Convert None to Empty string or an Integer in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
# Convert None to an Empty string in Python
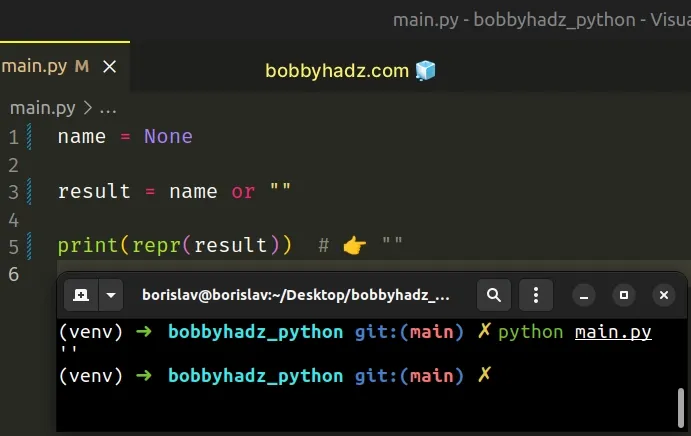
Use the boolean OR operator to convert None to an empty string in Python, e.g.
result = None or "".
The boolean OR operator returns the value to the left if it's truthy,
otherwise, the value to the right is returned. Since None is a falsy value,
the operation will return "".
name = None result = name or "" print(repr(result)) # 👉️ ""
If you need to convert the value to a string if it isn't one already, use the following code sample instead.
value = None my_str = str(value or '') print(repr(my_str)) # 👉️ ""
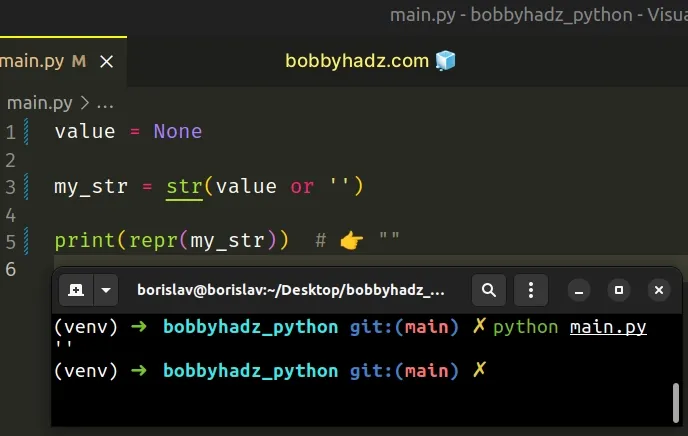
We used the boolean or operator to return an empty string if the value to the left is falsy.
All values that are not truthy are considered falsy. The falsy values in Python are:
- constants defined to be falsy:
NoneandFalse. 0(zero) of any numeric type- empty sequences and collections:
""(empty string),()(empty tuple),[](empty list),{}(empty dictionary),set()(empty set),range(0)(empty range).
x or y returns the value to the left if it's truthy, otherwise, the value to the right is returned.Since None is a falsy value, the expression None or y is always going to
return y.
name = None result = name or "" print(result) # 👉️ ""
x or y would also return y if x is any of the other falsy values, e.g. 0, False, or an empty list, dict or tuple.# Convert None to an Empty string using an if statement
Alternatively, you can use an if statement to check if the variable stores
None and reassign it to an empty string.
name = None if name is None: name = "" print(repr(name)) # 👉️ ""
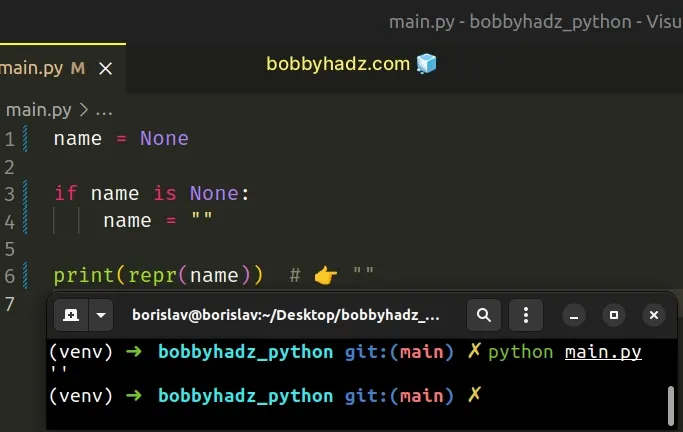
Checking for None is much more explicit and the if block will only run if
the variable stores a None value.
The condition wouldn't be satisfied if the variable stores any other falsy value.
