ReferenceError: window is not defined in JavaScript [Solved]
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# ReferenceError: window is not defined in JavaScript
The "ReferenceError: window is not defined" error occurs for multiple reasons:
- Using
windowin Node.js. - Using
windowon the server (e.g. server-side rendering in Next.js). - Misspelling the
windowglobal variable (should be all lowercase).
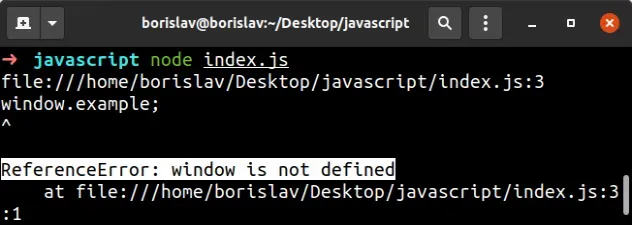
# The window object is not available in Node.js
Node.js does not provide a browser environment. It's a server-side runtime, so
we can't use the window variable in Node.
Trying to run the following line of code in Node.js causes the error.
// ⛔️ ReferenceError: window is not defined console.log(window.location.href);
The window object represents a window containing a DOM document and is only available in the browser.
The quickest way to solve the error is to use an if statement.
if (typeof window !== 'undefined') { // 👉️ can use window here console.log('You are on the browser') console.log(window.location.href); console.log(window.location.protocol); }
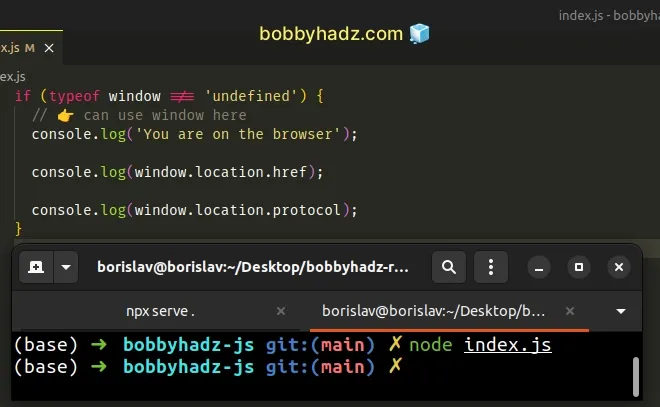
The if block only runs in a browser environment where the window object is
available.
# Place your JS script tag at the bottom of the body tag
If you got the error in the browser, try to move your JS script tag to the
bottom of the body tag.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <!-- Your HTML here --> <!-- 👇️ Script at bottom of body --> <script type="module" src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
You might have some add-ons that are run before the DOM is created.
window global variable represents the window in which the script is running (browser side).# Checking if you are on the browser before accessing window
If you use React.js or Next.js and you need to check if you're on the browser
(can use window) or on the server (can't use window), check that the
window variable is not undefined.
if (typeof window !== 'undefined') { console.log('You are on the browser'); // ✅ Can use window here console.log(window.innerWidth); window.addEventListener('mousemove', () => { console.log('Mouse moved'); }); } else { console.log('You are on the server'); // ⛔️ Don't use window here }
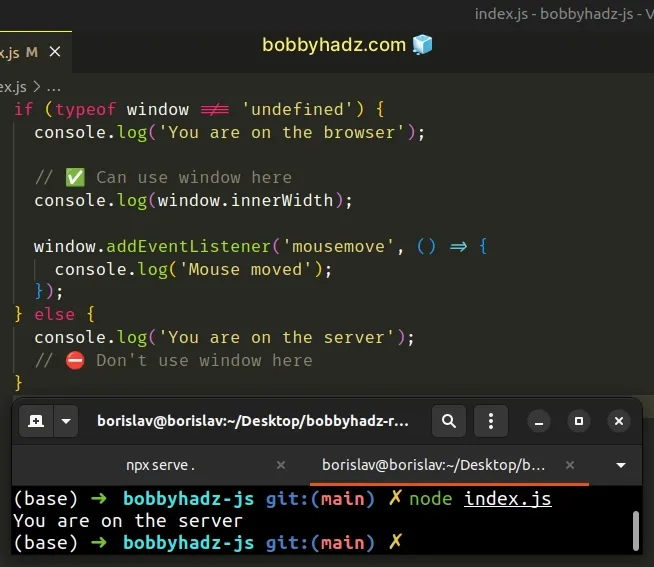
window variable doesn't have a type of undefined. If the window variable is defined, we are on the browser and can access it.To solve the error, make sure to only use the window global variable on the
browser.
