TypeError: push is not a function in JavaScript [Solved]
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# TypeError: push is not a function in JavaScript [Solved]
The "TypeError: push is not a function" occurs when the push() method is
called on a value that is not an array.
To solve the error, convert the value to an array before calling the method,
or make sure to only call the push() method on valid arrays.
Uncaught TypeError: object.push is not a function
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
const arr = {name: 'Tom'}; // ⛔️ Uncaught TypeError: arr.push is not a function arr.push({name: 'James'});
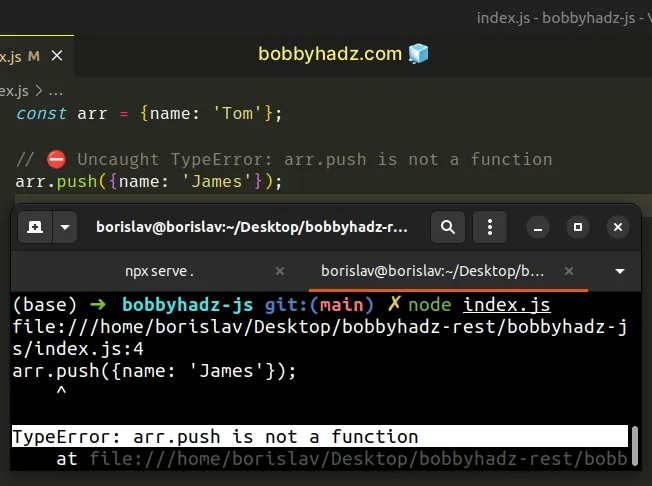
We called the Array.push() method on an object which caused the error.
# Pushing objects into an array
In this situation, we should place the object in an array, so we are able to push new objects into the array.
const arr = [{name: 'Tom'}]; arr.push({name: 'James'}); // 👇️ [{name: 'Tom'}, {name: 'James'}] console.log(arr);
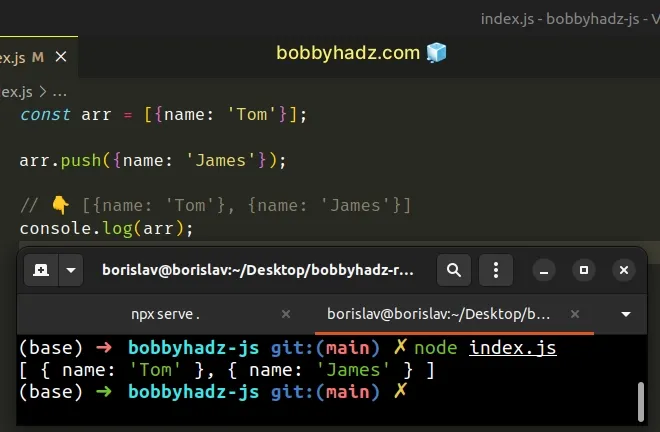
Array.push method to add other objects to the end of the array.# Adding key-value pairs to an object
If you need to add key-value pairs to an object, use bracket or dot notation.
const obj = { id: 1, name: 'Alice', }; // 👇️ dot notation obj.country = 'Chile'; // 👇️ bracket notation obj['street address'] = 'Example street 123'; // 👇️ {id: 1, name: 'Alice', country: 'Chile', 'street address': ...} console.log(obj);
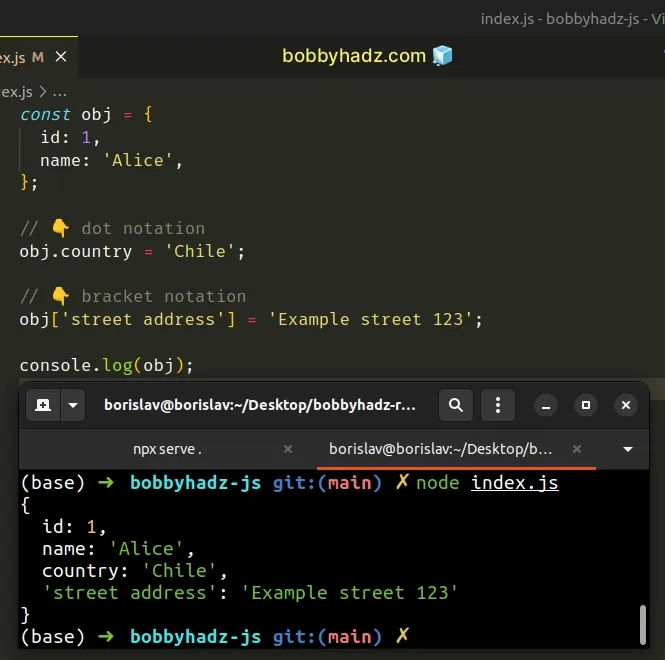
A general rule of thumb is to use bracket notation if the object's key contains a space, hyphen or starts with a digit or a special character. In all other cases, use dot notation as it is more concise and easier to read.
# Convert the value to an array before calling push()
If you got the error when working with a NodeList or another array-like
object, convert the array-like object to an array before calling the push()
method.
const set = new Set(['a', 'b']); const arr = Array.from(set); console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['a', 'b'] arr.push('c'); console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c']
We used the Array.from() method to convert a Set object to an array, so we
can call the push() method on the array.
You can also use the spread syntax (...) to convert a value to an array.
const set = new Set(['a', 'b']); const arr = [...set]; console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['a', 'b'] arr.push('c'); console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c']
We used the spread syntax (...) to unpack the values of the Set into a new
array before calling push().
console.log the value you're calling the push() method on and make sure it's an array.# Check if the value is an array before calling push()
You can also conditionally check if the value is an array before calling the
push() method to avoid getting errors.
const arr = null; if (Array.isArray(arr)) { arr.push('example'); } if (Array.isArray(arr)) { arr.push({id: 2, name: 'Brad'}); }
We used the
Array.isArray
method to check if the value is an array before calling the push method.
# Access a property on an object before calling push()
If have an object and you want to push values to a specific property that stores
an array, access the property and call the push() method on it.
const obj = { numbers: [1, 2], }; obj.numbers.push(3); // 👇️ {numbers: [1, 2, 3]} console.log(obj);
We accessed the numbers property, which stores an array and called the
push() method on the array.
# Solve the error if using local storage
If you use local storage to store an array, make sure to parse the array before calling the Array.push() method.
const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz']; localStorage.setItem('site', JSON.stringify(arr)); const arrAgain = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('site')); console.log(arrAgain); // 👉️ ['bobby', 'hadz'] arrAgain.push('com'); console.log(arrAgain); // 👉️ ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']
We used the JSON.stringify() method to convert an array to a JSON string and
added the string to local storage.
The next step is to use the JSON.parse() method to parse the string into an
array.
Lastly, we called the push() method on the array.

