TypeError: Cannot read properties of null (reading 'value')
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# TypeError: Cannot read properties of null (reading 'value')
There are 2 main reasons the "Cannot read properties of null (reading 'value')" error occurs:
- Accessing the
valueproperty on anullvalue (DOM element that doesn't exist). - Inserting the JS script tag above the HTML where the DOM elements are declared.
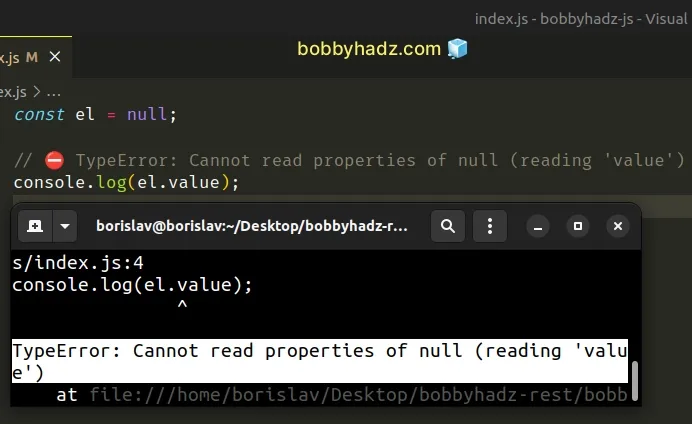
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
const el = null; // ⛔️ TypeError: Cannot read properties of null (reading 'value') console.log(el.value);

# Make sure the DOM element exists before accessing value
The error most commonly occurs if you use the getElementById() method and pass
it an id that is not present in the DOM.
const input = document.getElementById('does-not-exist'); console.log(input); // 👉️ null // ⛔️ Cannot read properties null (reading 'value') const value = input.value;
To solve the error, make sure you aren't accessing the value property on a
null value, e.g. a non-existent DOM element.
An element with the provided id doesn't exist in the DOM, so the
getElementById() method returns null.
value property on a null value, the error occurs.# Checking if the element exists before accessing its value property
You can use the
optional chaining (?.) operator, the
ternary operator or a simple if statement to avoid the error.
const input = document.getElementById('does-not-exist'); // ✅ Using optional chaining ?. const value1 = input?.value || ''; // --------------------------------------------- // ✅ Using ternary operator const value2 = input ? input.value : ''; // --------------------------------------------- // ✅ using if/else if (input) { const value3 = input.value; } else { console.log('input is falsy'); }
The optional chaining (?.) operator short-circuits instead of throwing an error if the reference is nullish.
If you want to read more on how to check if a DOM element exists, click on the following article.
# Place the JS script tag at the bottom of the body tag
Make sure that the JS script tag is placed at the bottom of the body, after the DOM elements have been declared.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <!-- ⛔️ BAD - Script is run before input is created ⛔️ --> <script src="index.js"></script> <input id="first_name" type="text" name="first_name" value="Initial Value" /> </body> </html>
Note that HTML code is parsed from top to bottom.
We placed the JS script tag above the code that creates the input element, so
the index.js file is run before the DOM element is created.
This means that the input will not be accessible in the index.js file.
const input = document.getElementById('first_name'); console.log(input); // 👉️ null // ⛔️ Cannot read properties null (reading 'value') const value = input.value;
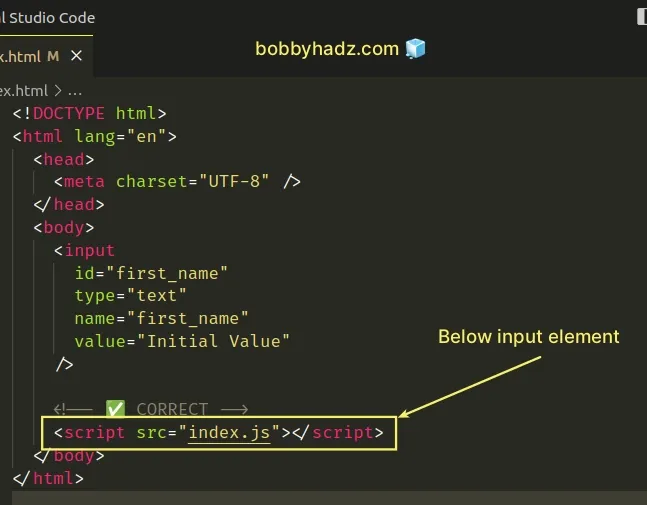
You have to move the JS script tag to the bottom of the body, after the HTML elements.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <input id="first_name" type="text" name="first_name" value="Initial Value" /> <!-- ✅ GOOD - Script is run after input is declared ✅ --> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
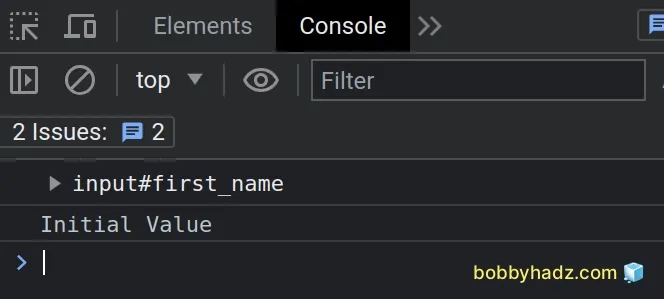
Now the input element is available in the index.js file.
const input = document.getElementById('first_name'); console.log(input); // 👉️ input#first_name // ✅ Works const value = input.value; console.log(value); // 👉️ "Initial value"
HTML code is parsed from top to bottom, so the JS script tag has to come after the code that declares the DOM elements.
Now the HTML element is created before the index.js script is run, so we are
able to access the input element.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

