bash: permission denied: /home/user/.bashrc error [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 5, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# bash: permission denied: /home/user/.bashrc error
The error "bash: permission denied: /home/user/.bashrc" occurs when you try to
execute the ~/.bashrc file from your terminal.
To resolve the issue, source the file by running source ~/.bashrc or edit it
with your preferred text editor.
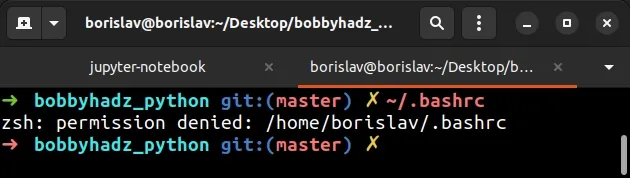
Directly running ~/.bashrc from your terminal causes the error.
# ⛔️ bash: permission denied: /home/user/.bashrc ~/.bashrc
# Sourcing your ~/.bashrc file
If you made changes to your ~/.bashrc file and you want to source it to update
your current shell session, issue the following command.
source ~/.bashrc

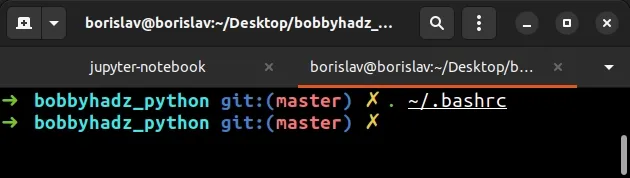
The command above does the same as the following command.
. ~/.bashrc
Make sure the path to the file is specified correctly - ~/.bashrc.
The ~/.bashrc path translates to /home/YOUR_USER/.bashrc.
.bashrc file somewhere else in your home directory which could cause the error.The source command will read and execute your ~/.bashrc file in the context
of the current shell session.
Any changes you've made to the file will be applied to the current shell.
The source command is an alias for ..
You can also source your ~/.bash_profile file if you've made changes to it.
# BASH source ~/.bashrc source ~/.bash_profile
If you use zsh, you would source the following 2 files instead.
# ZSH source ~/.zshrc source ~/.zprofile
# Editing your ~/.bashrc file
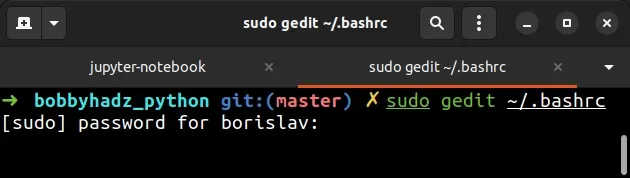
If you need to edit your ~/.bashrc file, issue the following command.
sudo gedit ~/.bashrc
The command uses the gedit text editor.
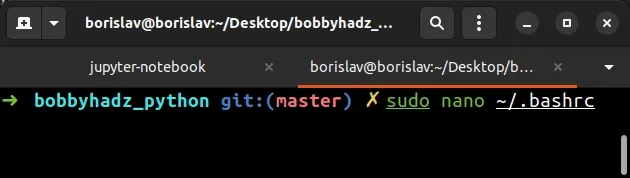
Alternatively, you can use nano.
sudo nano ~/.bashrc
You can use the same approach to edit your other profile files.
For example, you can edit your ~/.bash_profile file by using one of the
following commands.
# with Gedit sudo gedit ~/.bash_profile # or with Nano sudo nano ~/.bash_profile
And you can edit your ~/.zshrc profile file by issuing one of the following
commands.
sudo gedit ~/.zshrc sudo nano ~/.zshrc
Anytime you make changes to your profile file, you have to source it.
# BASH source ~/.bashrc source ~/.bash_profile # ZSH source ~/.zshrc
If the changes don't get applied to the current shell session for some reason, you have 2 options:
- Use the
exec bashcommand.
exec bash
The exec command is used to execute a command from within bash.
We simply execute the bash command to restart the shell.
- Alternatively, you can completely close the shell session and reopen it.
# Changing the permissions of your ~/.bashrc file
The following command can be used to change the ownership of your ~/.bashrc
file to the current user.
sudo chown <USERNAME>:<USERNAME> ~/.bashrc
You can get your username by issuing the echo $USER command.
echo $USER
If the error persists, try to set the permissions of your ~/.bashrc file to
644.
The 644 mode allows:
- the owner to read and write to the file
- the group to read the file
- other users to read the file
chmod 644 ~/.bashrc chmod 644 ~/.bash_profile
The error should be resolved after granting your user permission to read and
write to the ~/.bashrc file.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

