How to Extract a Number from a String in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 1, 2024
Reading time·7 min

# Table of Contents
- Extract a Number from a String in JavaScript
- Get the First Number in a String in JavaScript
- Get the Number from the End of a String in JavaScript
# Extract a Number from a String in JavaScript
Use the String.replace() method to extract a number from a string, e.g.
str.replace(/\D/g, '').
The String.replace() method will extract a number from the string by
replacing all non-digit characters with empty strings.
const str = 'hello 123 world'; const replaced = str.replace(/\D/g, ''); // 👉️ '123' console.log(replaced); let num; if (replaced !== '') { num = Number(replaced); // 👉️ 123 } console.log(num)
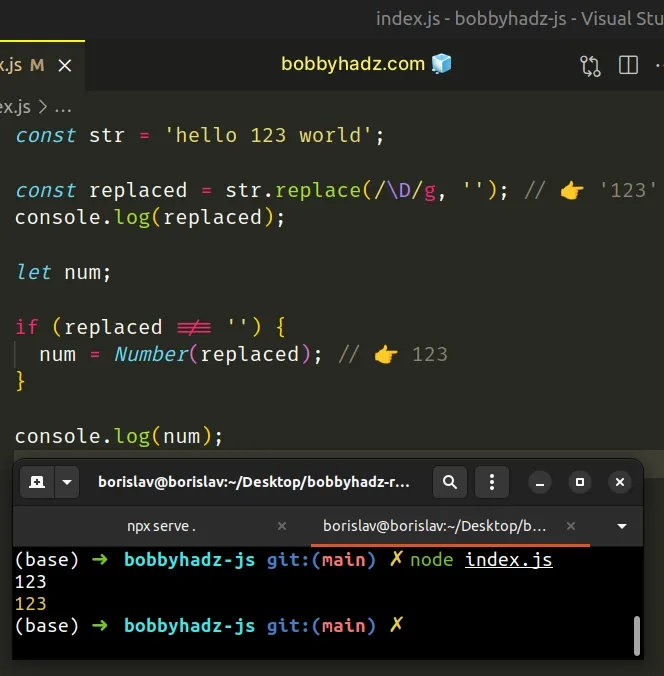
The replace method returns a new string containing all the numbers in the original string.
The first argument we passed to the String.replace() method is a regular expression that we want to match in the string.
The \D character matches any character that is NOT a digit.
We added the g (global) flag to match all non-digit characters and replaced
them with empty strings.
String.replace method would return an empty string.The if statement is there to check if the string contains any numbers.
If it doesn't, we don't want to convert an empty string to a number because that
evaluates to 0.
console.log(Number('')); // 👉️ 0
Here is a complete example of a case where the string doesn't contain numbers.
const str = 'hello world'; const replaced = str.replace(/\D/g, ''); // 👉️ '' console.log(replaced); let num; if (replaced !== '') { // 👇️ never runs num = Number(replaced); } console.log(num); // 👉️ undefined
We replace all non-digit characters with empty strings, and because the string
contains only non-digit characters, String.replace() returns an empty string.
String.replace method returns a new string, it doesn't mutate the original string. Strings are immutable in JavaScript.# Extract a number from a String using String.match()
Another commonly used approach, which I wouldn't recommend, is to use the String.match() method.
const str = 'hello 123 world'; const replaced = str.match(/\d+/); // 👉️ ['123'] let num; if (replaced !== null) { num = Number(replaced[0]); // 👉️ 123 } console.log(num);
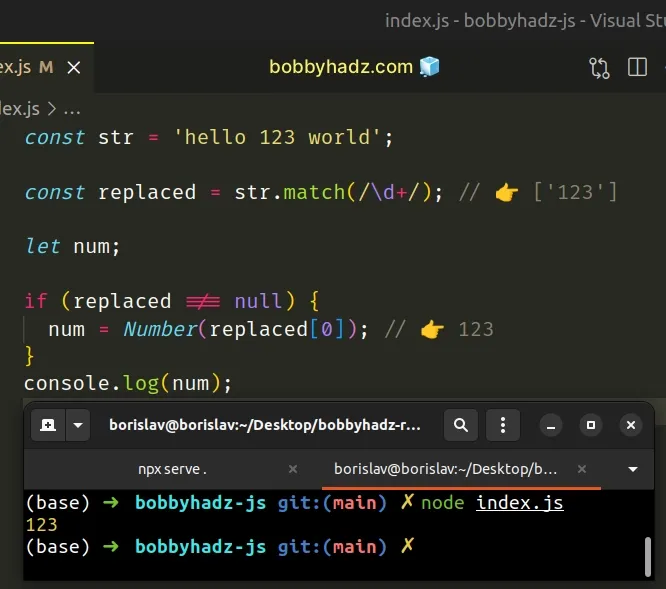
We passed a regular expression to the String.match() method.
