Calculate Percentage between Two Numbers in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Calculate the Percentage between Two Numbers in JavaScript
- Round to N decimal places using
toFixed() - Calculate the percentage between 2 numbers and round the result
- Get percentage increase/decrease between two numbers
- Convert Percentage to Decimal using JavaScript
# Calculate the Percentage between Two Numbers in JavaScript
To calculate the percentage between two numbers, divide one number by the
other and multiply the result by 100, e.g. (30 / 75) * 100.
This shows what percent the first number is of the second. In the example,
30 is 40% of 75.
function isWhatPercentOf(x, y) { return (x / y) * 100; } // 👇️ `30` is 40% of `75` console.log(isWhatPercentOf(30, 75)); // 👉️ 40 // 👇️ `20` is 26.666% of `75` console.log(isWhatPercentOf(20, 75)); // 👉️ 26.666666...
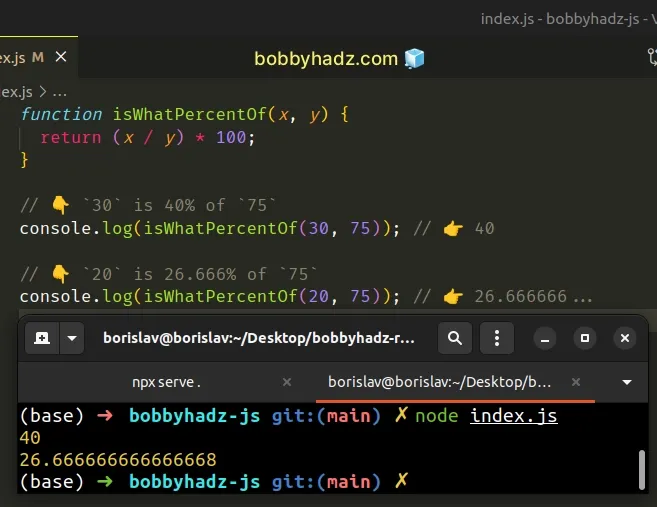
The function takes 2 numbers and returns what percent the first number is of second.
For example, 25 / 50 * 100 shows that 25 is 50% of 50.
// 👇️ `25` is 50% of `50` console.log((25 / 50) * 100);
# Round to N decimal places using toFixed()
When calculating percentages between two numbers, you might need to round to a specific number of digits after the decimal.
You can use the Number.toFixed() method to achieve this.
const percentage = (20 / 75) * 100; console.log(percentage); // 👇️ 26.666666666... // 👇️ 2 decimals const fixed = percentage.toFixed(2); console.log(fixed); // 👉️ "26.67"
The toFixed method formats the number to the provided number of digits after
the decimal and rounds the number if necessary.
Note that the toFixed method returns a string, not a number.
If the number doesn't have any decimal places, it gets padded with zeros.
const percentage = (50 / 100) * 100; console.log(percentage); // 👇️ 50 // 👇️ 2 decimals const fixed = percentage.toFixed(2); console.log(fixed); // 👉️ "50.00"
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
function isWhatPercentOf(x, y, decimals) { return ((x / y) * 100).toFixed(decimals); } console.log(isWhatPercentOf(20, 75, 2)); // 👉️ 26.67 console.log(isWhatPercentOf(20, 75, 3)); // 👉️ 26.667 console.log(isWhatPercentOf(20, 75, 4)); // 👉️ 26.6667
The function takes 2 numbers and the number of decimal places the result should have and calculates the percentage between the two numbers.
# Calculate the percentage between 2 numbers and round the result
If you need to calculate the percentage between two numbers and round the
result, pass the output of the calculation to the Math.round() method.
