How to check if a Line is Empty in Python
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Check if a line is Empty in Python
To check if a line is empty:
- Open the file in reading mode.
- Use the
file.readlines()method to get the lines in the file. - Use the
line.strip()method to check if the line is empty.
# ✅ check if a line is NOT empty with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding="utf-8") as f: lines = f.readlines() for line in lines: if line.strip(): print('The line is NOT empty ->', line) else: print('The line is empty') print('------------------------------------------') # ✅ check if a line is empty with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding="utf-8") as f: lines = f.readlines() for line in lines: if line.strip() == "": print('The line is empty') else: print('The line is NOT empty', line)
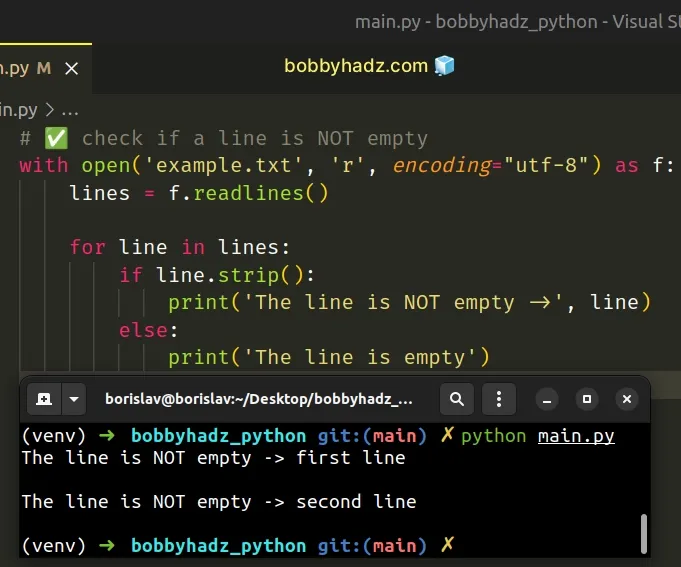
We used the with statement to open the file in reading mode.
The statement automatically takes care of closing the file for us.
We used the f.readlines() method to get a list of the lines in the file.
The str.strip method returns a copy of the string with the leading and trailing whitespace (including newline characters) removed.
print(repr('\n'.strip())) # 👉️ '' print(repr(' '.strip())) # 👉️ ''
The method doesn't change the original string, it returns a new string. Strings are immutable in Python.
# Checking if a line in a file isn't empty
The first example checks if each line isn't empty.
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding="utf-8") as f: lines = f.readlines() for line in lines: if line.strip(): print('The line is NOT empty ->', line) else: print('The line is empty')
If the str.strip() method returns a truthy value (not an empty string), then
the line isn't empty.
To check if a line is empty, compare the result of calling str.strip() with an
empty string.
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding="utf-8") as f: lines = f.readlines() for line in lines: if line.strip() == "": print('The line is empty') else: print('The line is NOT empty', line)
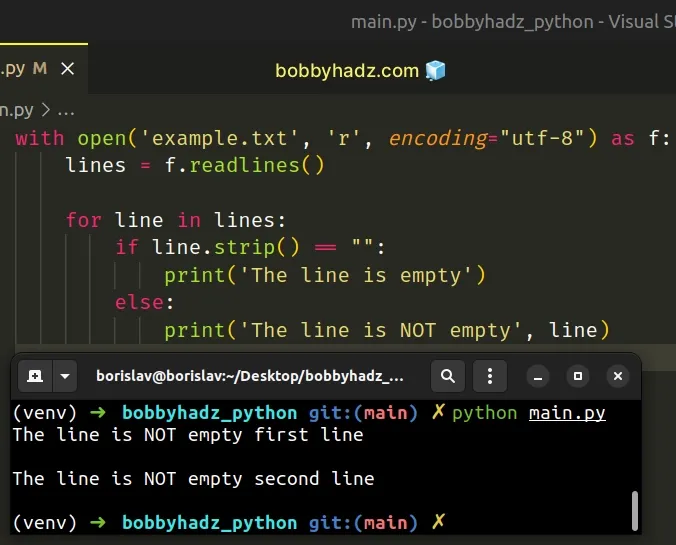
If the str.strip() method returns an empty string, then the line is empty.
This approach returns True if the line contains whitespace characters or
newlines.
If you only want to check for newline characters, use the in operator.
