Remove all non-alphanumeric Characters from a String in JS
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Remove all non-alphanumeric Characters from a String in JS
Use the String.replace() method to remove all non-alphanumeric characters
from a string, e.g. str.replace(/[^a-z0-9]/gi, '');.
The replace() method will remove all non-alphanumeric characters from the
string by replacing them with empty strings.
const str = 'A!@#b$%^c&*('; const replaced = str.replace(/[^a-z0-9]/gi, ''); console.log(replaced); // 👉️ Abc
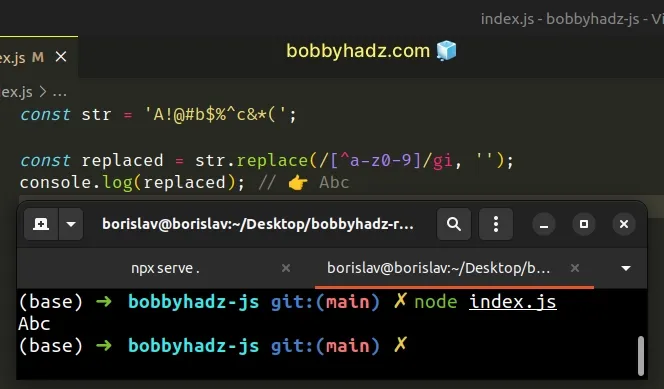
The String.replace() method returns a new string with one, some, or all matches of a regular expression replaced with the provided replacement.
The method takes the following parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| pattern | The pattern to look for in the string. Can be a string or a regular expression. |
| replacement | A string used to replace the substring match by the supplied pattern. |
String.replace() method returns a new string with the matches of the pattern replaced. The method doesn't change the original string.Strings are immutable in JavaScript.
The forward slashes / / mark the beginning and end of the regular expression.
const str = 'A!@#b$%^c&*('; const replaced = str.replace(/[^a-z0-9]/gi, ''); console.log(replaced); // 👉️ Abc
The square brackets [] are called a character class.
The caret ^ symbol means "NOT the following". In our case, this means not
any letter in the range of a-z and not any number in the range of 0-9.
g (global) flag because we want to match all occurrences of non-alphanumeric characters and not just the first occurrence.The i flag makes our match case-insensitive by targeting all uppercase and
lowercase characters.
If your use case requires you to also preserve spaces, hyphens or other
characters, add them between the square brackets [].
const str = 'A!@# b$% ^c&-*('; const replaced = str.replace(/[^a-z0-9 -]/gi, ''); console.log(replaced); // 👉️ A b c-
The code sample preserves all alphanumeric characters, spaces and hyphens. You
could adjust the regex to your needs by adding or removing characters between
the square brackets [].
# Creating a reusable function
If you have to remove the non-alphanumeric characters from a string often, define a reusable function.
function removeNonAlphanumeric(string) { return string.replace(/[^a-z0-9]/gi, ''); } console.log(removeNonAlphanumeric('A(@#(@B$C')); // 👉️ ABC console.log(removeNonAlphanumeric('A_@#B(***C((_D')); // 👉️ ABCD
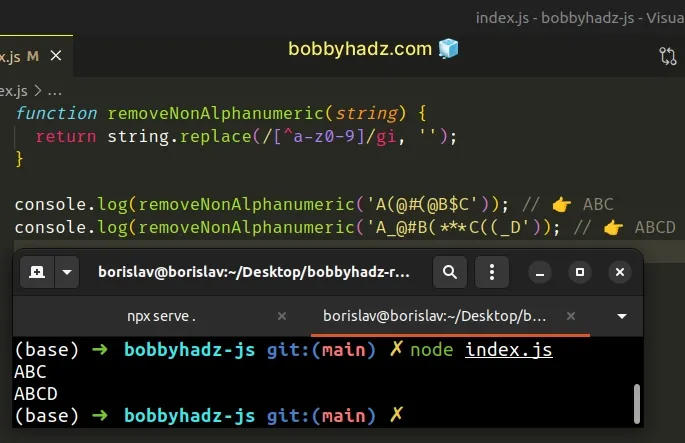
The removeNonAlphanumeric() function takes a string as a parameter and removes
all non-alphanumeric characters from the string.
# Remove all non-alphanumeric Characters from a String using \W
You can also use the \W special character to shorten your regex and remove all
non-alphanumeric characters from a string.
function removeNonAlphanumeric(string) { return string.replace(/\W/g, ''); } console.log(removeNonAlphanumeric('A(@#(@B$C')); // 👉️ ABC console.log(removeNonAlphanumeric('A_@#B(***C((_D')); // 👉️ ABCD
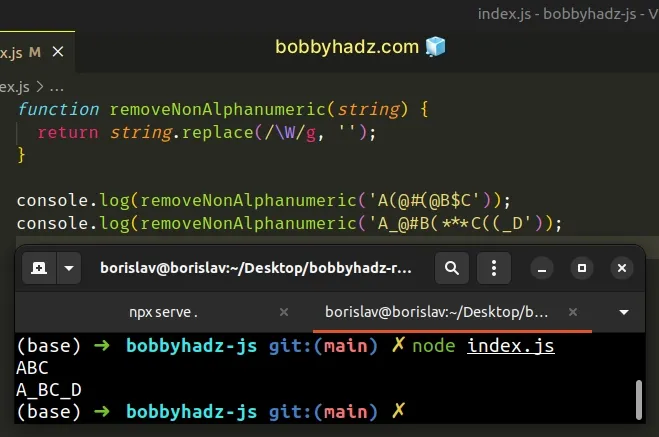
The \W special character is equivalent to [^A-Za-z0-9_].
In other words, the \W character matches:
- any character that is not a word character from the basic Latin alphabet
- non-digit characters
- not underscores
Note that the \W special character doesn't remove the underscores from the
string.
If you also need to remove the underscores, use the code sample from the previous subheading.
function removeNonAlphanumeric(string) { return string.replace(/[^a-z0-9]/gi, ''); } console.log(removeNonAlphanumeric('A(@#(@B$C')); // 👉️ ABC console.log(removeNonAlphanumeric('A_@#B(***C((_D')); // 👉️ ABCD
If you ever need help reading a regular expression, check out this regular expression cheat sheet by MDN.
It contains a table with the name and the meaning of each special character with examples.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Replace or Remove all Backslashes in a String in JavaScript
- Replace/Remove all Numbers in a String using JavaScript
- Replace the First Occurrence of Character in String in JS
- Replace the Last Character in a String in JavaScript
- Replace Last Occurrence of Character in String in JavaScript
- Replace Multiple Characters in a String using JavaScript

