Get the Mouse position (coordinates) in React
Last updated: Apr 7, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
# Get the Mouse position (coordinates) in React
To get the mouse position in React:
- Set the
onMouseMoveprop on an element or add an event listener on thewindowobject. - Provide an event handler function.
- Access relevant properties on the
eventobject.
import {useEffect, useState} from 'react'; export default function App() { const [coords, setCoords] = useState({x: 0, y: 0}); useEffect(() => { const handleWindowMouseMove = event => { setCoords({ x: event.clientX, y: event.clientY, }); }; window.addEventListener('mousemove', handleWindowMouseMove); return () => { window.removeEventListener( 'mousemove', handleWindowMouseMove, ); }; }, []); return ( <div> <p> Mouse positioned at:{' '} <b> ({coords.x}, {coords.y}) </b> </p> </div> ); }
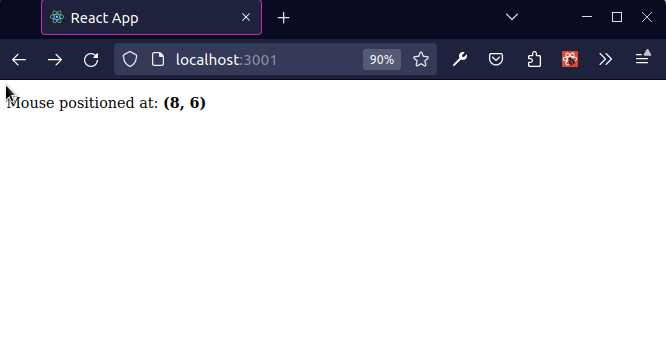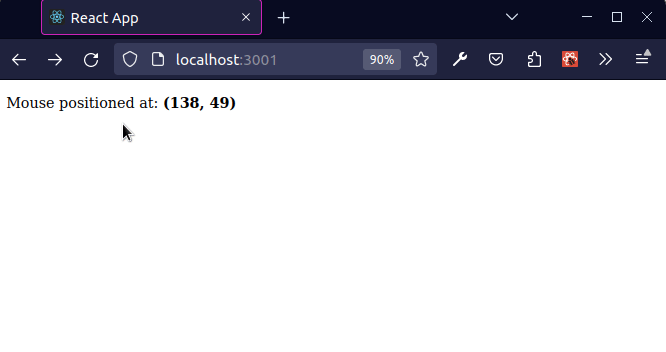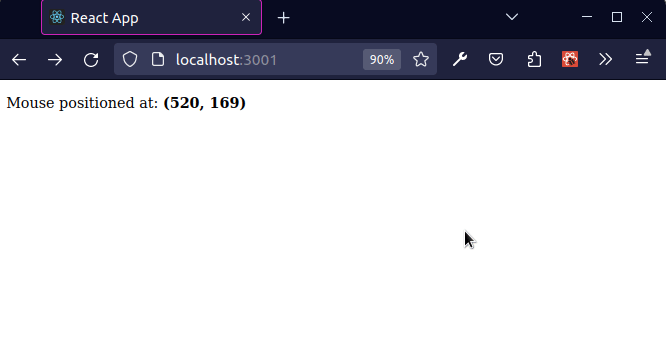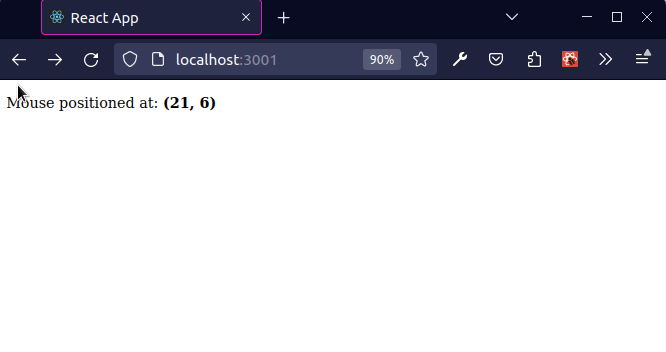
The mousemove event is triggered at an element when the user's mouse is moved while the cursor's hotspot is inside it.
We used the
addEventListener() method
to add the mousemove event listener to the window object.
We passed an empty dependencies array to the
useEffect hook because we only
want to register the paste event listener once - when the component mounts.
useEffect hook is called when the component unmounts.We used the removeEventListener() method to remove the event listener that we previously registered.
The cleanup step is important because we want to make sure we don't have any memory leaks in our application.
The mousemove event returns a MouseEvent object on which we can access the
clientX and clientY properties.
the clientX property returns the horizontal coordinate of the mouse within the application's viewport.
the clientY property returns the vertical coordinate of the mouse within the application's viewport.
# Get the Mouse position (coordinates) relative to an element in React
The previous subheading shows how to get the global coordinates of the mouse.
As shown in the screenshot, the coordinates in the top left position of the viewport are (x 0, y 0) and the coordinates at the bottom right position of the viewport at (x MAX, y MAX).

