Insert String at specific Index of another String in JS
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Insert String at specific Index of another String in JavaScript
To insert a string at a specific index of another string:
- Use the
slice()method to get the characters up to the index. - Use the
slice()method to get the characters after the index. - Add the string between the characters using the addition operator.
function insertAtIndex(str, substring, index) { return str.slice(0, index) + substring + str.slice(index); } const str = 'he world'; const substring = 'llo'; const index = 2; // 👇️ hello world console.log(insertAtIndex(str, substring, index));
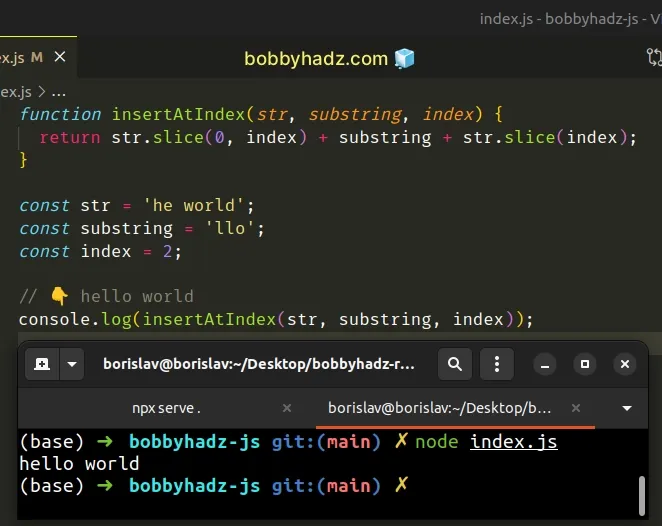
The insertAtIndex() function takes a string, a substring and an index as
parameters.
The function inserts the substring into the string at the supplied index.
The String.slice() method extracts a section of a string and returns it, without modifying the original string.
The String.slice() method takes the following arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| start index | The index of the first character to include in the returned substring |
| end index | The index of the first character to exclude from the returned substring |
To get the portion of the string before the specified index, we go from index
0 up to, but not including the provided index.
const str = 'he world'; // 👇️ "he" console.log(str.slice(0, 2));
0, and the last character has an index of string.length - 1.When only a single argument is passed to the String.slice() method, the slice
goes to the end of the string.
const str = 'he world'; const index = 2; // 👇️ ' world' console.dir(str.slice(index));
The slice starts at index 2 and goes to the end of the string.
We used the addition (+) operator to insert the string at the index.
const str = 'he world'; const index = 2; const result = str.slice(0, index) + 'llo' + str.slice(index); // 👇️ "hello world" console.log(result);
The addition (+) operator can be used to concatenate two or more strings.
# Insert String at specific Index of another String using splice
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
split()method to split the string into an array of characters. - Use the
splice()method to add the new string to the array at the specified index. - Use the
join()method to join the array into a string.
function insertAtIndex(str, substring, index) { const arr = str.split(''); arr.splice(index, 0, substring); return arr.join(''); } const str = 'he world'; const substring = 'llo'; const index = 2; // 👇️ hello world console.log(insertAtIndex(str, substring, index));
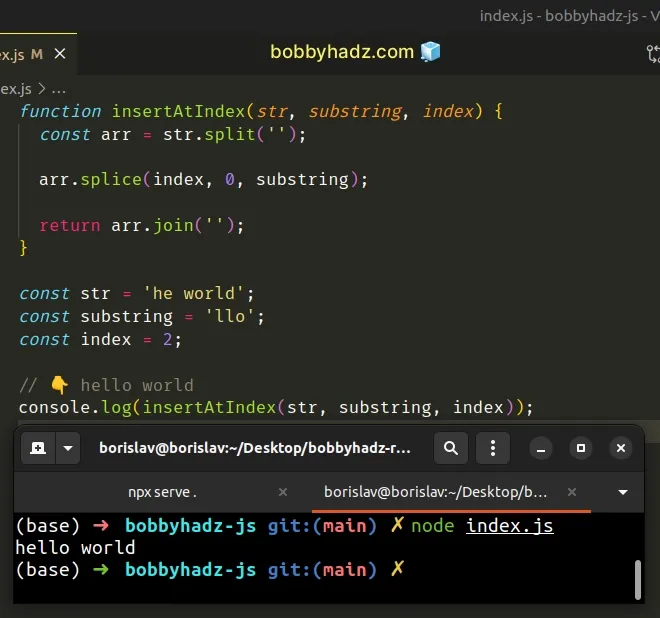
We used the String.split() method to split the string into an array of characters.