You can also extract the logic into a reusable function.
def convert_to_str(value): if value is None: return '' return str(value) # 👇️ "" print(convert_to_str(None)) # 👇️ "bobbyhadz.com" print(convert_to_str('bobbyhadz.com'))
# Convert None to an Empty string using a one-line if/else statement
You can also use a one-liner if/else statement.
name = None name = "" if name is None else name print(repr(name)) # 👉️ ""
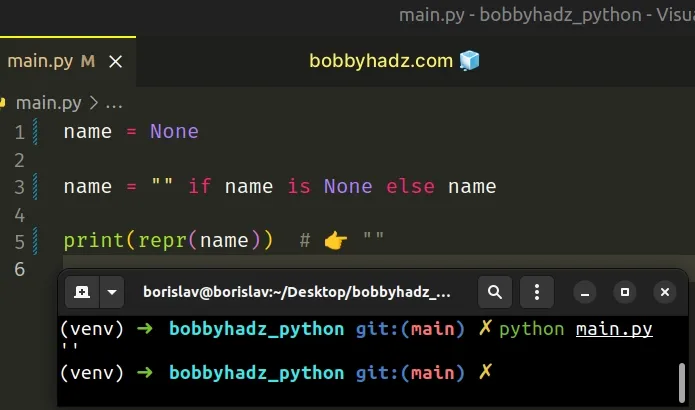
If the variable stores None, it gets set to an empty string, otherwise it gets
set to its current value.
name = 'hello' name = "" if name is None else name print(name) # 👉️ "hello"
# Convert None to an Empty string using a custom function
You can also use a custom function to convert None to an empty string.
def convert_to_str(value): return '' if value is None else str(value) print(convert_to_str(None)) # 👉️ "" print(convert_to_str('hello')) # 👉️ 'hello' print(convert_to_str(100)) # 👉️ '100'
The function takes a value as a parameter and returns an empty string if the
supplied value is None.
If the value is not None, the value is converted to a string and passed to the
str() class.
# Convert None to an Integer (e.g. 0) in Python
Use the boolean OR operator to convert NoneType to an integer in Python, e.g.
result = None or 0.
The boolean OR operator will return the value to the right-hand side because the
value to the left (None) is falsy.
my_var = None # ✅ Convert None to 0 result_1 = my_var or 0 print(result_1) # 👉️ 0 # ✅ Convert None to 100 result_2 = my_var or 100 print(result_2) # 👉️ 100
The first code sample converts None to 0.
If you need to convert the value to an integer if it isn't one already, use the int() class.
value = None my_int = int(value or 0) print(my_int) # 👉️ 0
We used the boolean or operator to return an integer if the value to the left is falsy.
All values that are not truthy are considered falsy. The falsy values in Python are:
- constants defined to be falsy:
NoneandFalse. 0(zero) of any numeric type- empty sequences and collections:
""(empty string),()(empty tuple),[](empty list),{}(empty dictionary),set()(empty set),range(0)(empty range).
x or y returns the value to the left if it's truthy, otherwise, the value to the right is returned.Since None is a falsy value, the expression None or y is always going to
return y.
x or y would also return y if x is any of the other falsy values, e.g. an empty string, False, or an empty list, dict or tuple.# Convert None to an Integer (e.g. 0) using an if statement
Alternatively, you can use an if statement to check if the variable stores
None and reassign it to an integer.
my_var = None if my_var is None: my_var = 0 print(my_var) # 👉️ 0
Checking for None is much more explicit and the if block will only run if
the variable stores a None value.
The condition wouldn't be satisfied if the variable stores any other falsy value.
# Convert None to an Integer using a one-liner if/else statement
You can also use a one-liner if/else statement.
my_var = None # ✅ Convert None to 0 my_var = 0 if my_var is None else my_var print(my_var) # 👉️ 0
If the variable stores None, it gets set to 0, otherwise it gets set to its
current value.
my_var = 123 my_var = 0 if my_var is None else my_var print(my_var) # 👉️ 123
The variable in the example doesn't store a None value, so its value remains
unchanged.
# Convert None to an Integer using a custom function
You can also define a reusable function that converts None to an integer.
def convert_to_int(value): if value is None: return 0 return int(value) print(convert_to_int(None)) # 👉️ 0 print(convert_to_int(100)) # 👉️ 100 print(convert_to_int('500')) # 👉️ 500
The function takes a value as a parameter and checks if the value is None.
If the condition is met, 0 is returned, otherwise, the result of passing the
value to the int() class is returned.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

