How to get the current Date and Time in TypeScript
Last updated: Feb 26, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Get the current date and time in TypeScript
Use the Date() constructor to get the current date and time in TypeScript,
e.g. const now = new Date().
When the Date() constructor is called without any arguments, it returns a
Date object that represents the current date and time.
// 👇️ const now: Date const now = new Date(); console.log(now); // 👉️ 2024-02-26T16:26:39.971Z
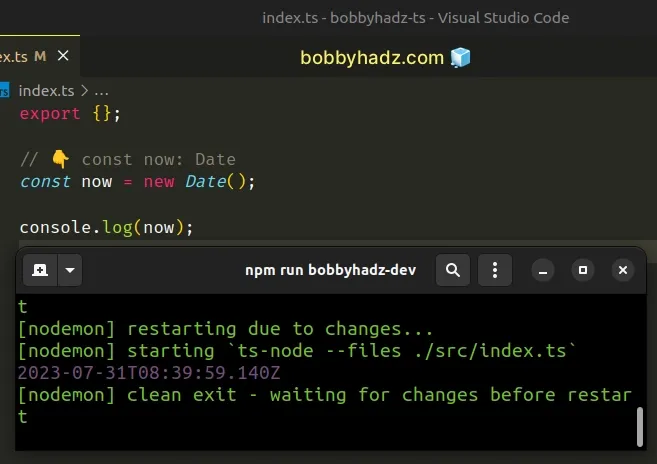
We called the Date() constructor to get a Date
object that represents the current date and time in TypeScript.
The type of the now variable is correctly inferred to be Date which enables
us to use any of the built-in methods the Date object implements.
# Examples of commonly used Date object methods
Here are some examples of methods you might use on the Date object.
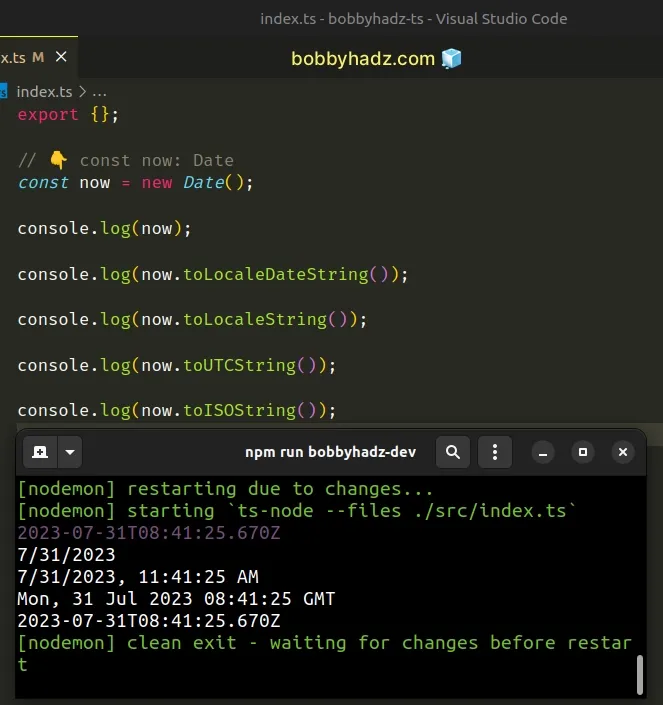
// 👇️ const now: Date const now = new Date(); console.log(now); // 👉️ 2024-02-26T16:27:15.563Z console.log(now.toLocaleDateString()); // 👉️ 2/26/2024 console.log(now.toLocaleString()); // 👉️ 2/26/2024, 6:27:15 PM console.log(now.toUTCString()); // 👉️ Mon, 26 Feb 2024 16:27:15 GMT console.log(now.toISOString()); // 👉️ 2024-02-26T16:27:15.563Z
# Formatting the current date and time using TypeScript
Here is an example that formats the date and time as YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss, but
can easily be tweaked to other formats, e.g. to MM/DD/YYYY or
MM/DD/YYYY hh:mm:ss.
