Unexpected token. A constructor, method Error in TS [Fixed]
Last updated: Feb 27, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Unexpected token. A constructor, method Error in TS
The "Unexpected token. A constructor, method, accessor, or property was
expected" error occurs when we use the var or let keywords to declare a
class property or the function keyword in a class.
To solve the error, remove the var, let and function keywords from your
class.
Here are 2 examples of how the error occurs.
class A { // ⛔️ Error (using var, let) var a: number = 100; let b: string = 'hello'; // ⛔️ Error: Unexpected token. A constructor, // method, accessor, or property was expected.ts(1068) function myFunction() { } }
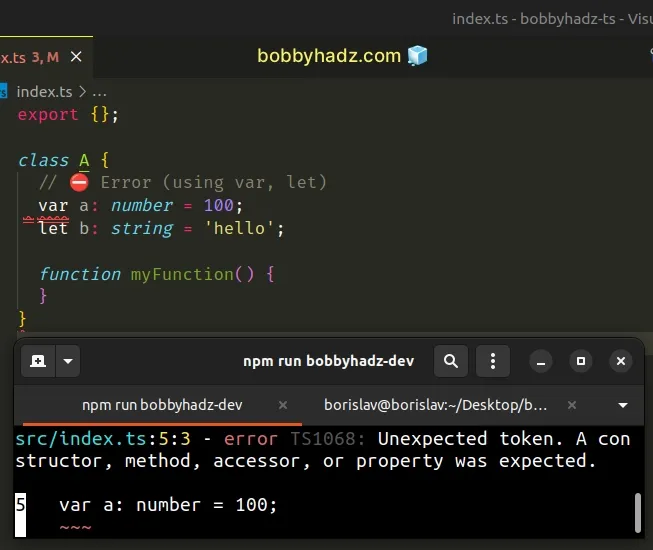
We used the var and let keywords to assign properties to the class and the
function keyword to declare class method.
To resolve the issue, remove the var, let and function keywords from your
class.
class A { a = 100; b = 'bobbyhadz.com'; myFunction() { console.log(this.a); } } const myInstance = new A(); console.log(myInstance.a); // 👉️ 100 console.log(myInstance.b); // 👉️ "bobbyhadz.com" myInstance.myFunction(); // 👉️ 100
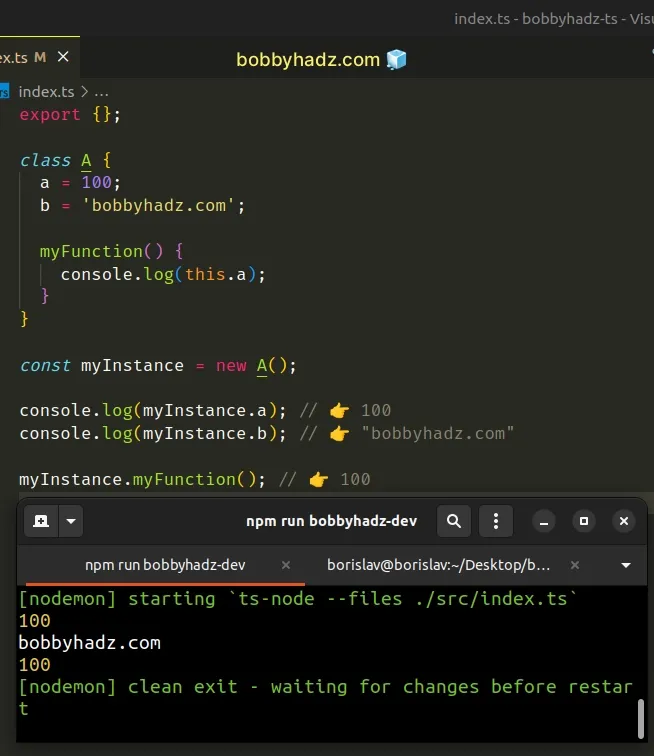
The class has 2
propertied - a and b and a method named myFunction.
