How to Check if a DOM element exists using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 5, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Check if a DOM element exists using getElementById
To check if an element does not exist in the DOM:
- Use the
getElementByIdorquerySelectormethods to select the element. - Check if the value is not equal to
null. - If the value is not equal to
null, the element exists in the DOM.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <title>bobbyhadz.com</title> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div id="box">Box content</div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
// ✅ Using getElementById const el1 = document.getElementById('box'); console.log(el1); // 👉️ div#box if (el1 !== null) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('The element exists in the DOM'); } else { console.log('The element does NOT exist in the DOM'); }
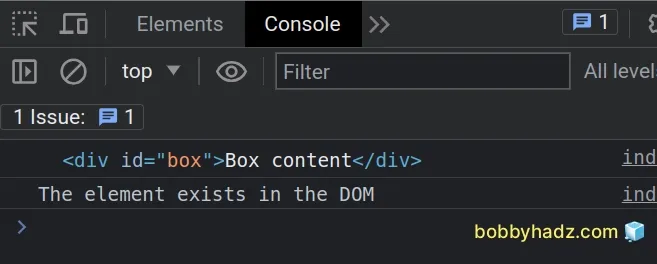
We used the document.getElementById()
method to select an element by id.
The method returns the element, whose id property matches the provided string.
id that is passed to the getElementById method is case-sensitive, so box is not equal to Box.If no element with the provided id exists in the document, a null value is
returned.
Our if statement
checks if the variable doesn't store a null value.
The if block is only run if the element exists in the DOM, otherwise, the
else block runs.
<body> <div id="box">Box content</div> <!-- ✅ Placed at bottom of body tag --> <script src="index.js"></script> </body>
HTML code is parsed from top to bottom, so if your script tag is placed above that code that declares the DOM elements, they won't be available.
# Check if a DOM element exists using querySelector
You can also use the document.querySelector() method to check if an element exists in the DOM.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<body> <div id="box">Box content</div> <div class="big-box">Big box content</div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body>
And here is the related Javascript code.
// ✅ select by ID const el1 = document.querySelector('#box'); console.log(el1); // 👉️ div#box if (el1 !== null) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('the element exists in the DOM'); } else { console.log('the element does NOT exist in the DOM'); }
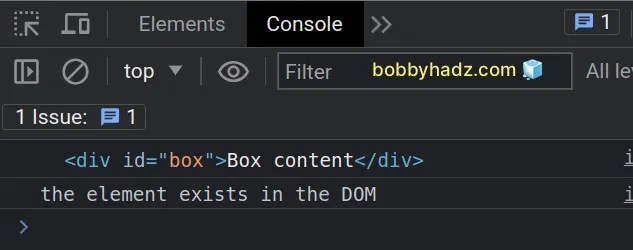
Notice that we passed a
CSS selector
to the document.querySelector() method.
The selector in the example selects an element with an id of box.
Here is an example of selecting an element with a class of big-box.
// ✅ select by Class const el1 = document.querySelector('.big-box'); console.log(el1); // 👉️ div.big-box if (el1 !== null) { console.log('the element exists in the DOM'); } else { console.log('the element does NOT exist in the DOM'); }
The querySelector() method takes a string that represents a valid CSS selector
as a parameter.
null value, just like the getElementById method.You can also provide multiple, comma-separated selectors to the
querySelector() method.
const el = document.querySelector('.my-class, #my-id'); if (el !== null) { console.log('the element exists in the DOM'); } else { console.log('the element does NOT exist in the DOM'); }
The example tries to select an element with a class of my-class or an id set
to my-id.
If neither element is found, the querySelector() method returns null.