To get the mouse coordinates relative to an element on the page:
- Set the
onMouseMoveprop on an element or add an event listener on thewindowobject. - Subtract
offsetLeftfromclientXandoffsetTopfromclientY.
import {useEffect, useState} from 'react'; export default function App() { const [globalCoords, setGlobalCoords] = useState({x: 0, y: 0}); const [localCoords, setLocalCoords] = useState({x: 0, y: 0}); const handleMouseMove = event => { // 👇️ Get the mouse position relative to the element setLocalCoords({ x: event.clientX - event.target.offsetLeft, y: event.clientY - event.target.offsetTop, }); }; useEffect(() => { const handleGlobalMouseMove = event => { setGlobalCoords({ x: event.clientX, y: event.clientY, }); }; window.addEventListener('mousemove', handleGlobalMouseMove); return () => { window.removeEventListener( 'mousemove', handleGlobalMouseMove, ); }; }, []); return ( <div> <div onMouseMove={handleMouseMove} style={{ padding: '4rem', backgroundColor: 'lightgray', border: '1px solid black', width: '300px', }} > <h2> Relative: ({localCoords.x}, {localCoords.y}) </h2> </div> <br /> <h2> Global: ({globalCoords.x}, {globalCoords.y}) </h2> </div> ); }
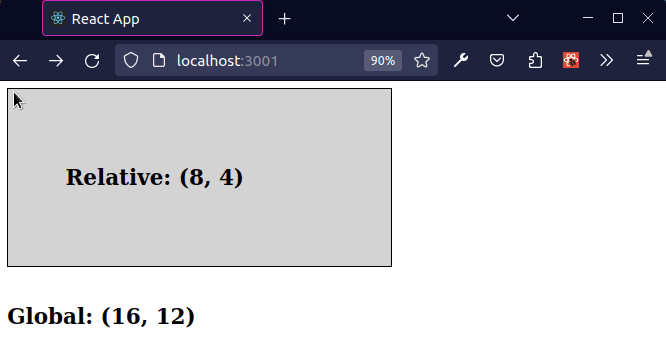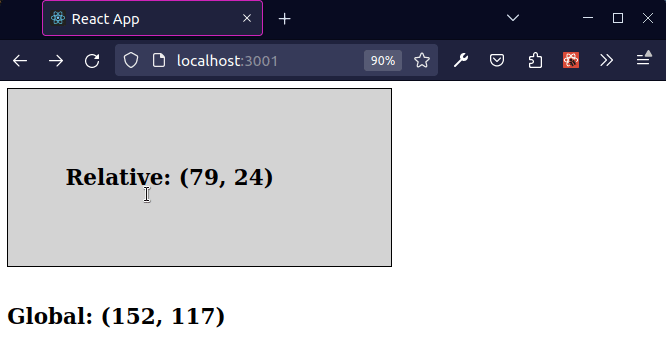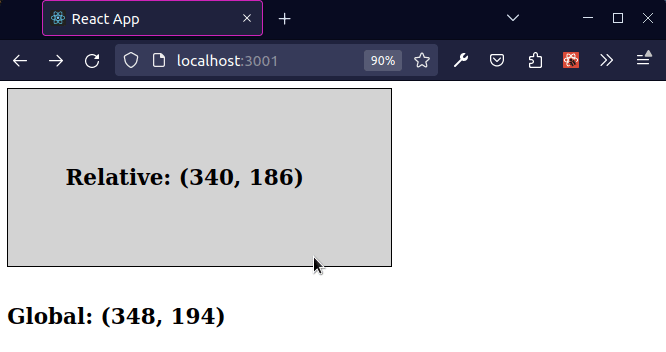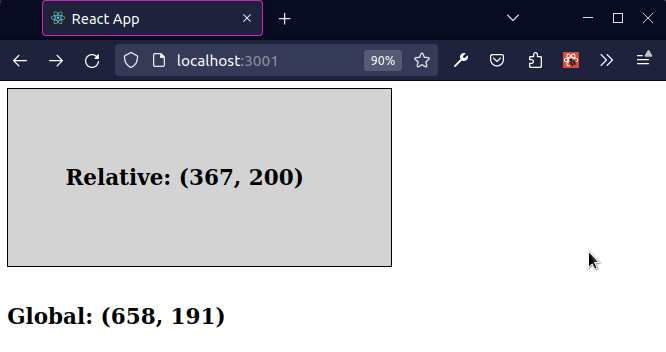
Subtracting offsetLeft from clientX returns the X coordinate of the mouse
relative to the div element.
The offsetLeft property returns the number of pixels that the upper left corner of the current element is offset to the left within its parent.
const handleMouseMove = event => { // 👇️ Get the mouse position relative to the element setLocalCoords({ x: event.clientX - event.target.offsetLeft, y: event.clientY - event.target.offsetTop, }); };
Subtracting offsetTop from clientY returns the Y coordinate of the mouse
relative to the div element.
The offsetTop property returns the number of pixels between the outer border of the current element relative to the inner border of the closest-positioned parent.
If you need to check if an element is in the viewport, click on the following article.

