
The defaultValue prop sets an initial value for the input field, but the value is not static and can be changed.
defaultValue prop is often used for uncontrolled (by the developer) fields. This means that you would have to access the value of the input field using a ref or as an element in a form.import {useRef} from 'react'; // 👇️ Example of uncontrolled input field export default function App() { const ref = useRef(null); const handleClick = () => { console.log(ref.current.value); }; return ( <div> <input ref={ref} type="text" id="message" defaultValue="Initial value" /> <button onClick={handleClick}>Click</button> </div> ); }
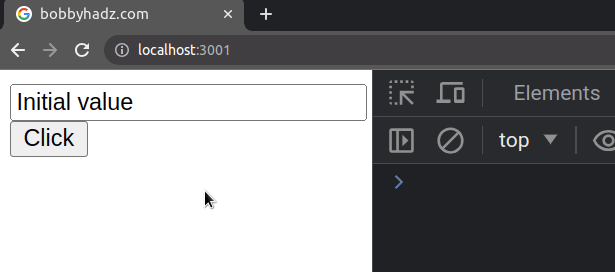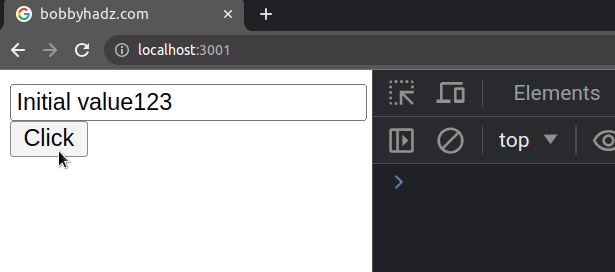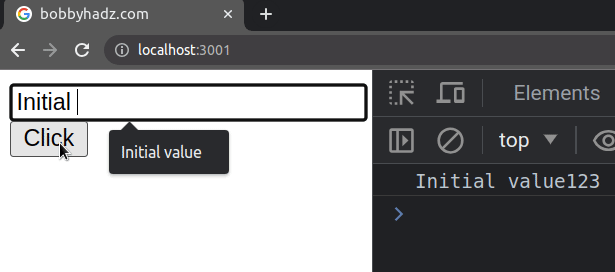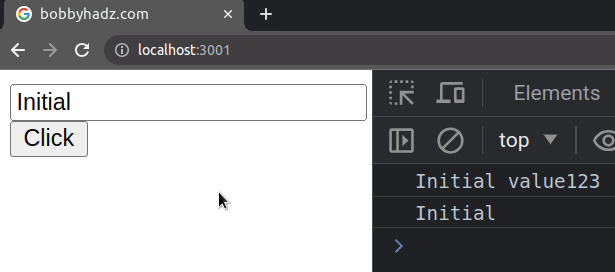
Every time you click on the button, the value of the input field will be
logged to the console.
# Setting an onChange prop on the input to solve the error
Alternatively, we can set an onChange prop on the input field and handle the
event.
import {useState} from 'react'; export default function App() { const [message, setMessage] = useState(''); const handleChange = event => { setMessage(event.target.value); // 👇️ This is the input field itself console.log(event.target); // 👇️ This is the new value of the input console.log(event.target.value); }; return ( <div> <input type="text" id="message" placeholder="Your message" onChange={handleChange} value={message} /> </div> ); }
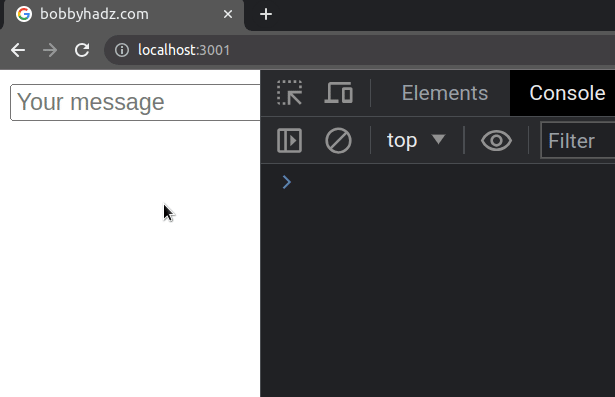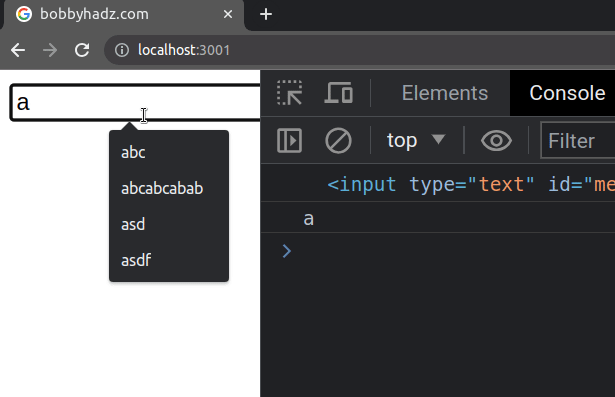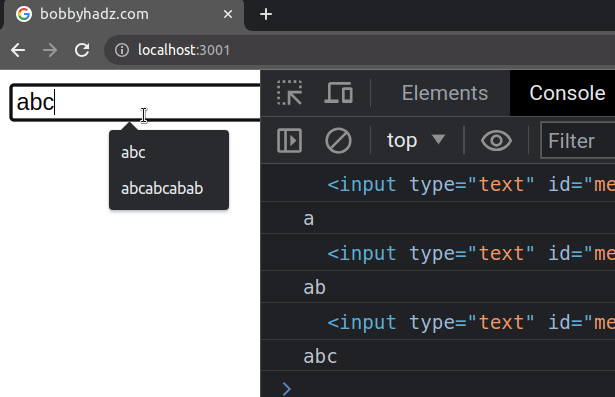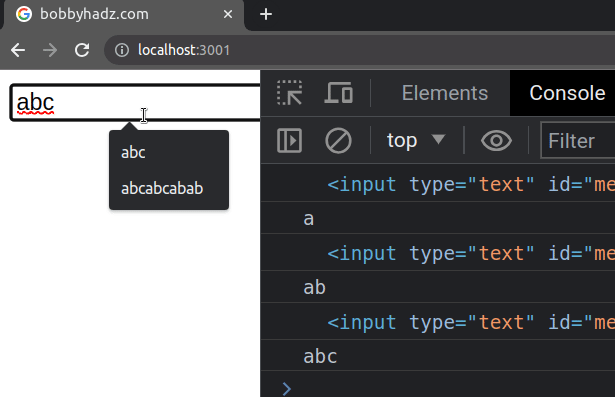
The first thing we did was store the input value in a state variable called
message.
