How to check if type is Boolean using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Check if a value's type is Boolean using JavaScript
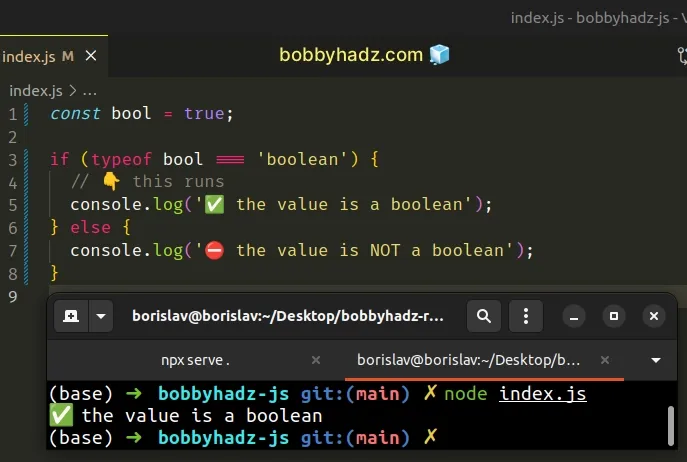
Use the typeof operator to check if a value is of boolean type.
The typeof operator will return "boolean" if the type of the value is
boolean.
const bool = true; if (typeof bool === 'boolean') { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ the value is a boolean'); } else { console.log('⛔️ the value is NOT a boolean'); }
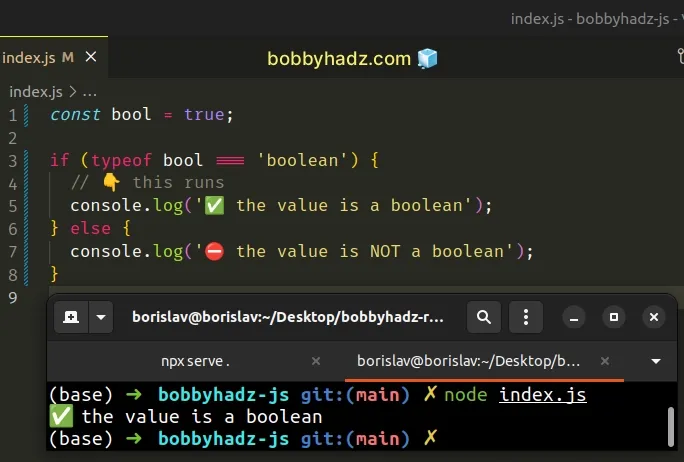
The typeof operator returns a string that indicates the type of a value.
Here are some examples:
console.log(typeof true); // 👉️ "boolean" console.log(typeof false); // 👉️ "boolean" console.log(typeof function () {}); // 👉️ "function" console.log(typeof null); // 👉️ "object" console.log(typeof []); // 👉️ "object" console.log(typeof {}); // 👉️ "object" console.log(typeof ''); // 👉️ "string" console.log(typeof 0); // 👉️ "number"
When used with a value of true or false, the typeof operator returns the
string "boolean" and that's exactly what we check for in the if statement.
const bool = true; if (typeof bool === 'boolean') { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ the value is a boolean'); } else { console.log('⛔️ the value is NOT a boolean'); }
If the condition is met, the if block runs, otherwise, the else block runs.
If you have to check if a value is of type boolean often, define a reusable function.
function isBoolean(value) { return typeof value === 'boolean'; } console.log(isBoolean(true)); // 👉️ true console.log(isBoolean(false)); // 👉️ true console.log(isBoolean(undefined)); // 👉️ false console.log(isBoolean('')); // 👉️ false console.log(isBoolean(null)); // 👉️ false
The isBoolean function takes a value as a parameter and returns true if the
value is of type boolean and false otherwise.
An alternative approach is to use the logical OR (||) operator.
# Check if a value is of type boolean using logical OR (||) operator
This is a three-step process:
- Check if the value is equal to
false. - Check if the value is equal to
true. - If either condition is met, the value is a boolean.
const bool = true; if (bool === true || bool === false) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ type is boolean'); } else { console.log('⛔️ type is NOT boolean'); }
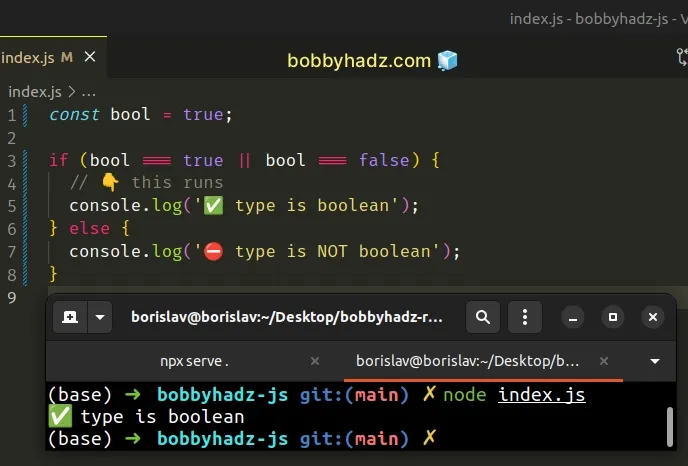
We used the logical or (||) operator to chain 2 conditions.
If either condition evaluates to true, the if block runs.
Our conditions
check if the value is equal to true
or equal to false.
true and false, so if either condition is met, the value has a type of boolean.If you have to check if a value is a boolean often, define a reusable function.
function isBoolean(value) { return value === true || value === false; } console.log(isBoolean(true)); // 👉️ true console.log(isBoolean(false)); // 👉️ true console.log(isBoolean(undefined)); // 👉️ false console.log(isBoolean('')); // 👉️ false console.log(isBoolean(null)); // 👉️ false
The function takes a value as a parameter and returns true if the value is a
boolean and false otherwise.