const str = 'he world'; // [ // 'h', 'e', ' ', // 'w', 'o', 'r', // 'l', 'd' // ] console.log(str.split(''));
The next step is to use the Array.splice() method to add the new string to the
array at the specified index.
const str = 'he world'; const substring = 'llo'; const index = 2; const arr = str.split(''); arr.splice(index, 0, substring); // [ // 'h', 'e', 'llo', // ' ', 'w', 'o', // 'r', 'l', 'd' // ] console.log(arr);
The Array.splice() method changes the contents of an array by removing or replacing existing elements or adding new elements to the array.
The method takes the following arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| start | A zero-based index at which to start changing the array |
| deleteCount | The number of elements to be deleted from the array |
| item1,..., itemN | One or more values to add to the array from the start index onwards |
We used 0 for the deleteCount argument because we don't want to delete any
elements.
The last step is to use the Array.join() method to join the array without a
separator.
function insertAtIndex(str, substring, index) { const arr = str.split(''); arr.splice(index, 0, substring); return arr.join(''); } const str = 'he world'; const substring = 'llo'; const index = 2; const arr = str.split(''); // 👇️ hello world console.log(insertAtIndex(str, substring, index));
The Array.join() method concatenates all of the elements in an array using a separator.
The only argument the Array.join() method takes is a separator - the string
used to separate the elements of the array.
If the separator argument is set to an empty string, the array elements are
joined without any characters in between them.
# Insert String at specific Index of another String using substring
Alternatively, you can use the String.substring() method.
function insertAtIndex(str, substring, index) { return ( str.substring(0, index) + substring + str.substring(index) ); } const str = 'he world'; const substring = 'llo'; const index = 2; // 👇️ hello world console.log(insertAtIndex(str, substring, index));
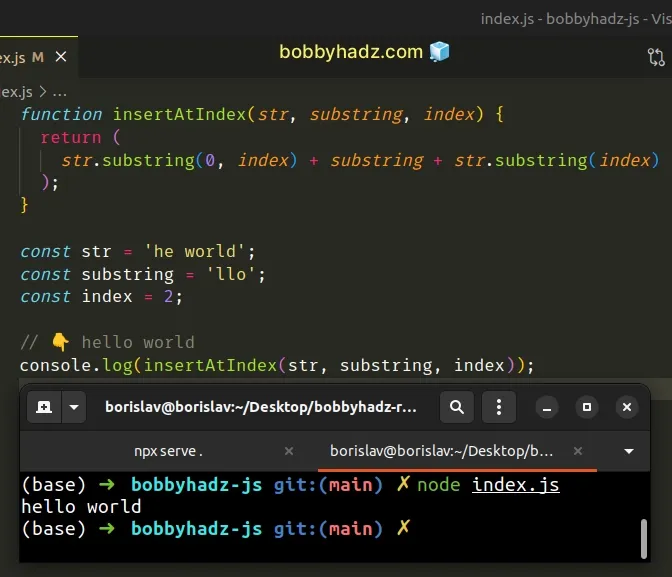
The String.substring() method returns a slice of the string from the start index to the excluding end index.
The method takes the following parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| start index | The index of the first character to include in the returned substring |
| end index | The index of the first character to exclude from the returned substring |
We used the slice() and substring() methods in the same way.
There are a couple of
differences
between the String.substring() and the String.slice() methods:
- The
substring()method swaps its start and end index if the start index is greater than the end index. Theslice()method returns an empty string in this case.
const str = 'bobby'; console.log(str.substring(3, 0)); // 👉️ bob console.log(str.slice(3, 0)); // 👉️ ''
- If either of both arguments passed to
substring()are negative, they are treated as if they were0.
const str = 'bobby'; console.log(str.substring(-3)); // 👉️ bobby console.log(str.slice(-3)); // 👉️ bby
When given a negative index, the slice() method counts backward from the end
of the string to find the indexes.
For these reasons, you should use the String.slice() method instead of
String.substring().
The slice() method is implemented in a much more predictable way.
I've also written an article on how to add a space between the characters of a string.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