onChange prop on the input field, so every time the input's value is changed, the handleChange function is invoked.We can access the input field via the target property on the event object.
Similarly, we can access the input's value via event.target.value.
# Specifying an initial value for the input field
If you want to
provide an initial value for the input,
you can just pass it to the useState() hook.
import {useState} from 'react'; export default function App() { // 👇️ Set initial value in call to useState const [message, setMessage] = useState('Your initial value'); const handleChange = event => { setMessage(event.target.value); console.log(event.target.value); }; return ( <div> <input type="text" id="message" placeholder="Your message" onChange={handleChange} value={message} /> </div> ); }
The string we passed to the useState hook will be set as the initial value for
the message variable.
# You provided 'checked' prop to a form field without onChange handler
The error "You provided a checked prop to a form field without an onChange
handler" occurs when we set a checked prop on a checkbox that has no
onChange handler.
To solve the error, use the defaultChecked prop or set an onChange prop on
the field.
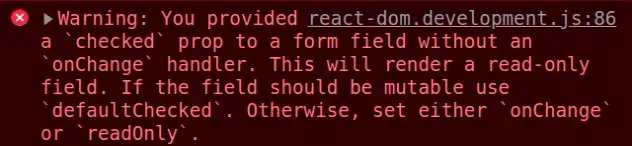
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
export default function App() { // ⛔️ Warning: You provided a `checked` prop to a form field // without an `onChange` handler. This will render a read-only field. // If the field should be mutable use `defaultChecked`. // Otherwise, set either `onChange` or `readOnly`. return ( <div> <input type="checkbox" id="subscribe" name="subscribe" checked={true} /> </div> ); }
The issue is that we've set the checked prop on the input field without
providing an onChange event handler. This makes the input's checked prop
static.