function isWhatPercentOf(x, y) { return Math.round((x / y) * 100); } console.log(isWhatPercentOf(20, 75)); // 👉️ 27 console.log((20 / 75) * 100); // 👉️ 26.66666666
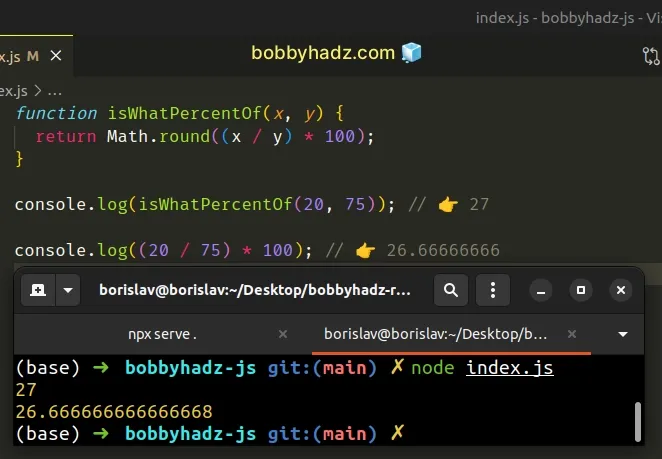
The Math.round() method takes a number and rounds it to the nearest integer.
console.log(Math.round(2.49)); // 👉️ 2 console.log(Math.round(2.5)); // 👉️ 3
0.5, it gets rounded to the next higher absolute value.If the number is positive and its fractional portion is less than 0.5, it gets
rounded to the lower absolute value.
If you don't round the result, you might get a floating-point number that has N decimal places.
console.log((20 / 75) * 100); // 👉️ 26.66666666
# Get percentage increase/decrease between two numbers
You can use the same approach to get the percentage increase/decrease between two numbers.
function getPercentageIncrease(numA, numB) { return ((numA - numB) / numB) * 100; } // 👇️ `50` is 66.66% increase from `30` console.log(getPercentageIncrease(50, 30)); // 👉️ 66.666 // 👇️ `50` is 50% decrease from `100` console.log(getPercentageIncrease(50, 100)); // 👉️ -50
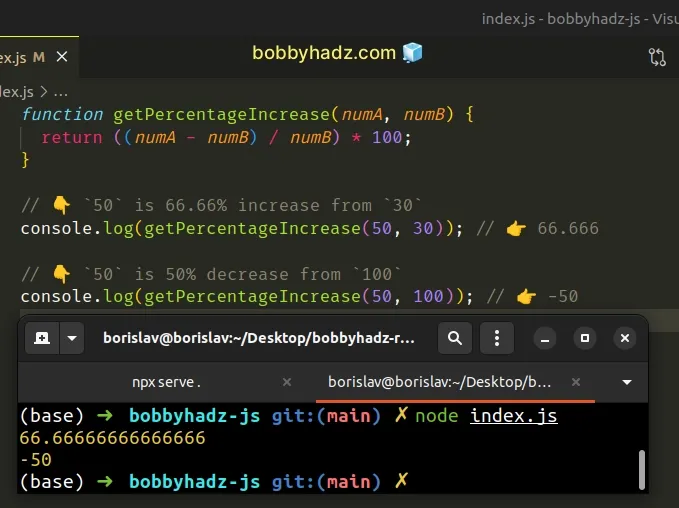
The first example shows that the percentage increase from 30 to 50 is
66.6666...%.
And the second example shows that the percentage increase from 100 to 50 is
-50%.
# Convert Percentage to Decimal using JavaScript
To convert a percentage to a decimal, pass the percent string to the
parseFloat() function and divide the result by 100.
The parseFloat() function parses the provided string and returns a
floating-point number.
function toDecimal(percent) { return parseFloat(percent) / 100; } console.log(toDecimal('25%')); // 👉️ 0.25 console.log(toDecimal('55%')); // 👉️ 0.55 console.log(toDecimal('0%')); // 👉️ 0 console.log(toDecimal('100%')); // 👉️ 1
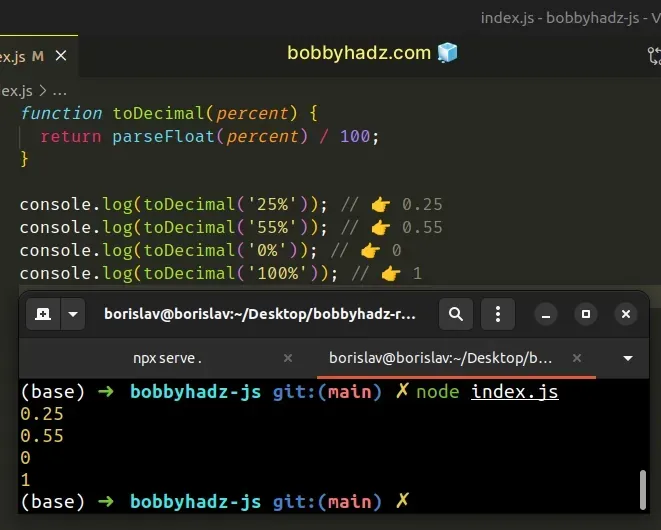
The toDecimal() function takes a percentage string and converts the value to a
decimal.
