Get the first N elements of an Array in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 1, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Get the first N elements of an Array in JavaScript
To get the first N elements of an array, call the slice() method passing it
0 and N as arguments.
For example, arr.slice(0, 2); returns a new array containing the first two
elements of the original array.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']; // ✅ get first 2 elements on an array const first2 = arr.slice(0, 2); console.log(first2); // 👉️ ['a', 'b'] // ✅ get first 3 elements on an array const first3 = arr.slice(0, 3); console.log(first3); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c']
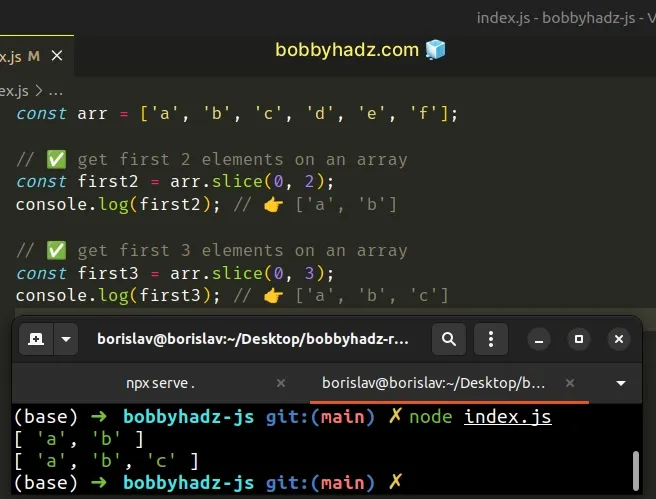
The Array.slice() method returns a copy of a portion of an array.
The method takes the following 2 arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| start index | The index of the first element to include in the returned array |
| end index | The index of the first element to exclude from the returned array |
We used a start index of 0 to start extracting elements from the start of the
array.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']; const first2 = arr.slice(0, 2); console.log(first2); // 👉️ ['a', 'b']
When the start index is 0, you can think of the end index as the number of
elements the new array should contain.
arr.slice(0, 3) returns a new array containing the first 3 elements of the original array (array elements at index 0, 1 and 2).The end index is exclusive, so the slice goes up to, but not including the specified end index.
If the specified end index exceeds the array's length, the slice() method
doesn't throw an error, it returns the entire array.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c']; const first100 = arr.slice(0, 100); console.log(first100); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c']
We tried to get the first 100 elements of an array that only contains 3
elements.
As a result, the new array contains all 3 elements of the original array.
The slice method doesn't change the contents of the original array, it returns a new array.
You can also use the destructuring assignment to get the first N elements of an array.
# Get the first N elements of an Array using destructuring
The destructuring assignment syntax enables us to assign the first N elements of an array to variables.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']; const [first, second] = arr; console.log(first); // 👉️ 'a' console.log(second); // 👉️ 'b'
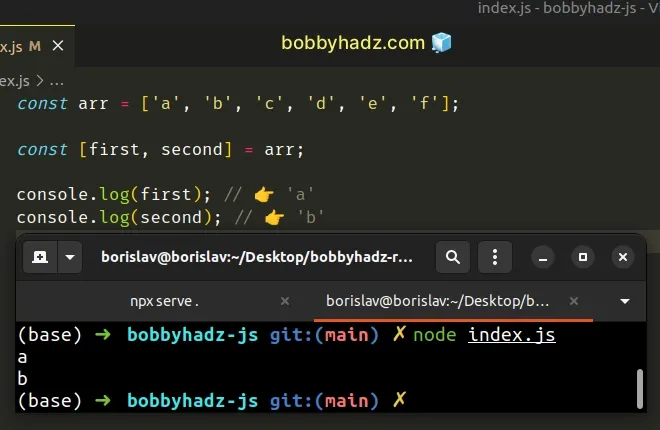
The first and second variables were assigned the values of the first and
second array elements.
You can skip an element when destructuring by using a comma.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']; const [, second, third] = arr; console.log(second); // 👉️ 'b' console.log(third); // 👉️ 'c'
We used a comma to skip the array element at index 0 and assigned the second
and third array elements to variables.