# Check if a DOM element exists using getElementsByClassName
You can also use the document.getElementsByClassName() to check if an element
with a given class exists.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<body> <div class="box">Box content</div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
const elements = document.getElementsByClassName('box'); console.log(elements); // 👉️ HTMLCollection [div.box] if (elements.length > 0) { // 👇️ div.box console.log('At least one element with a class of box exists'); } else { console.log('No elements with a class of box exist'); } console.log(elements[0]); // 👉️ div.box
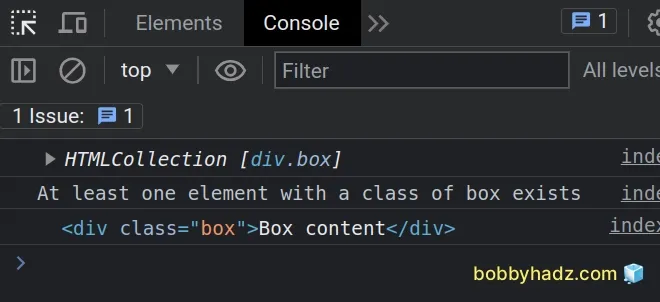
The code sample
checks if at least 1 element with a class of box exists
on the page.
The document.getElementsByClassName() method returns an array-like object of all elements that have the specified class name.
Note that the method returns an array-like object and not an array.
If you need to convert the HTMLCollection to an array, use the Array.from()
method.
const elements = Array.from( document.getElementsByClassName('box'), ); console.log(elements); // 👉️ [div.box] if (elements.length > 0) { // 👇️ div.box console.log('At least one element with a class of box exists'); } else { console.log('No elements with a class of box exist'); } // ✅ iterate over the array elements.forEach(element => { console.log(element); });
We used the Array.from() method to convert the collection of HTML elements to
an array and used the Array.forEach() method to iterate over the collection.
# Check if a DOM element exists using querySelectorAll
The document.querySelectorAll() method can also be used to check if a DOM element exists.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<body> <div class="box">Box content</div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
const elements = document.querySelectorAll('.box'); console.log(elements); // 👉️ NodeList [div.box] if (elements.length > 0) { // 👇️ div.box console.log('At least one element with a class of box exists'); } else { console.log('No elements with a class of box exist'); } console.log(elements[0]); // 👉️ div.box
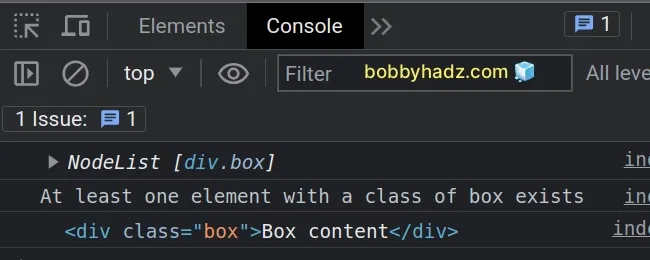
Notice that we passed a valid CSS selector to the querySelectorAll() method.
The method returns a NodeList that contains all of the elements that match the
specified selector.
If the NodeList has a length that is greater than 0, then at least one
element with the specified class exists.
# Check if a DOM element exists using getElementsByTagName
You can also use the getElementsByTagName() method to check if an element
exists in the DOM.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<body> <p>bobbyhadz.com</p> <script src="index.js"></script> </body>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
const elements = document.getElementsByTagName('p'); console.log(elements); // 👉️ HTMLCollection [p] if (elements.length > 0) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('At least one p element exists'); } else { console.log('No p elements exists on the page'); } console.log(elements[0]); // 👉️ p
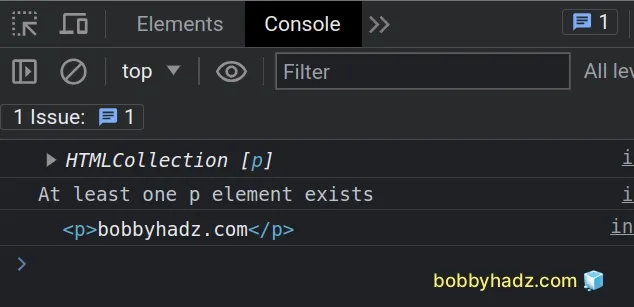
The code sample uses the
getElementsByTagName()
method to select all p elements on the page.
If the length property on the HTML collection returns a value greater than
0, then at least one p element exists.