The variable represents a window containing a DOM document and can't be used on the server side (e.g. in Node.js).
# Use the global object to define global variables in Node.js
If you need to define global variables in Node.js, use global, not window.
// 👇️ in Node.js global.test = 'EXAMPLE';
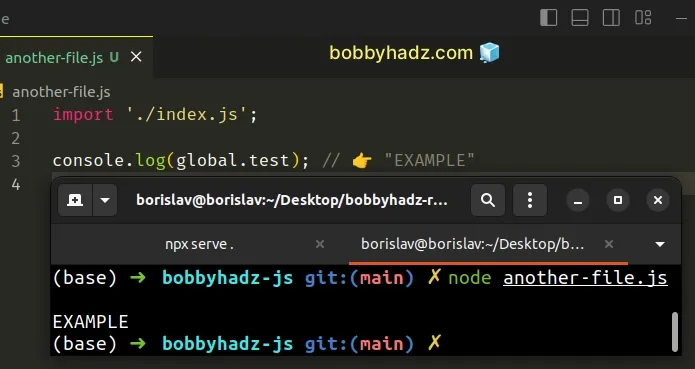
And now we can use the variable in some other file:
import './index.js'; console.log(global.test); // 👉️ "EXAMPLE"
But it's much better to simply export a variable from the index.js file and
import it as needed.
export const test = 'example';
Now we can import the variable into another file.
import {test} from './index.js'; console.log(test); // 👉️ "example"
This is a much better and more explicit approach than defining global variables.
# Move the code that uses window to your useEffect hook
If you got the error in React.js, move the code that uses window in your
useEffect hook.
useEffect hook runs after React renders your component in the browser environment, so you can safely access the window object in useEffect.import {useEffect} from 'react'; const App = () => { useEffect(() => { // ✅ Use window in useEffect hook const handleScroll = event => { console.log('window.scrollY', window.scrollY); }; window.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll); return () => { window.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll); }; }, []); return ( <div style={{ border: '3px solid black', width: '400px', height: '1000rem', }} > <p>Content</p> <p>Content</p> <p>Content</p> <p>Content</p> <p>Content</p> <p>Content</p> <p>Content</p> <p>Content</p> <p>Content</p> <p>Content</p> <p>Content</p> </div> ); }; export default App;
The useEffect hook runs only on the browser after the component has mounted.
useEffect(() => { // ✅ Use window in useEffect hook const handleScroll = event => { console.log('window.scrollY', window.scrollY); }; window.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll); return () => { window.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll); }; }, []);
You can safely use the window object in your useEffect hook in React.js and
Next.js.
# Checking if you are on the browser or the server
If that doesn't work, you have to use an if statement to check if you're on
the browser (can use window) or server (can't use window).
if (typeof window !== 'undefined') { console.log('You are on the browser'); // ✅ Can use window here console.log(window.innerWidth); window.addEventListener('mousemove', () => { console.log('Mouse moved'); }); } else { console.log('You are on the server'); // ⛔️ Don't use window here }
The if block only runs if the window object is not undefined (we are on
the browser).
If the else block runs, the code is not in a browser environment and doesn't
have access to the window object.
# Make sure you haven't misspelled window
Another common cause of the error is misspelling window (it's all lowercase).
// ⛔️ ReferenceError: Window is not defined console.log(Window.location.href);
The code sample uses Window (capital W) instead of window which caused the
error.
Instead, the object is spelled in all lowercase.
console.log(window.location.href); console.log(window.location.protocol);
# Conclusion
To solve the "ReferenceError: window is not defined" error, make sure:
- You aren't trying to access the
windowobject in Node.js. - You aren't using
windowon the server (e.g. server-side rendering in Next.js). - You haven't misspelled the
windowglobal variable (should be all lowercase).

