How to Add Hours to a Date in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 6, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Add Hours to a Date in JavaScript
To add hours to a Date in JavaScript:
- Use the
getTime()method to get the number of milliseconds since the Unix Epoch. - Use the
setTime()method, passing it the result of callinggetTimeplus the hours converted to milliseconds.
function addHours(date, hours) { date.setTime(date.getTime() + hours * 60 * 60 * 1000); return date; } // ✅ Add 1 hour to the current date const result1 = addHours(new Date(), 1); console.log(result1); // 👉️ 2023-07-26T07:23:49.670Z // ✅ Add 2 hours to a different date const date = new Date('2024-03-14T18:30:05.000Z'); const result2 = addHours(date, 2); console.log(result2); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T20:30:05.000Z
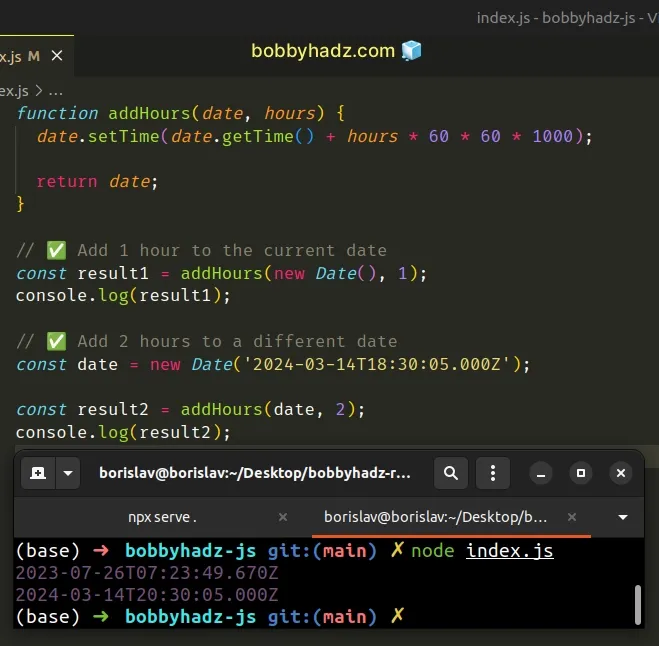
The addHours function takes a Date object and N as parameters and adds N
hours to the date.
If you need to add hours to the current date, call the Date() constructor
without passing it any parameters.
function addHours(date, hours) { date.setTime(date.getTime() + hours * 60 * 60 * 1000); return date; } const currentDate = new Date(); // ✅ Add 1 hour to the current date const result1 = addHours(currentDate, 1); console.log(result1); // 👉️ 2023-07-26T07:25:17.030Z
The getTime() method returns the number of milliseconds elapsed between the 1st of January, 1970 00:00:00 and the given date.
We multiplied the number of hours by 60 * 60 * 1000 because we need to convert
the value to milliseconds, when passing it to the
setTime()
method.
The setTime() method takes a number that represents the milliseconds since the
1st of January, 1970 and sets the value on the date.
This approach automatically takes care of the scenario where adding X hours pushes us into the next day, month or year.
function addHours(date, hours) { date.setTime(date.getTime() + hours * 60 * 60 * 1000); return date; } const date = new Date('2024-03-14T23:30:05.000Z'); const result = addHours(date, 10); console.log(result); // 👉️ 2024-03-15T09:30:05.000Z
Adding 10 hours to the date successfully changed the day of the month to the
15th.
# Add Hours to a Date without mutation
The setTime method mutates the Date object it was called on.
If you don't want to change the Date in place, create a copy before calling
the method.