The \d character matches a digit from 0 to 9.
The + is used to match one or more of the preceding characters (the digits in
the range 0-9).
String.match method is confusing, but for our purposes, it returns an array containing the match.If the String.match() method doesn't match anything, it returns null.
The if statement is there to make sure we don't try to convert null to a
number, which would return 0.
console.log(Number(null)); // 👉️ 0
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I find the approach
using String.replace() more direct and intuitive.
Here is an example of a case where the string contains no digits when using
String.match().
const str = 'hello world'; const replaced = str.match(/\d+/); // 👉️ null let num; if (replaced !== null) { // 👇️ never runs num = replaced[0]; } console.log(num); // 👉️ undefined
The String.match() method returns null because the string contains no
digits.
# Get the First Number in a String in JavaScript
To get the first number in a string:
- Use the
search()method to get the index of the first number in the string. - Access the string at the index.
- Convert the character to a number.
// ✅ get the first digit in a string function getFirstDigit(str) { const index = str.search(/[0-9]/); return Number(str[index]); } console.log(getFirstDigit('one 2 three 4')); // 👉️ 2 console.log(getFirstDigit('a 100 b 200')); // 👉️ 1 // -------------------------------------------------- // ✅ get the first number in a string function getFirstNumber(str) { const match = str.match(/[0-9]+/); return parseInt(match[0]); } console.log(getFirstNumber('one 2 three 4')); // 👉️ 2 console.log(getFirstNumber('a 100 b 200')); // 👉️ 100
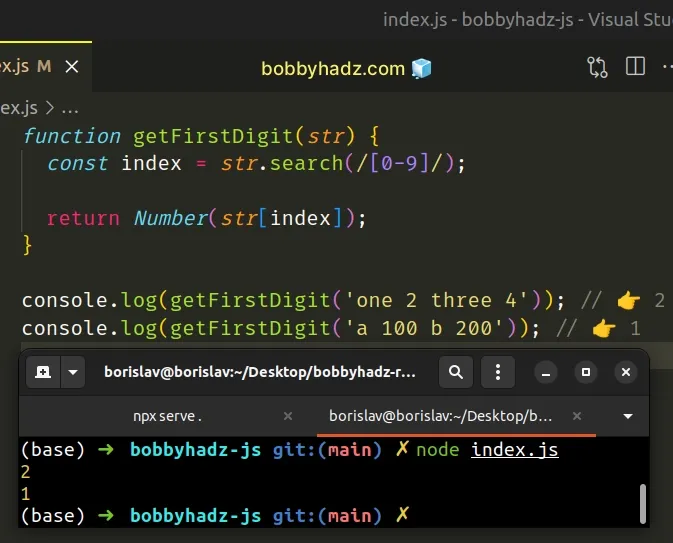
The first code sample uses the String.search() method to get the index of the first digit in the string.
The only parameter the method takes is a regular expression.
The forward slashes / / mark the beginning and end of the regular expression.
The part between the square brackets [] is called a character class and
matches a range of digits from 0 to 9.
function getFirstDigit(str) { const index = str.search(/[0-9]/); return Number(str[index]); }
The next step is to access the string at the index and convert the character to a number.
search method doesn't match any digits in the string, it will return -1.console.log('test'.search(/[0-9]/)); // 👉️ -1
If you then try to access the string at index -1, you will get undefined
back.
console.log('test'[-1]); // 👉️ undefined
If you have to handle this scenario, use an if statement.
const str = 'one 2 three 4'; const index = str.search(/[0-9]/); if (index !== -1) { console.log('✅ String contains at least 1 number'); const firstNum = Number(str[index]); // firstNum is defined only here } else { console.log('⛔️ String does not contain any numbers'); }
We only declare the firstNum variable if the search() method matches at
least 1 digit in the string.