The parseFloat() function takes a string as a parameter and parses the string to a floating-point number.
console.log(parseFloat('25%')); // 👉️ 25 console.log(parseFloat('55%')); // 👉️ 55 console.log(parseFloat('55.5%')); // 👉️ 55.5
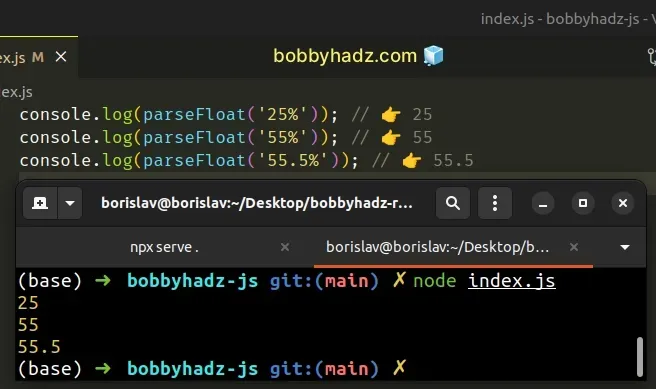
If the parseFloat() function encounters a character other than a plus +,
minus -, numeral 0-9 or decimal point ., it returns the value up to that
characters and ignores the invalid character and the rest of the string.
In our scenario, when the parseFloat() function encounters the percent sign
%, it short-circuits and returns the floating-point number up to that point.
If the first character of the provided string cannot be converted to a number,
the parseFloat function returns NaN (not a number).
console.log(parseFloat('%25')); // 👉️ NaN
The last step is to divide the result of calling the parseFloat() function by
100 to get the decimal value.
# Handle invalid numbers
If you need to handle the scenario where the provided string is not a valid
percent, you can check if the result of calling the parseFloat() function
returns NaN.
This would handle the edge case where you are dividing NaN by 100 which
would still return NaN.
function toDecimal(percent) { const parsed = parseFloat(percent); if (!Number.isNaN(parsed)) { return parseFloat(percent) / 100; } else { return 0; } } console.log(toDecimal('25%')); // 👉️ 0.25 console.log(toDecimal('hello')); // 👉️ 0
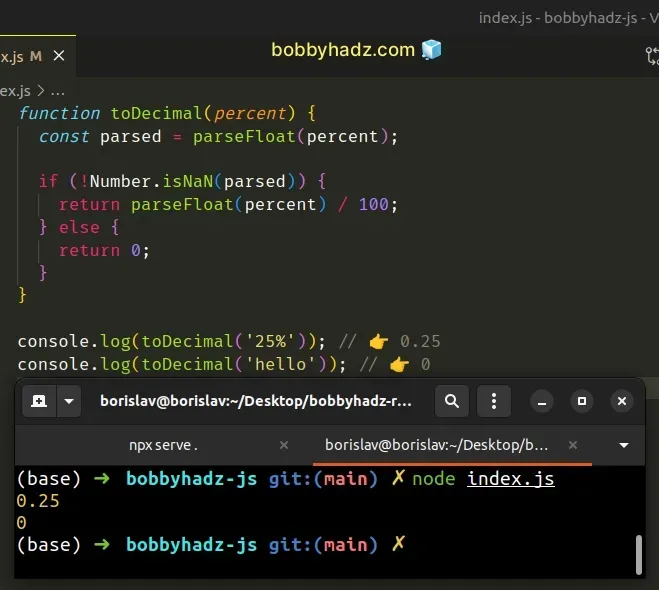
We check if the result of calling the parseFloat() function is not NaN
before dividing it by 100.
In the case that we get a NaN value, we simply return 0.
You might need to handle the else block differently depending on your use
case.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

