How to Sum a Property in an Array of Objects in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Sum a Property in an Array of Objects in JavaScript
- Sum a Property in an Array of Objects using
Array.forEach() - Sum a Property in an Array of Objects using a
forloop - Sum a Property in an Array of Objects using
map()andreduce()
# Sum a Property in an Array of Objects in JavaScript
To sum a property in an array of objects:
- Use the
reduce()method to iterate over the array. - On each iteration increment the sum with the specific value.
- The result will contain the sum of the values for the specific property.
const arr = [ {id: 1, salary: 10}, {id: 2, salary: 20}, {id: 3, salary: 30}, ]; const sum = arr.reduce((accumulator, object) => { return accumulator + object.salary; }, 0); console.log(sum); // 👉️ 60
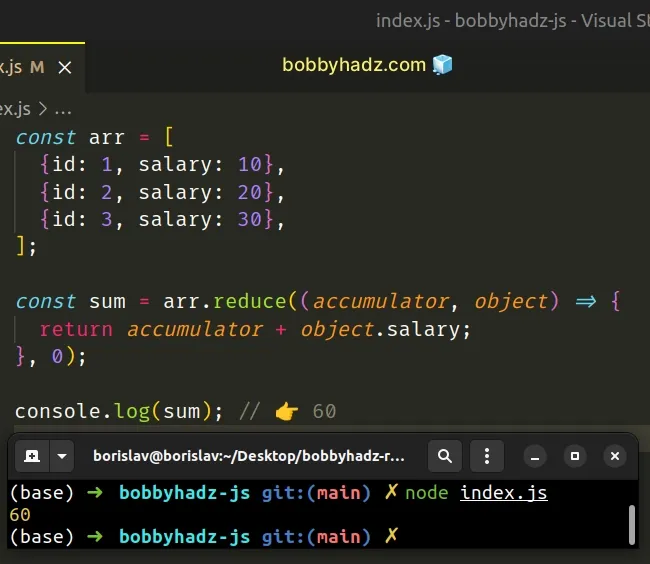
The function we passed to the Array.reduce() method gets invoked for each element (object) in the array.
accumulator parameter gets an initial value of 0 because that's what we supplied as the second argument to the reduce() method.We increment the accumulator by the value of the salary property for each
object in the array.
The reduce() method returns the sum of the salary values of all objects in
the array.
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
function calculateSum(array, property) { const total = array.reduce((accumulator, object) => { return accumulator + object[property]; }, 0); return total; } const arr = [ {id: 1, salary: 10, age: 20}, {id: 2, salary: 20, age: 30}, {id: 3, salary: 30, age: 40}, ]; const result1 = calculateSum(arr, 'salary'); console.log(result1); // 👉️ 60 const result2 = calculateSum(arr, 'age'); console.log(result2); // 👉️ 90
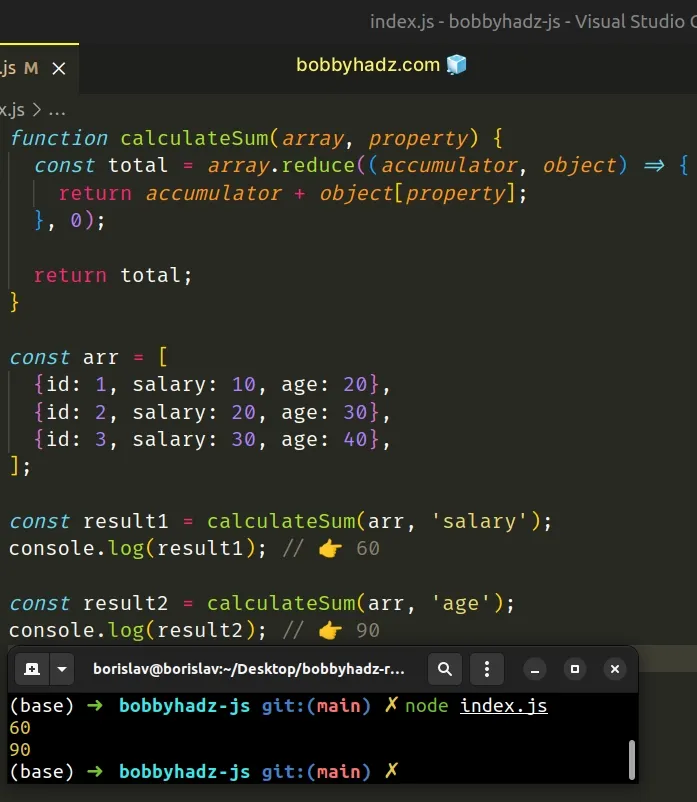
The calculateSum function takes an array and a property as parameters and
calculates the sum of the specified property in the array of objects.
If you need to sum the values of an object, check out the following article.
An alternative and perhaps simpler approach is to use the forEach method.