# Check if a value is of type boolean using toString.call()
You can also use the toString.call() method to check if a value is a boolean.
const value = true; if ( Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === '[object Boolean]' ) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ type is boolean'); } else { console.log('⛔️ type is NOT boolean'); }
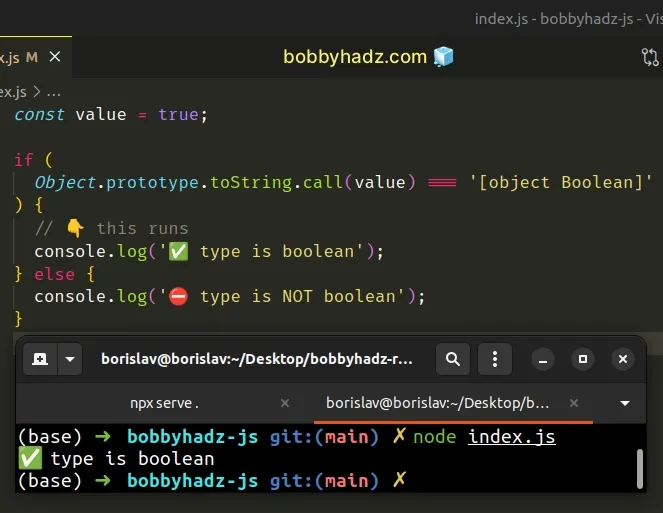
Here is an example of defining a reusable function.
function isBoolean(value) { return Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === '[object Boolean]'; } console.log(isBoolean(true)); // 👉️ true console.log(isBoolean(false)); // 👉️ true console.log(isBoolean(undefined)); // 👉️ false console.log(isBoolean('')); // 👉️ false console.log(isBoolean(null)); // 👉️ false
The Object.prototype.toString.call() method can be used to stringify a value.
When a boolean value is stringified, the string '[object Boolean]' is
returned.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I'd use the typeof
operator as I find it quite direct and intuitive.
One thing to note about the typeof operator is that it doesn't throw an error
even if the variable has not been declared.
if (typeof value === 'boolean') { console.log('✅ type is boolean'); } else { // 👇️ this runs console.log('⛔️ type is NOT boolean'); }
A variable with the name value has not been declared in the code sample, but
the code didn't throw an error.
The typeof operator returns undefined for variables that have not been
declared and doesn't throw an error.
If you use the lodash library, you can also check if a value is a boolean
using the isBoolean() method.
# Check if a value is of type boolean using lodash
First, make sure you have lodash installed by running the following command
from your terminal.
# 👇️ initialize package.json if you don't have one npm init -y npm install lodash
Now you can import and use the isBoolean() method to check if a value is a boolean.
import _ from 'lodash'; console.log(_.isBoolean(true)); // 👉️ true console.log(_.isBoolean(false)); // 👉️ true console.log(_.isBoolean('hello')); // 👉️ false console.log(_.isBoolean(null)); // 👉️ false
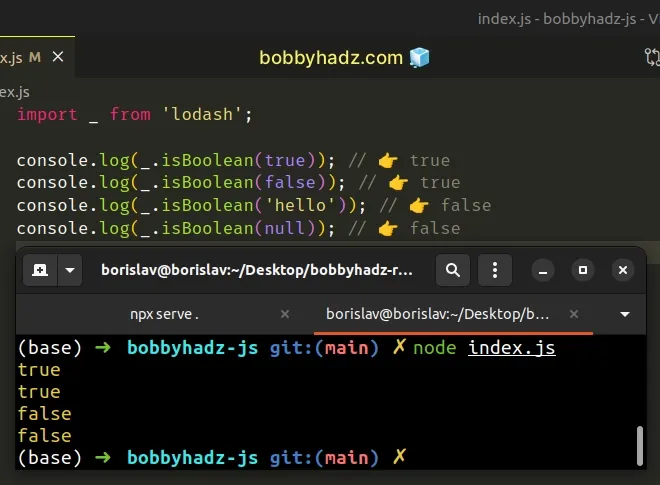
The isBoolean function returns true if the supplied value is a boolean and
false otherwise.
Even if you already use lodash in your project, I would advise against using
the isBoolean method as the typeof operator is sufficient and doesn't
require you to use an external library.
# Don't use the instanceof operator to check if a value is a boolean
You should never use the instanceof operator to check if a value is of type
boolean.
// ⛔️ BAD - don't do this function isBoolean(value) { return value instanceof Boolean; } console.log(isBoolean(true)); // 👉️ false console.log(isBoolean(false)); // 👉️ false console.log(isBoolean('hello')); // 👉️ false console.log(isBoolean(new Boolean(true))); // 👉️ true console.log(isBoolean(new Boolean(false))); // 👉️ true
The syntax for the
instanceof operator
is object instanceof constructor.
The operator returns true if the prototype property of the constructor
appears anywhere in the prototype chain of the object.
Notice that the operator returns true only for object-wrapped booleans.
These are booleans that were created with the new Boolean() constructor.
You should never use the new Boolean() constructor in your code, so you should
never have to use the instanceof operator to check if a value is a boolean.
The typeof operator is all you need in order to check if a value stores a
boolean in JavaScript.
const bool = true; if (typeof bool === 'boolean') { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ the value is a boolean'); } else { console.log('⛔️ the value is NOT a boolean'); }