# Using the defaultChecked prop to solve the error
One way to solve the error is to
use the defaultChecked prop instead.
export default function App() { return ( <div> <input type="checkbox" id="subscribe" name="subscribe" defaultChecked={true} /> </div> ); }
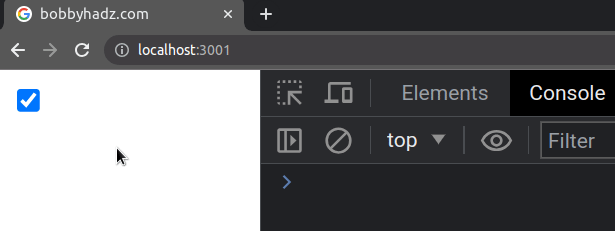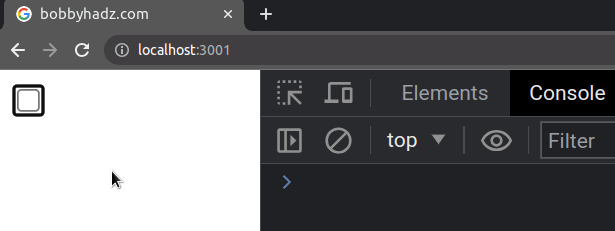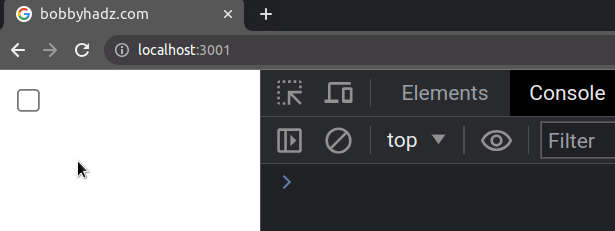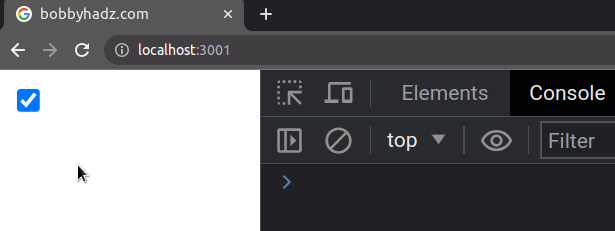
The defaultChecked prop sets an initial value for the checkbox, but the value
is not static and can be changed.
defaultChecked prop is often used for uncontrolled (by the developer) checkboxes. This means that you would have to access the value of the field using a ref or as an element in a form.import {useRef} from 'react'; // 👇️ Example of uncontrolled checkbox export default function App() { const ref = useRef(null); const handleClick = () => { console.log(ref.current.checked); }; return ( <div> <input ref={ref} type="checkbox" id="subscribe" name="subscribe" defaultChecked={true} /> <button onClick={handleClick}>Click</button> </div> ); }
Every time you click on the button, the checked value of the checkbox will be
logged to the console.
# Setting an onChange prop on the checkbox
Alternatively, we can set an onChange prop on the input field and handle the
event.
import {useState} from 'react'; export default function App() { const [isSubscribed, setIsSubscribed] = useState(false); const handleChange = event => { setIsSubscribed(event.target.checked); // 👇️ This is the checkbox itself console.log(event.target); // 👇️ This is the checked value of the field console.log(event.target.checked); }; return ( <div> <input type="checkbox" id="subscribe" name="subscribe" onChange={handleChange} checked={isSubscribed} /> </div> ); }
The first thing we did is store the checked input value in a state variable
called isSubscribed.
onChange prop on the checkbox, so every time its value is changed, the handleChange function is invoked.We can access the checkbox via the target property on the event object.
Similarly, we can access its value via event.target.checked.
# Providing an initial value for the checkbox
If you want to provide an initial value for the checkbox, you can just pass it
to the useState() hook.
import {useState} from 'react'; export default function App() { // 👇️ Set checked to true initially const [isSubscribed, setIsSubscribed] = useState(true); const handleChange = event => { setIsSubscribed(event.target.checked); // 👇️ This is the checkbox itself console.log(event.target); // 👇️ This is the checked value of the field console.log(event.target.checked); }; return ( <div> <input type="checkbox" id="subscribe" name="subscribe" onChange={handleChange} checked={isSubscribed} /> </div> ); }
We passed true to the useState hook, so the initial value for the checkbox
will be checked.
I've also written an article on how to set the default checked value of a checkbox.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

