Await is only valid in async function error in JS and NodeJS
Last updated: Jan 14, 2023
Reading time·3 min

# Await is only valid in async function Error in NodeJS
The error "await is only valid in async functions and the top level bodies of
modules" occurs when the await keyword is used inside of a function that was
not marked as async.
To solve the error, mark the directly enclosing function as async.
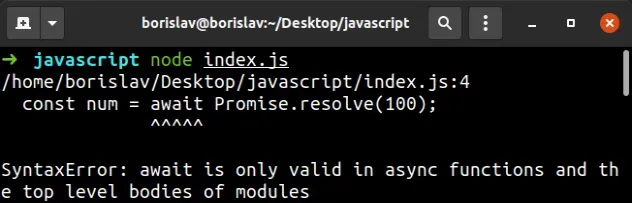
Here are 2 examples of how the error occurs.
// 👇️ Cause: Function not marked as async function getNum() { // ⛔️ Error: SyntaxError: await is only valid in async functions and the top-level bodies of modules const num = await Promise.resolve(100); return num; } // ---------------------------------------------- // 👇️ Cause: Using top-level await without setting // `type` to `module` in `package.json` const result = await Promise.resolve(42);
We didn't declare the getNum function as async, so we aren't able to use the
await keyword in it.
# Mark the directly enclosing function as async
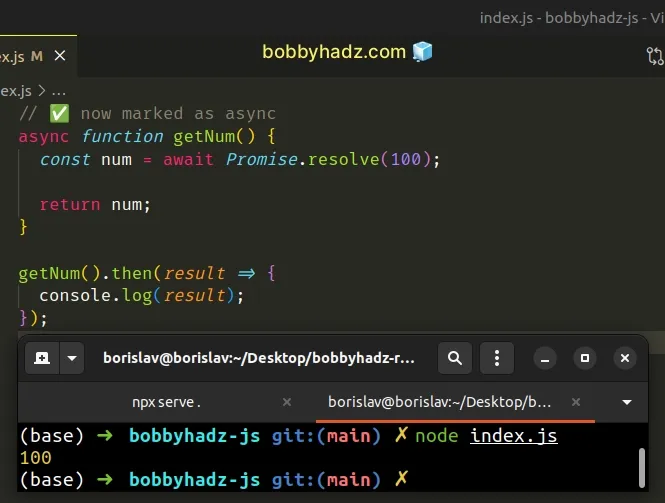
To solve this, we have to mark the directly enclosing function as async.
// ✅ now marked as async async function getNum() { const num = await Promise.resolve(100); return num; } getNum().then(result => { console.log(result); });
await, scroll down to the next subheading.A very common cause of the error is forgetting to set an inner function as
async, e.g. the ones we pass to methods like forEach(), map(), etc.
Note that the directly enclosing function of the one that uses the await
keyword has to be marked as async.
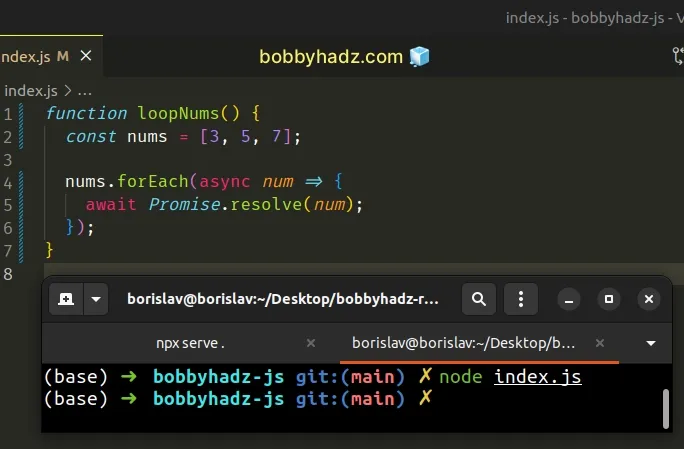
async function loopNums() { const nums = [3, 5, 7]; nums.forEach(num => { // ⛔️ SyntaxError: await is only valid in async functions and the top level bodies of modules await Promise.resolve(num); }); }
We marked the loopNums function as async, but we're using the await
keyword inside of the function we passed to the forEach() method.
Instead, we should have marked the function we passed to forEach as async.
function loopNums() { const nums = [3, 5, 7]; nums.forEach(async num => { await Promise.resolve(num); }); }
Now, the function we passed to the forEach method is async, so we are able
to use the await keyword in it.
async for us to be able to use the await keyword.# Using top-level await in Node.js and a browser environment
If you're trying to use the await keyword on the top level of your Node.js
application, make sure to set the type attribute to module in your
package.json file.
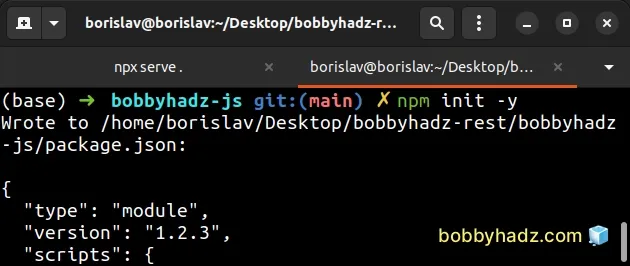
If you don't have a package.json file, create one by using the npm init -y
command (only if you don't have one already).
npm init -y
Open the package.json file at the root directory of your project and set the
type attribute to module.
{ "type": "module", // ... your other settings }
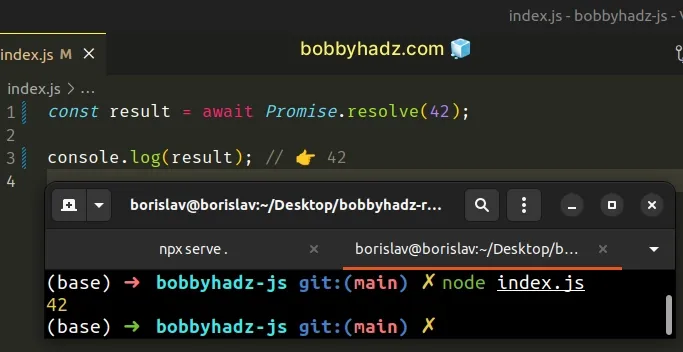
Now you can use top-level await in your Node.js code.
const result = await Promise.resolve(42); console.log(result); // 👉️ 42
If you're on the browser, set the type attribute to module on your script
tag.
<script type="module" src="index.js"></script>
Now you can use the top-level await syntax on the browser.
const result = await Promise.resolve(42); console.log(result); // 👉️ 42
I've also written a detailed guide on how to import and export classes and functions in JavaScript.
If you need to conditionally import ES6 modules, check out the following article.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

