Find elements in one List that are not in the other (Python)
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Find elements in one list that are not in the other (Python)
- Find elements in one list that are not in the other using list comprehension
- Find elements in one list that are not in the other using a for loop
- Find elements in one list that are not in the other using NumPy
# Find elements in one list that are not in the other (Python)
To find the elements in one list that are not in the other:
- Use the
set()class to convert the first list to asetobject. - Use the
difference()method to get the elements in thesetthat are not in the list. - Use the
list()class to convert thesetobject to a list.
list_1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'] list_2 = ['a', 'd', 'e'] result_1 = list(set(list_2).difference(list_1)) print(result_1) # 👉️ ['e', 'd'] # -------------------------------------- result_2 = list(set(list_1).difference(list_2)) print(result_2) # 👉️ ['b', 'c']
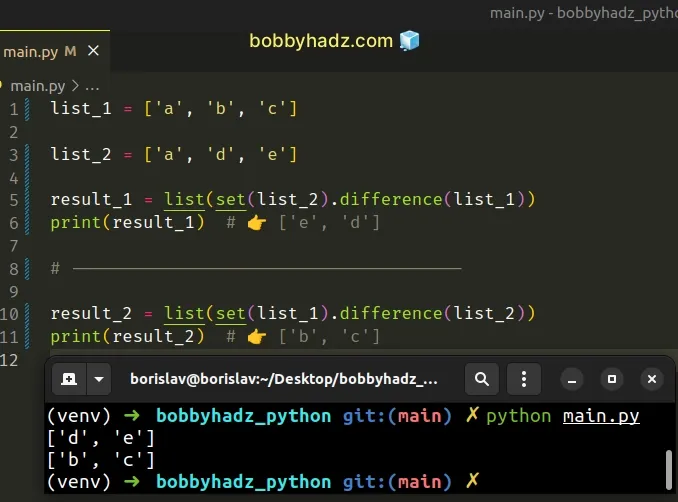
The first step is to use the
set() class to convert
the list to a set object.
Set objects have a
difference()
method that returns a new set with elements in the set that are not in the
provided iterable.
In other words, set(list_2).difference(list_1) returns a new set that
contains the items in list_2 that are not in list_1.
list_1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'] list_2 = ['a', 'd', 'e'] # 👇️ {'d', 'e'} print(set(list_2).difference(list_1))
The last step is to use the list() class to convert the result to a list.
list_1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'] list_2 = ['a', 'd', 'e'] result_1 = list(set(list_2).difference(list_1)) print(result_1) # 👉️ ['d', 'e']
Alternatively, you can use a list comprehension.
# Find elements in one list that are not in the other using list comprehension
This is a three-step process:
- Use a list comprehension to iterate over the list.
- Check if each element is not contained in the other list and return the result.
- The new list will only contain items from the first list that are not in the second list.
list_1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'] list_2 = ['a', 'd', 'e'] result_1 = [item for item in list_2 if item not in list_1] print(result_1) # 👉️ ['d', 'e'] # -------------------------------------- result_2 = [item for item in list_1 if item not in list_2] print(result_2) # 👉️ ['b', 'c']
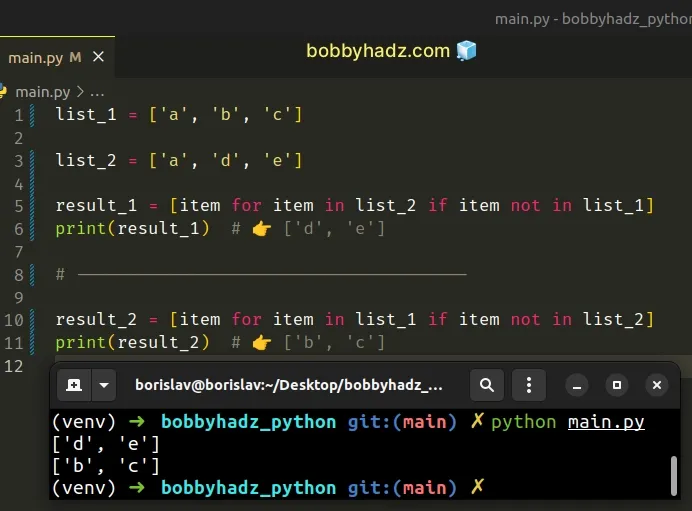
We used a list comprehension to iterate over one of the lists.
On each iteration, we check if the item is not contained in the other list and return the result.