# Get the first number in a string using String.match()
If you need to match more than one digit, use the String.match() method.
function getFirstNumber(str) { const match = str.match(/[0-9]+/); return parseInt(match[0]); } console.log(getFirstNumber('one 2 three 4')); // 👉️ 2 console.log(getFirstNumber('a 100 b 200')); // 👉️ 100
The String.match method matches a string against a regular expression.
The method returns an array containing the matches (if any) or null if no
matches are found.
const str = 'a 100 b 200'; // 👇️ [ '100', index: 2, input: 'a 100 b 200', groups: undefined ] console.log(str.match(/[0-9]+/));
The plus + matches the preceding item (the 0-9 range) 1 or more times.
The last step is to access the array at index 0 and convert the string to a
number.
Note that the match() method will return null if the string doesn't contain
any numbers.
const str = 'abc'; // 👇️ null console.log(str.match(/[0-9]+/));
If you need to handle this scenario, use an if/else statement.
const str = 'a 100 b 200'; const match = str.match(/[0-9]+/); const num = parseInt(match[0]); if (num !== null) { console.log('The string contains a number'); console.log(num); // 👉️ 100 } else { console.log('The string does NOT contain any numbers'); }
The if block is only run if the string contains a number, otherwise, the
else block runs.
We used the [0-9] character class to match digits in the string, however, you
might also see examples online that use the \d special character.
const str = 'one 2 three 4'; const index = str.search(/\d/); console.log(index); // 👉️ 4 const firstNum = Number(str[index]); console.log(firstNum); // 👉️ 2
The \d special character matches any digit from 0 to 9. Specifying the
\d character is the same as specifying a range of [0-9].
function getFirstNumber(str) { const match = str.match(/\d+/); return parseInt(match[0]); } console.log(getFirstNumber('one 2 three 4')); // 👉️ 2 console.log(getFirstNumber('a 100 b 200')); // 👉️ 100
If you ever need help reading a regular expression, check out this regular expression cheat sheet by MDN.
It contains a table with the name and the meaning of each special character with examples.
# Get the Number from the End of a String
Use the String.match() method to get the number from the end of a string,
e.g. str.match(/[0-9]+$/);.
The match method will return an array containing the number from the end of
the string at index 0.
function getNumberFromEnd(str) { const matches = str.match(/[0-9]+$/); if (matches) { return parseInt(matches[0], 10); } return null; } // 👇️ 456 console.log(getNumberFromEnd('one 2 three 456')); // 👇️ 987 console.log(getNumberFromEnd('bobbyhadz 987'));
The String.match method matches a string against a regular expression.
The method returns an array containing the matches (if any) or null if no
matches are found.
The only parameter the method takes is a regular expression.
The forward slashes / / mark the beginning and end of the regular expression.
The square brackets [] part is called a character class and matches a range
of digits from 0 to 9.
+ matches the preceding item (the digits range) one or more times.The dollar sign $ matches the end of the input.
The match() method returns an array containing the matches.
const str = 'one 2 three 456'; // 👇️ [ '456', index: 12, input: 'one 2 three 456', groups: undefined ] const match = str.match(/[0-9]+$/); const result = parseInt(match[0]); console.log(result); // 👉️ 456
Once we have the array containing the matches, we use the parseInt function to parse the string into a number.
match() method will return null.const str = 'one 2 three 456 seven'; const arr = str.match(/[0-9]+$/); console.log(arr); // 👉️ null
If you need to handle this scenario, you can use an if statement.
const str = 'one 2 three 456 seven'; const arr = str.match(/[0-9]+$/); console.log(arr); // 👉️ null let num; if (arr !== null) { console.log('✅ String contains digits at the end'); num = parseInt(arr[0], 10); } else { // 👇️ this runs console.log('⛔️ String contains NO digits at the end'); }
In this example, we only call the parseInt function if the string contains
digits at the end.
nullue at index 0, you would get an error, so it's much safer to have a conditional in place.We used the [0-9] character class in the examples, however, you can also use
the \d special character.
function getNumberFromEnd(str) { // 👇️ using \d special character const matches = str.match(/\d+$/); if (matches) { return parseInt(matches[0], 10); } return null; } // 👇️ 456 console.log(getNumberFromEnd('one 2 three 456')); // 👇️ 987 console.log(getNumberFromEnd('bobbyhadz 987'));
The \d character matches any digit from 0 to 9.
The special character is equivalent to the [0-9] character class.
If you ever need help reading a regular expression, check out this regular expression cheat sheet by MDN.
It contains a table with the name and the meaning of each special character with examples.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

