window.location.href is not a function Error in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# window.location.href is not a function Error in JavaScript
The "window.location.href is not a function" error occurs when we try to
invoke the href property on the window.location object.
To solve the error, use the assign method on the window.location
property.
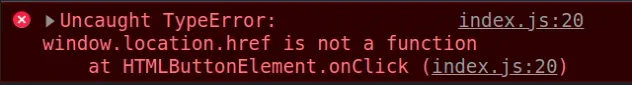
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <button id="btn">Change location</button> <!-- ✅ Your JS script here ✅ --> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And this is the code in our index.js file.
const btn = document.getElementById('btn'); btn.addEventListener('click', function onClick() { // ⛔️ TypeError: window.location.href is not a function window.location.href('https://google.com'); });
We tried to invoke the href property as a function, so the error occurred.
Instead, you should use the window.location.assign() method.
const btn = document.getElementById('btn'); btn.addEventListener('click', function onClick() { // ✅ works window.location.assign('https://google.com'); });
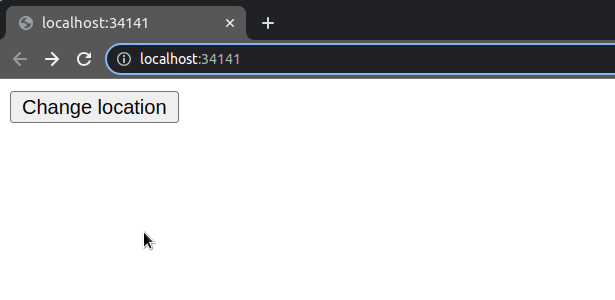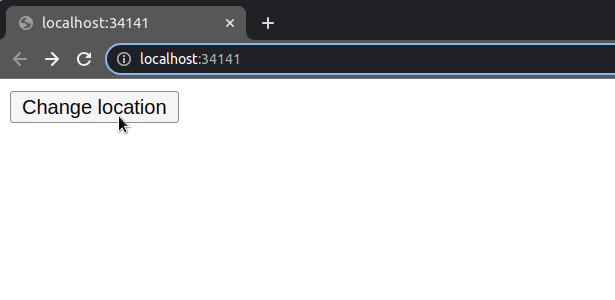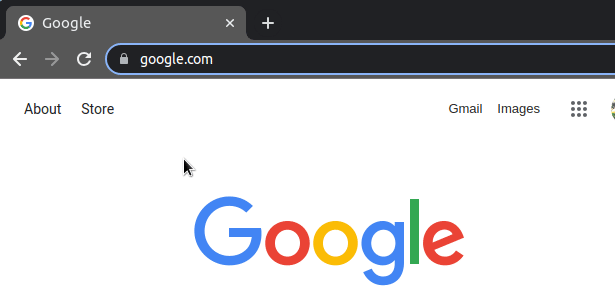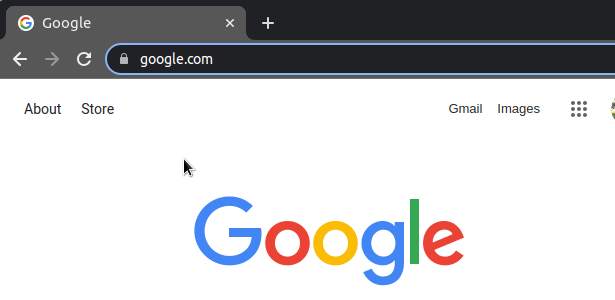
The window.location.assign() method enables us to navigate to a new page.
You could achieve the same result if you assign a string to the
window.location.href property.
btn.addEventListener('click', function onClick() { // ✅ works window.location.href = 'https://google.com'; });
If you load the page and click on the button, you will navigate to the webpage you assigned to the property.
If you need to check out all of the properties on the location object, here is a link from the MDN docs.
Similar methods to assign include:
window.location.reload()- reloads the current URL (like the refresh button).window.location.replace()- redirects to the provided URL. The difference from theassign()method is that when using thereplace()method, the current page is not saved in the session history, so users are not able to use the back button to navigate to it.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