The new list contains all of the elements in the first list that are not in the second.
In other words, [item for item in list_2 if item not in list_1] returns all of
the elements in list_2 that are not in list_1.
# Find elements in one list that are not in the other using a for loop
You can also use a for loop to find elements in one list that are not in the other.
list_1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'] list_2 = ['a', 'd', 'e'] new_list = [] for item in list_2: if item not in list_1: new_list.append(item) print(new_list) # 👉️ ['d', 'e']
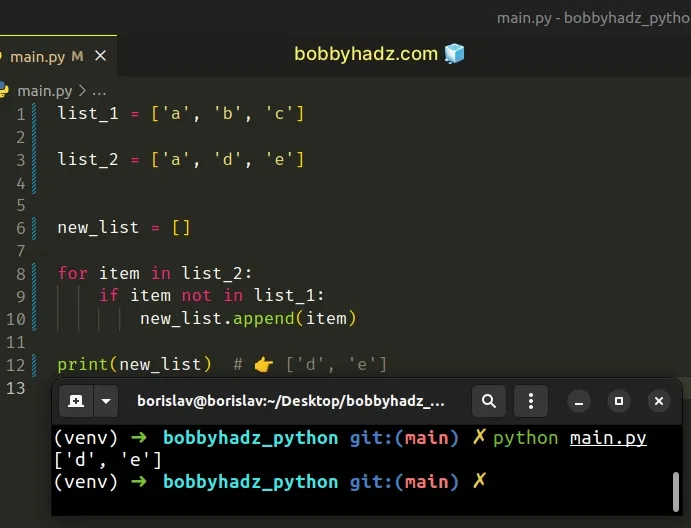
We used a for loop to iterate over the second list.
On each iteration, we check if the current item is not contained in the first list.
If the condition is met, we append the item to a new list.
The new list only contains the items from the second list that are not contained in the first.
# Find elements in one list that are not in the other using NumPy
You can also use the NumPy module to find the elements in one list that are not in the other.
import numpy as np list_1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'] list_2 = ['a', 'd', 'e'] result_1 = np.setdiff1d(list_2, list_1) print(result_1) # 👉️ ['d' 'e'] result_2 = np.setdiff1d(list_1, list_2) print(result_2) # 👉️ ['b' 'c']
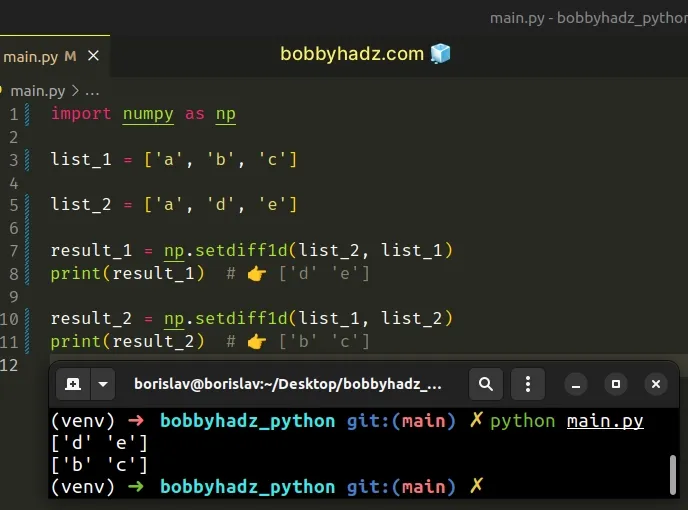
Make sure to install NumPy to be able to import and use the module.
pip install numpy pip3 install numpy
The numpy.setdiff1d method finds the set difference between two arrays.
The method returns the unique values in the first array that are not contained in the second array.
If you need to convert the results array to a native Python list, use the
tolist() method.
import numpy as np list_1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'] list_2 = ['a', 'd', 'e'] result_1 = np.setdiff1d(list_2, list_1).tolist() print(result_1) # 👉️ ['d', 'e'] print(type(result_1)) # 👉️ <class 'list'>
The
tolist()
method converts a numpy array to a list.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Find common values in multiple Lists in Python
- Find the indices of duplicate items in a List in Python
- Find Max and Min in List without max() and min() in Python
- Find Min and Max values in Tuple or List of Tuples in Python
- Find the most/least common element in a List in Python
- Find object(s) in a List of objects in Python
- Find second Smallest or Largest number in a List in Python

