Find the Next/Previous Element with specific Class in JS
Last updated: Mar 5, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
- Find the Next Element with a specific Class using JS
- Find the Previous Element with a specific Class using JS
# Find the Next Element with a specific Class using JS
To find the next element with a specific class:
- Use the
nextElementSiblingto get the next element sibling. - In a
whileloop iterate over the next siblings. - Check if each element's class list contains the specific class.
Here is the HTML for the examples.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <title>bobbyhadz.com</title> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div id="box">Box 1</div> <div class="second">Box 2</div> <div class="third">Box 3</div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
const box = document.getElementById('box'); let third; let placeholder = box.nextElementSibling; while (placeholder) { if (placeholder.classList.contains('third')) { third = placeholder; break; } placeholder = placeholder.nextElementSibling; } console.log(third); // 👉️ div.third
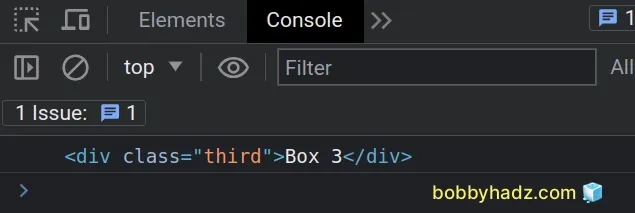
We used a while loop to iterate over the next siblings of the element with an
id of box.
The
nextElementSibling
property returns the element immediately following the element the method was
called on, or null if the element is the first in the list.
while loop basically works is - it keeps iterating until the expression between the parentheses returns a falsy value or we break out of it.The falsy values in JavaScript are: null, undefined, false, 0, ""
(empty string), NaN (not a number).
third or we will reach the last element in the list and break out of the while loop.We used the
classList.contains()
method to check if the class third is contained in the element's class list.
If it is, we assign the element to the third variable and break out of the
while loop.
Otherwise, we assign the placeholder variable to the next sibling element.
If the element with the specific class doesn't exist in the element's next
siblings, the third variable will never get assigned an element and will
remain to be set to an undefined value.
# Find the Previous Element with a specific Class using JS
To find the previous element with a specific class:
- Use the
previousElementSiblingto get the previous element. - In a
whileloop iterate over the previous siblings. - Check if each element's class list contains the specific class.
Here is the HTML for the examples.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div class="first">Box 1</div> <div class="second">Box 2</div> <div id="box">Box 3</div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
const box = document.getElementById('box'); let first; let placeholder = box.previousElementSibling; while (placeholder) { if (placeholder.classList.contains('first')) { first = placeholder; break; } placeholder = placeholder.previousElementSibling; } console.log(first); // 👉️ div.first
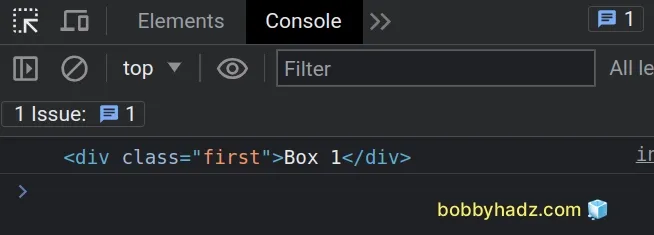
We used a while loop to iterate over the previous siblings of the element with
an id of box.
The
previousElementSibling
property returns the element immediately prior to the element the method was
called on, or null if the element is the first in the list.
while loop basically works is - it keeps iterating until the expression between the parentheses returns a falsy value or we break out of it.The falsy values in JavaScript are: null, undefined, false, 0, ""
(empty string), NaN (not a number).
first or we will reach the first element in the list and break out of the while loop.We used the
classList.contains()
method to check if the class first is contained in the element's class list.
If it is, we assign the element to the first variable and break out of the
while loop.
Otherwise, we assign the placeholder variable to the previous sibling element.
If the element with the specific class does not exist in the element's previous
siblings, the first variable will never get assigned an element and will
remain to store an undefined value.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