# Check if a line is Empty using the in operator
This is a three-step process:
- Open the file in reading mode.
- Use the
file.readlines()method to get the lines in the file. - Use the
inoperator to check if the line is empty.
# ✅ check if a line is NOT empty with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding="utf-8") as f: lines = f.readlines() for line in lines: if line not in ['\n', '\r', '\r\n']: print('The line is NOT empty ->', line) else: print('The line is empty') print('------------------------------------------') # ✅ check if a line is empty with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding="utf-8") as f: lines = f.readlines() for line in lines: if line in ['\n', '\r', '\r\n']: print('The line is empty') else: print('The line is NOT empty', line)
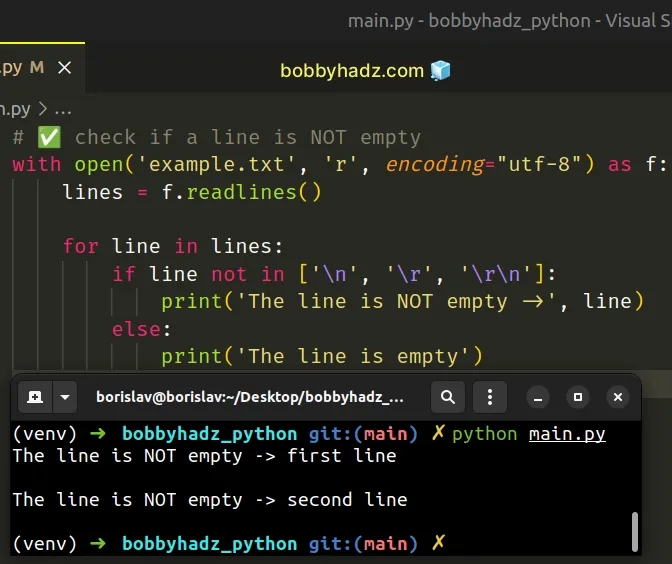
The in operator tests
for membership. For example, x in l evaluates to True if x is a member of
l, otherwise, it evaluates to False.
x not in l returns the negation of x in l.The first example checks if each line in the file isn't empty.
If the string stored in the line variable is not equal to \n, \r and
\r\n, then it's not an empty line.
The newline characters are:
\nfor POSIX style encoded files\r\nfor Windows-style encoded files\rfor old Mac encoded files
To check if the line is empty, use the in operator instead.
with open('example.txt', 'r', encoding="utf-8") as f: lines = f.readlines() for line in lines: if line in ['\n', '\r', '\r\n']: print('The line is empty') else: print('The line is NOT empty', line)
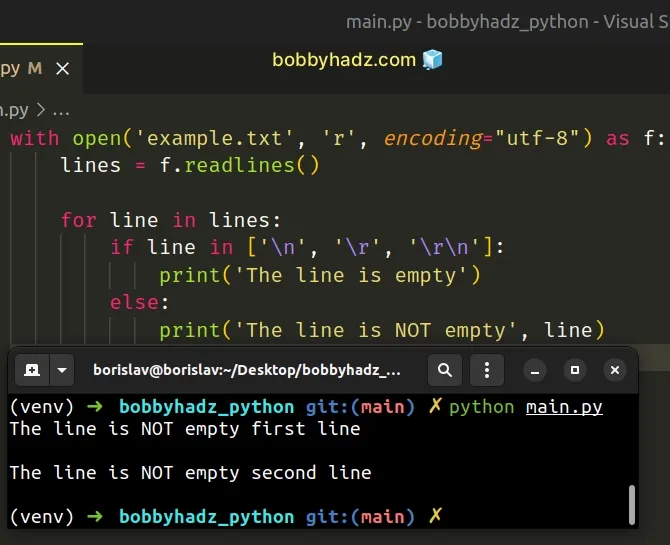
If the line variable is one of \n, \r or \r\n, then it's an empty line.
I've also written an article on how to check if user input is empty.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Check if a String contains an Element from a List in Python
- Check if a String contains a Number in Python
- Check if a string contains any Uppercase letters in Python
- How to Check if a String contains Vowels in Python
- Check if a string does NOT contain substring in Python
- Check if String ends with a Substring using Regex in Python
- Check if List contains a String case-insensitive in Python
- Check if String starts with any Element from List in Python
- Check if a String starts with a Number or Letter in Python
- Check if two Strings have the same Characters in Python