function padTo2Digits(num: number) { return num.toString().padStart(2, '0'); } function formatDate(date: Date) { return ( [ date.getFullYear(), padTo2Digits(date.getMonth() + 1), padTo2Digits(date.getDate()), ].join('-') + ' ' + [ padTo2Digits(date.getHours()), padTo2Digits(date.getMinutes()), padTo2Digits(date.getSeconds()), ].join(':') ); } // 👇️ YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss // 👇️ "2024-02-26 18:28:11" (Current date and time) console.log(formatDate(new Date())); // 👇️️ 2025-05-04 05:24:07 (yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss) console.log(formatDate(new Date('May 04, 2025 05:24:07')));
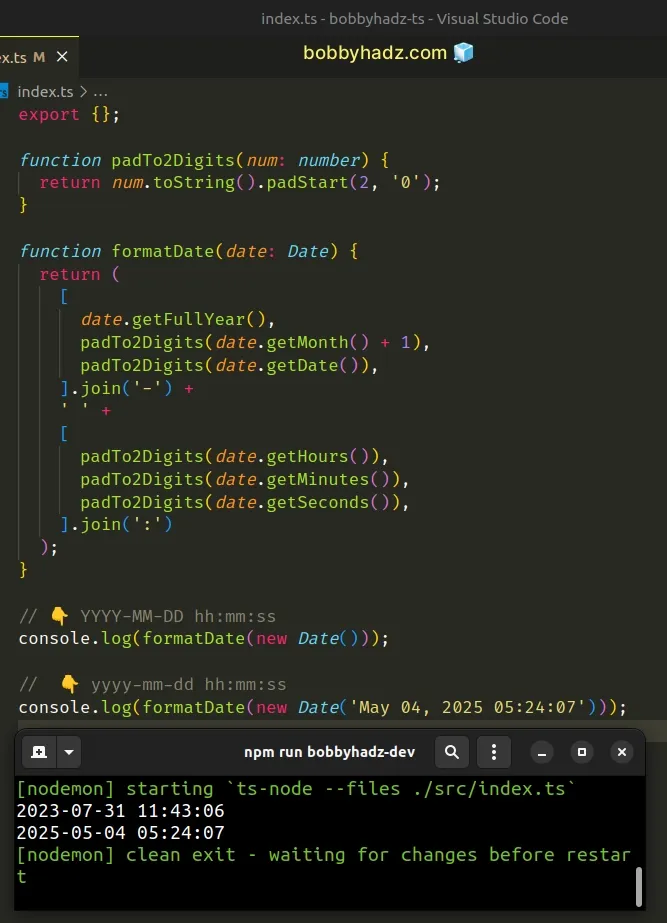
The function makes use of the following 6 methods on the Date object:
Date.getFullYear method - returns a four-digit number representing the year that corresponds to a date.
Date.getMonth - returns an integer between
0(January) and11(December) and represents the month for a given date. Yes, unfortunately, thegetMonthmethod is off by1.Date.getDate - returns an integer between
1and31representing the day of the month for a specific date.Date.getHours - returns the hour for the specified date.
Date.getMinutes - returns the minutes for a date.
Date.getSeconds - returns the seconds of a specific date.
getMonth method returns a zero-based month index from 0 to 11, meaning January is 0 and December is 11.The getMonth method is zero-based, so we added 1 to its return value.
We first created a padTo2Digits function that takes care of adding a leading
zero if the month, day, hours, minutes or seconds only contain a single digit
(are less than 10).
function padTo2Digits(num: number) { return num.toString().padStart(2, '0'); } console.log(padTo2Digits(3)); // 👉️ '03' console.log(padTo2Digits(7)); // 👉️ '07' console.log(padTo2Digits(10)); // 👉️ '10'
We want to make sure that the result is always consistent and has 2 digits for the months, days, hours, minutes and seconds, so we used the padStart method.
padTo2Digits function is the total length of the string, so it will never pad a value if it already has 2 digits.We placed the year, month and day in an array, so we could join them with a hyphen separator.
console.log(['2023', '02', '17'].join('-')); // 👉️ '2023-02-17' console.log(['2024', '07', '24'].join('-')); // 👉️ '2024-07-24'
This could have been any other separator, e.g. a forward slash /.
You could also easily reorder the date components if necessary (e.g. to
MM/DD/YYYY) by switching the places of the elements in the array.
This gets us the date formatted as YYYY-MM-DD.
The next step is to place the return values of the time-related methods in an array and join them with a colon separator.
console.log(['06', '30', '17'].join(':')); // 👉️ '06:30:17' console.log(['09', '11', '49'].join(':')); // 👉️ '09:11:49'
We used the same approach to format the time component as we did with the date components.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

