How to Remove an imported module in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# Remove an imported module in Python
To remove an imported module in Python:
- Use the
delstatement to delete thesysreference to the module. - Use the
delstatement to remove the direct reference to the module.
import sys import requests # 👇️ <function get at 0x7f8c7d30e4d0> print(requests.get) # ✅ remove an imported module del sys.modules['requests'] del requests # ⛔️ NameError: name 'X' is not defined print(requests.get)
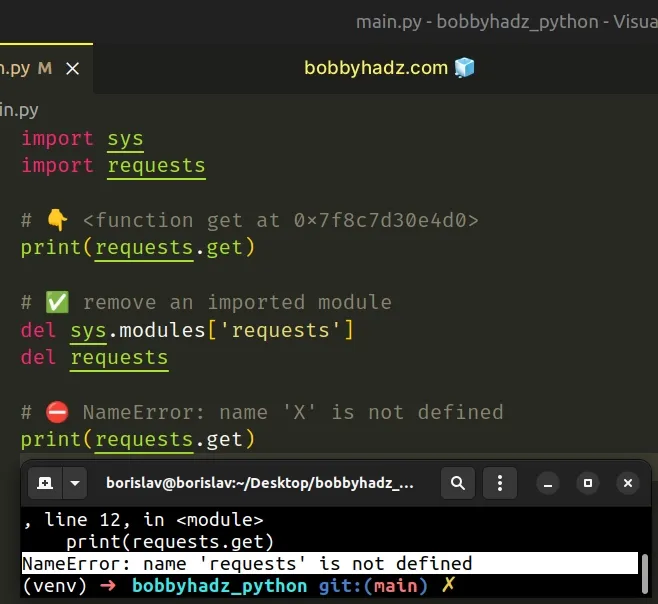
The first step is to delete the sys.modules reference to the module we are
trying to unload.
Sys.modules is a dictionary that maps module names to modules that have already been loaded.
The dictionary is most commonly used to force reload modules.
This is necessary because even if we delete the direct reference to the module,
we'd still have a reference to it with the sys.modules dictionary.
import sys import requests # 👇️ <function get at 0x7f8c7d30e4d0> print(requests.get) del requests # 👇️ <module 'requests' from '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/requests/__init__.py'> print(sys.modules['requests'])
For the module to get garbage collected, we have to delete the key from the
sys.modules dictionary and delete the direct reference to the module.
# Reloading a previously imported module
It can sometimes be tricky to unload a module. An alternative you can try is to
reload the module using the importlib.reload() method.
from importlib import reload import requests if len('a') == 1: requests = reload(requests) # 👇️ <function get at 0x7f5cddf024d0> print(requests.get)
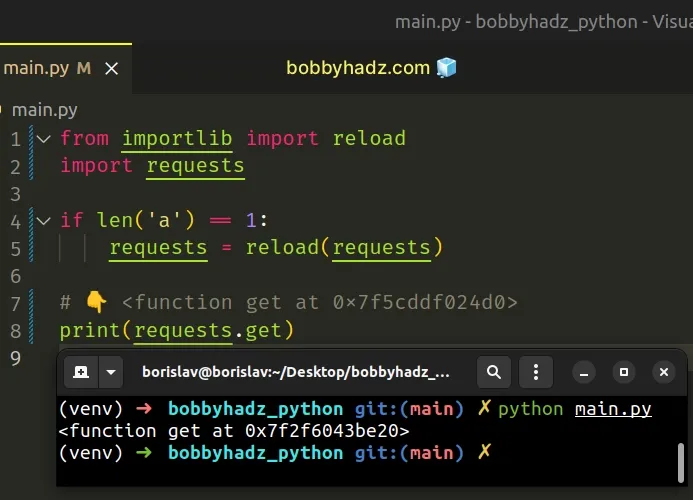
The importlib.reload() method reloads a previously imported module.
The argument to the method must be a module object that has been successfully imported (prior to reloading it).
importlib.reload() method is most often used when we have edited the source of the module using an external editor and we want to get access to the newer version without exiting the interpreter.The reload() method returns the module object, so you can directly reassign
the module to the result of calling reload(module).
I've also written an article on how to not run a module's code when it is imported.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Remove Newline characters from a List or a String in Python
- Remove non-alphanumeric characters from a Python string
- Remove non-ASCII characters from a string in Python
- Remove the non utf-8 characters from a String in Python
- How to Remove the None values from a Dictionary in Python
- How to Remove the None values from a List in Python
- 'EntryPoints' object has no attribute 'get' error [Solved]
- How to import all Functions from a File in Python