function addHours(date, hours) { const dateCopy = new Date(date); dateCopy.setTime(dateCopy.getTime() + hours * 60 * 60 * 1000); return dateCopy; } const date = new Date('2024-03-14T12:30:05.000Z'); const result = addHours(date, 2); console.log(result); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T14:30:05.000Z console.log(date); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T12:30:05.000Z
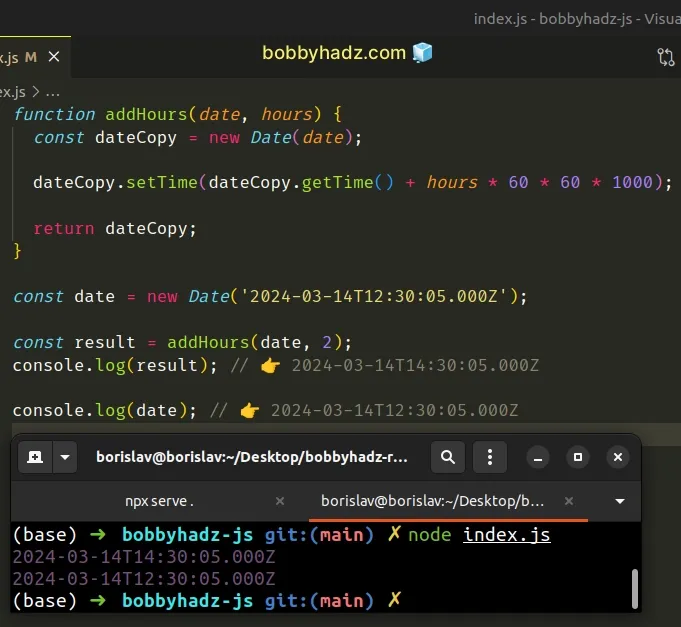
When a Date object is passed to the Date() constructor, it gets converted to
a timestamp and can be used to create a copy of the date.
Mutating function parameters is a bad practice because calling the function with the same parameter multiple times returns different results.
Instead, pure functions like the one above return the same output when called with the same parameters.
# Add Hours to a Date using date-fns
You can also use date-fns module to add hours to a date.
import {addHours} from 'date-fns'; const date = new Date('2024-03-14T12:30:05.000Z'); const result1 = addHours(date, 2); console.log(result1); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T14:30:05.000Z const result2 = addHours(date, 4); console.log(result2); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T16:30:05.000Z console.log(date); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T12:30:05.000Z
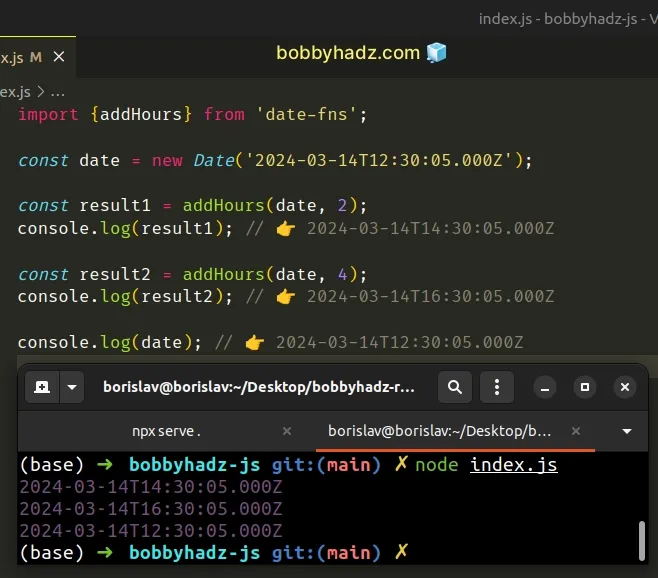
The addHours() function takes a date and the number of hours to be added to
the date as parameters.
The function doesn't mutate the original date as shown in the example.
If you don't have date-fns installed, you can install it by running the
following command from your terminal.
# 👇️ create package.json if you don't have one npm init -y # ✅ install with NPM npm install date-fns # ✅ install with YARN yarn add date-fns
# Add Hours to a Date using moment.js
You can also use the moment.js module to add hours to a date.
import moment from 'moment'; const date = new Date('2024-03-14T12:30:05.000Z'); const result1 = moment(date).add(2, 'hours'); console.log(result1); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T09:55:40.000Z const result2 = moment(date).add(4, 'hours'); console.log(result2); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T09:56:01.000Z console.log(date); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T12:30:05.000Z
We used the moment().add() method to add hours to a date.
The method can be used to add years, quarters, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes, seconds or milliseconds to a date.
If you don't have moment installed, you can install it by running the
following command from your terminal.
# 👇️ create package.json if you don't have one npm init -y # ✅ install with NPM npm install moment # ✅ install with YARN yarn add moment
The call to the add() method actually returns a moment object and not a
native JavaScript date.
If you need to convert the value to a JavaScript date, use the toDate()
method.
import moment from 'moment'; const date = new Date('2024-03-14T12:30:05.000Z'); const result1 = moment(date).add(2, 'hours').toDate(); console.log(result1); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T09:55:40.000Z const result2 = moment(date).add(4, 'hours').toDate(); console.log(result2); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T09:56:01.000Z console.log(date); // 👉️ 2024-03-14T12:30:05.000Z
The toDate() method takes care of converting the moment object to a native
JavaScript Date object.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