# Taking arguments via the constructor method
You will often have to take arguments when creating class instances. You can do that via the constructor method.
class A { constructor( public a: number, public b: string, ) { this.a = a; this.b = b; } myFunction() { console.log(this.a); } } const myInstance = new A(42, 'bobbyhadz.com'); console.log(myInstance.a); // 👉️ 42 console.log(myInstance.b); // 👉️ "bobbyhadz.com"
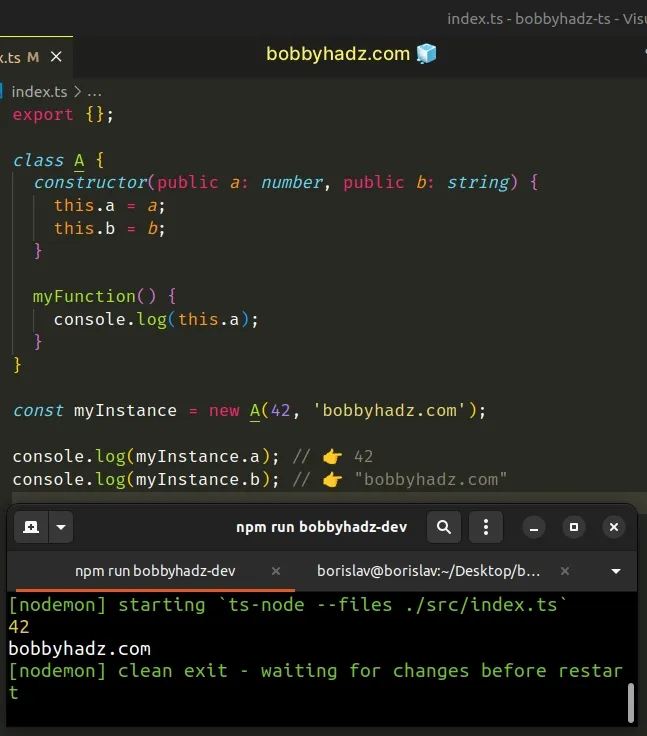
Notice that we assigned the a and b properties inside the constructor method
and we aren't using the var, let or function keywords anywhere inside the
class.
The class in the example is a more concise version of the following class.
class A { a: number; b: string; constructor(a: number, b: string) { this.a = a; this.b = b; } myFunction() { console.log(this.a); } } const myInstance = new A(42, 'bobbyhadz.com'); console.log(myInstance.a); // 👉️ 42 console.log(myInstance.b); // 👉️ "bobbyhadz.com"
We had to type the a and b class properties twice to achieve the same
result.
public keyword in the constructor is more widely used.# Using default values for constructor parameters
You can also use default values for constructor parameters.
class A { constructor( public a = 100, public b = 'bobbyhadz.com', ) { this.a = a; this.b = b; } myFunction() { console.log(this.a); } } const myInstance = new A(); console.log(myInstance.a); // 👉️ 100 console.log(myInstance.b); // 👉️ "bobbyhadz.com"
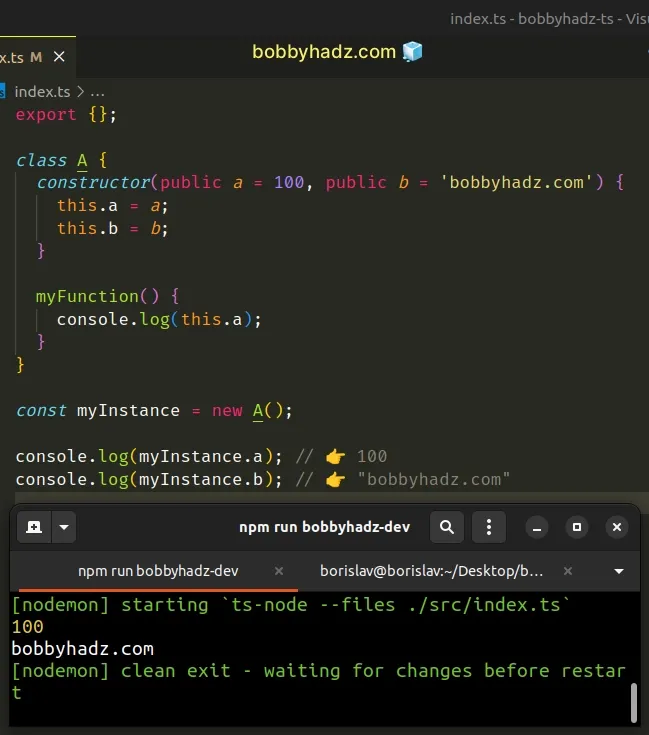
We created an instance of the class without passing any parameters to the
constructor function, so the a and b properties are set to the default
values.
# Using arrow functions for class methods
You can also use arrow functions for class methods.
class A { constructor( public a = 100, public b = 'bobbyhadz.com', ) { this.a = a; this.b = b; } myFunction = () => { console.log(this.a); }; } const myInstance = new A(); console.log(myInstance.a); // 👉️ 100 console.log(myInstance.b); // 👉️ "bobbyhadz.com" myInstance.myFunction(); // 👉️ 100
Notice that we aren't using the const, let or var keywords in the method's
definition.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