You can also use a basic for loop.
# Get the first N elements of an Array using a for loop
This is a three-step process:
- Declare a new variable that stores an empty array.
- Use a
forloop to iterate for N - 1 iterations. - Push the element at the current index into the new array.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']; const newArray = []; const n = 3; for (let index = 0; index < n; index++) { newArray.push(arr[index]); } console.log(newArray); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b', 'c' ]
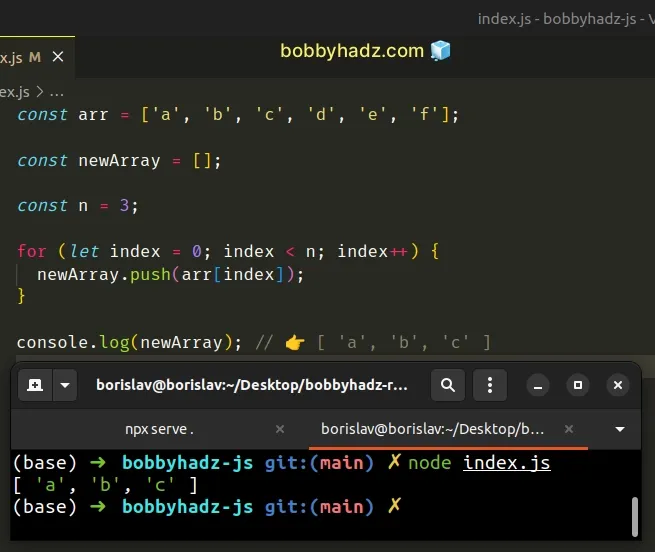
We used a for loop to iterate for n - 1 iterations.
On each iteration, we access the array element at the current index and push it into a new array.
The Array.push method adds an element to the end of an array.
The for loop only iterates for as many iterations as necessary.
You might also see the filter() method used to get the first N elements of an
array, however, it is not a good choice.
# Get the first N elements of an Array using filter
The filter() method is not suitable for this task because it iterates over the
entire array.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']; const n = 3; const first3 = arr.filter((element, index) => index < n); console.log(first3); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b', 'c' ]
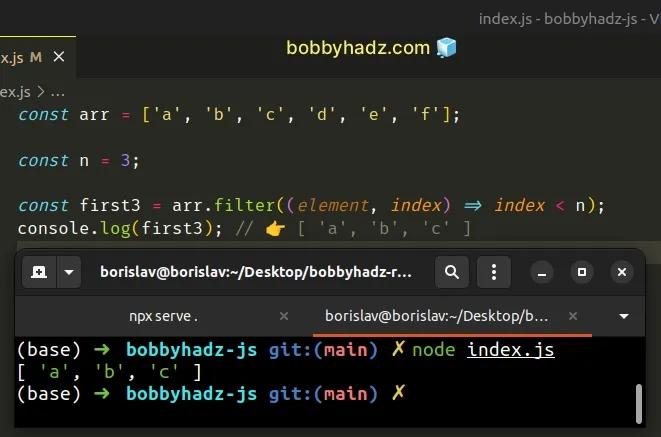
The function we passed to the Array.filter method gets called with each element in the array.
On each iteration, we check if the current index is less than n and return the
result.
The filter() method returns a new array that only contains the elements that
meet the condition.
filter() method is not suitable for the task because it keeps iterating over the array even after we've selected the first N elements.This is bad for performance, especially when working with large arrays with thousands of elements.
# Get the first N elements of an Array using lodash
You can also use the take() method from lodash to get the first N elements
of an array.
First, make sure you have lodash installed by running the following command
from your terminal.
# 👇️ initialize package.json if you don't have one npm init -y npm install lodash
Now you can import and use the take
function from lodash.
import _ from 'lodash'; const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']; const first2 = _.take(arr, 2); console.log(first2); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b' ] const first3 = _.take(arr, 3); console.log(first3); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b', 'c' ]
The function returns a new array that contains the first n elements of the
supplied array.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I'd use the
Array.slice() method as I find it quite direct and intuitive.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