# Sum a Property in an Array of Objects using Array.forEach()
This is a three-step process:
- Declare a
sumvariable using theletkeyword and set it to0. - Call the
forEach()method to iterate over the array. - On each iteration, increment the
sumvariable with the value of the object.
const arr = [ {id: 1, salary: 10}, {id: 2, salary: 20}, {id: 3, salary: 30}, ]; let sum = 0; arr.forEach(element => { sum += element.salary; }); console.log(sum); // 👉️ 60
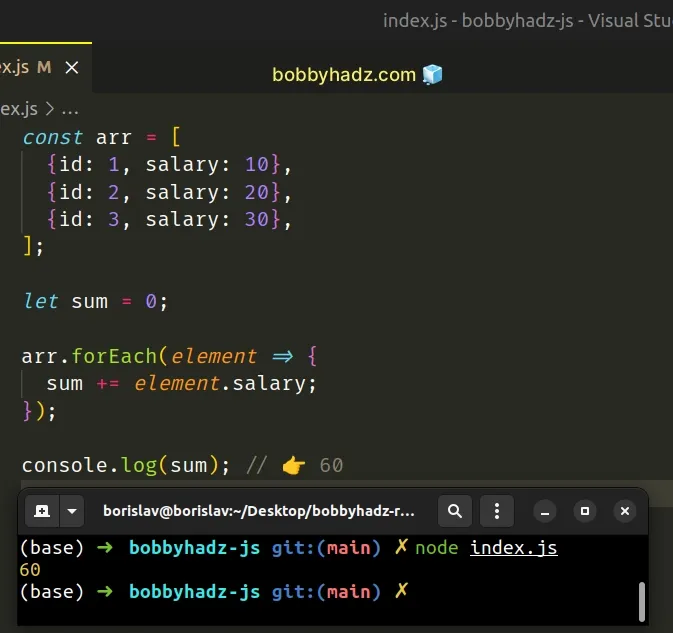
The function we passed to the Array.forEach() method gets called with each element (object) in the array.
sum variable using the let keyword. We can't reassign variables declared using const.On each iteration of the loop, we increment the value stored in the sum
variable to get the total amount.
This approach is more readable and intuitive, especially if you aren't used to
how the reduce() method works.
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
function calculateSum(array, property) { let sum = 0; array.forEach(element => { sum += element[property]; }); return sum; } const arr = [ {id: 1, salary: 10, age: 20}, {id: 2, salary: 20, age: 30}, {id: 3, salary: 30, age: 40}, ]; const result1 = calculateSum(arr, 'salary'); console.log(result1); // 👉️ 60 const result2 = calculateSum(arr, 'age'); console.log(result2); // 👉️ 90
The calculateSum function takes an array of objects and a property as
parameters and calculates the sum of the specified property.
You can also achieve the same result by using a basic for loop.
# Sum a Property in an Array of Objects using a for loop
This is a three-step process:
- Declare a
sumvariable using theletkeyword and set it to0. - Use a
forloop to iterate over the array. - On each iteration, increment the
sumvariable with the value of the object.
const arr = [ {id: 1, salary: 10}, {id: 2, salary: 20}, {id: 3, salary: 30}, ]; let sum = 0; for (let index = 0; index < arr.length; index++) { sum += arr[index].salary; } console.log(sum); // 👉️ 60
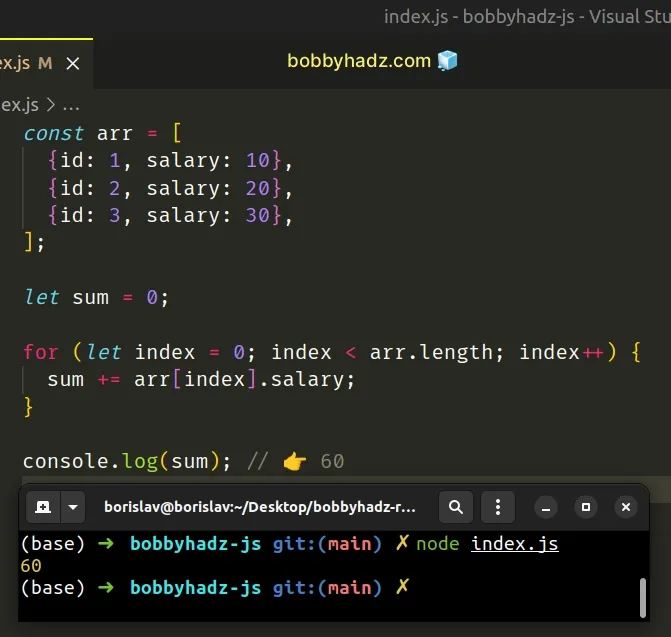
This code sample achieves the same result, however, instead of the forEach()
method, we use a basic for loop.
Instead of accessing the element directly, we have to use the index of each iteration.
This is a bit indirect and cluttered, however, most developers are used to
reading for loops.
You can also use a combination of the Array.map() and Array.reduce() methods
to sum a property in an array of objects.
# Sum a Property in an Array of Objects using map() and reduce()
This is a two-step process:
- Use the
Array.map()method to get an array of the values of the specific property. - Use the
Array.reduce()method to sum the values in the array.
const arr = [ {id: 1, salary: 10}, {id: 2, salary: 20}, {id: 3, salary: 30}, ]; const sum = arr .map(obj => obj.salary) .reduce((accumulator, current) => accumulator + current, 0); console.log(sum); // 👉️ 60
The function we passed to the Array.map() method gets called with each element
(object) in the array.
On each iteration, we access the salary property and return its value.
const arr = [ {id: 1, salary: 10}, {id: 2, salary: 20}, {id: 3, salary: 30}, ]; // 👇️ [ 10, 20, 30 ] console.log(arr.map(obj => obj.salary));
The Array.map() method returns a new array that only contains the values of
the specified property.
The next step is to use the Array.reduce() method to calculate the sum of the
values in the array.
const arr = [ {id: 1, salary: 10}, {id: 2, salary: 20}, {id: 3, salary: 30}, ]; const sum = arr .map(obj => obj.salary) .reduce((accumulator, current) => accumulator + current, 0); console.log(sum); // 👉️ 60
We used 0 as the initial value of the accumulator variable.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I'd use the
Array.forEach() method or Array.reduce() as I find both options quite direct
and easy to read.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

