How to set Text color in React
Last updated: Apr 6, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Set Text color in React
Use inline styles to set the text color of an element in React.js.
The text color will only be applied to the element to which it was added and its children.
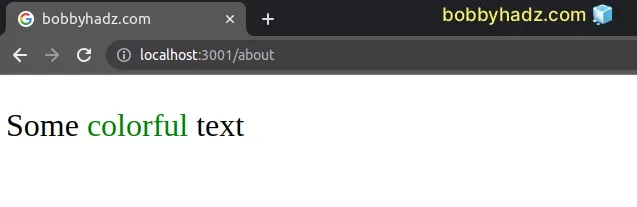
const App = () => { return ( <div> <p style={{fontSize: '2rem'}}> Some{' '} <span style={{color: 'white', backgroundColor: 'lime'}}>colorful</span>{' '} text </p> </div> ); }; export default App;

We used inline styles to change the text color of an element.
The first set of curly braces in the inline style marks the beginning of an expression and the second set of curly braces is the object containing styles and values.
The changed text color is only going to be applied to the span element.
# Extract the style into a component
If you need to do this often, you can extract the span element into a
component that renders its children.
function ColorfulText({children}) { return <span style={{color: 'green'}}>{children}</span>; } const App = () => { return ( <div> <p style={{fontSize: '2rem'}}> Some <ColorfulText>colorful</ColorfulText> text </p> </div> ); }; export default App;
Whatever we pass between the opening and closing tags of the ColorfulText
component will have the specific text color applied.
If you need to bold specific text, click on the link and follow the instructions.
# Set Text color in React using a global CSS file
An alternative solution is to define a class in a global CSS file.
.red-text { color: red; }
And here is how we would import the App.css file and use the red-text class.
import './App.css'; const App = () => { return ( <div> <p style={{fontSize: '2rem'}}> Some <span className="red-text">colorful</span> text </p> </div> ); }; export default App;

This approach enables us to reuse commonly used styles by defining them in a global CSS file.
It's a best practice to import your global CSS files in your index.js file
because then they wouldn't only get loaded when a certain component is mounted.
If you need to set a global font family in React, click on the following link.
# Conditionally setting text color
You can use the ternary operator to conditionally set the text color in React.
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const [isColored, setIsColored] = useState(false); return ( <div> <p> bobby <span style={{color: isColored ? 'green' : ''}}>hadz</span> .com </p> <button onClick={() => setIsColored(isColored => !isColored)}> Toggle isColored </button> </div> ); }; export default App;
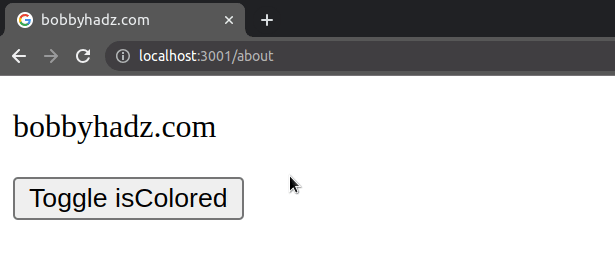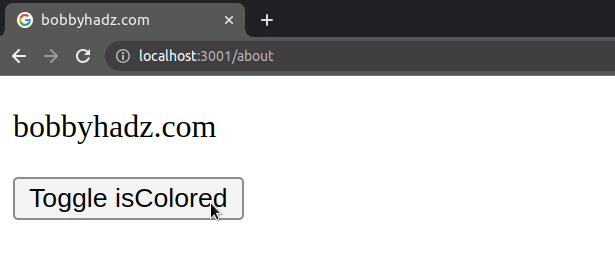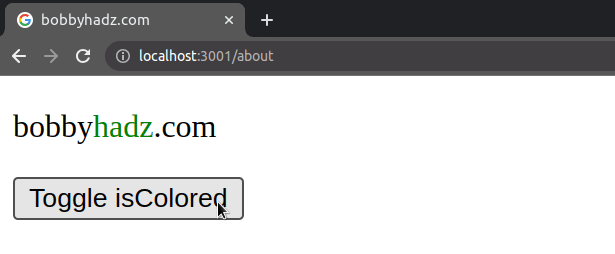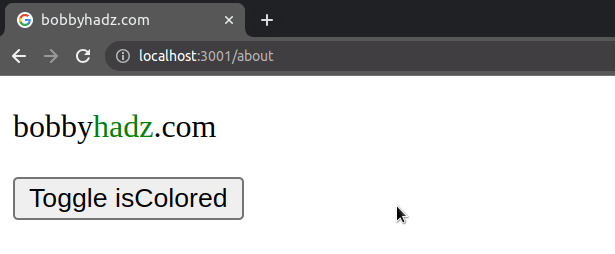
The code sample only sets the text color when the isColored state variable is
is true.
The ternary operator is
very similar to an if/else statement.
If the expression to the left of the question mark is truthy, the operator returns the value to the left of the colon, otherwise, the value to the right of the colon is returned.
<p> bobby <span style={{color: isColored ? 'green' : ''}}>hadz</span> .com </p>
You can imagine that the value before the colon is the if block and the value
after the colon is the else block.
If the isColored variable stores a true value, the string green is
returned, otherwise, an empty string is returned.
I've also written an article on how to cross out (strikethrough) text.

