Check if an Element exists in an Array in React
Last updated: Apr 7, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Check if an Object exists in an Array in React
- Check if a primitive value exists in an Array in React
If you need to check if a string or a number is contained in an array, click on the second subheading.
# Check if an Object exists in an Array in React
To check if an object exists in an array in React:
- Use the
some()method to iterate over the array. - Check if a condition is met on each iteration.
- If the condition is met,
some()will returntrue, otherwise,falseis returned.
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const initialEmployees = [ {id: 1, name: 'Alice'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bobby Hadz'}, ]; const [employees, setEmployees] = useState(initialEmployees); // 👇️ Check if array contains object const isFound = employees.some(element => { if (element.id === 1) { return true; } return false; }); if (isFound) { console.log('✅ array contains object with id = 1'); } return ( <div> {employees.map(employee => { return ( <div key={employee.id}> <h2>id: {employee.id}</h2> <h2>name: {employee.name}</h2> </div> ); })} </div> ); }; export default App;
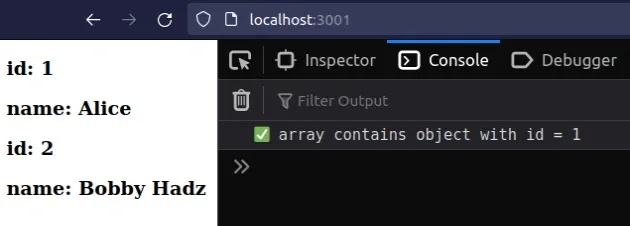
The first example shows how to check if an object exists in an array.
// 👇️ Check if array contains object const isFound = employees.some(element => { if (element.id === 1) { return true; } return false; }); if (isFound) { console.log('✅ array contains object with id = 1'); }
The function we passed to the Array.some() method gets called with each element (object) of the array.
Array.some method short-circuits and returns true.On each iteration, we check if the id property of the object is equal to a
specific value. If it is, we know that the object exists in the array.
We explicitly return true if an object with an id of 1 exists in the array,
otherwise, we return false.
You could also return the conditional check to make your code more concise.
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const initialEmployees = [ {id: 1, name: 'Alice'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bobby Hadz'}, ]; const [employees, setEmployees] = useState(initialEmployees); // 👇️ Check if array contains object const isFound = employees.some(element => { return element.id === 1; }); if (isFound) { console.log('✅ array contains object with id = 1'); } return ( <div> {employees.map(employee => { return ( <div key={employee.id}> <h2>id: {employee.id}</h2> <h2>name: {employee.name}</h2> </div> ); })} </div> ); }; export default App;
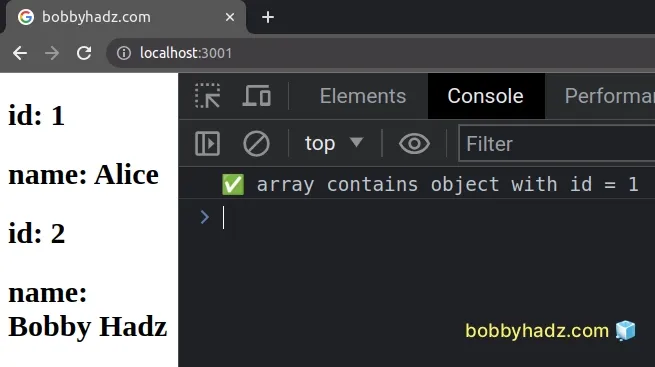
The isFound() function now directly returns the result of comparing the
object's id value to the specified value.
const isFound = employees.some(element => { return element.id === 1; });
If the comparison evaluates to true for one of the objects, the Array.some()
method short-circuits and returns true.
If the condition is never met, the Array.some() method returns false.
If you need to find the object if it exists,
use the Array.find() method instead of some().
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const initialEmployees = [ {id: 1, name: 'Alice'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bobby Hadz'}, ]; const [employees, setEmployees] = useState(initialEmployees); // 👇️ Check if array contains object const found = employees.find(element => { return element.id === 2; }); if (found) { // 👇️ {id: 2, name: 'Bobby Hadz'} console.log('✅ object found', found); } return ( <div> {employees.map(employee => { return ( <div key={employee.id}> <h2>id: {employee.id}</h2> <h2>name: {employee.name}</h2> </div> ); })} </div> ); }; export default App;
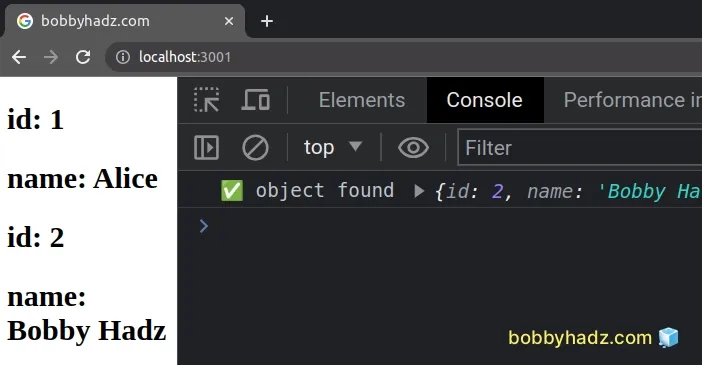
The Array.find() method returns the first array element that meets the
condition or undefined if the condition is never met.
# Check if an Object exists in an Array on Click in React
The same approach can be used to check if an object exists in an array on click.
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const initialEmployees = [ {id: 1, name: 'Alice'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bobby Hadz'}, ]; const [employees, setEmployees] = useState(initialEmployees); const handleClick = () => { const isFound = employees.some(element => { return element.id === 1; }); if (isFound) { console.log('✅ array contains object with id = 1'); } else { console.log( '⛔️ array does NOT contain object with id = 1', ); } }; return ( <div> {employees.map(employee => { return ( <div key={employee.id}> <h2>id: {employee.id}</h2> <h2>name: {employee.name}</h2> </div> ); })} <button onClick={() => setEmployees(emps => emps.filter(emp => emp.id !== 1)) } > Remove object with ID 1 </button> <br /> <br /> <button onClick={handleClick}> Check if Array contains Object </button> </div> ); }; export default App;
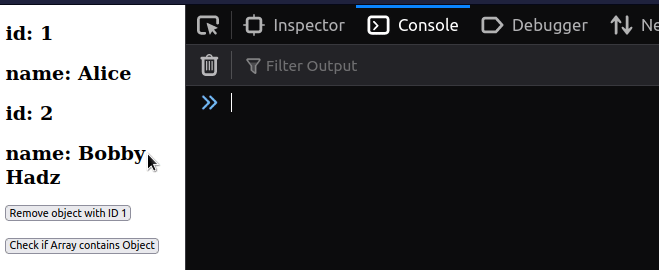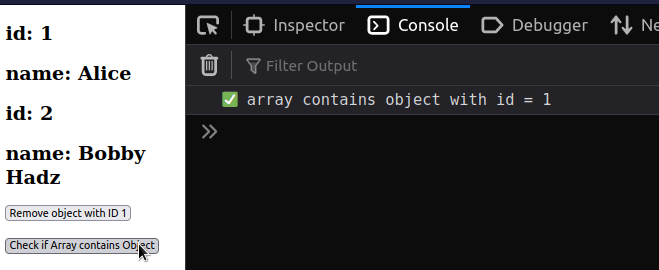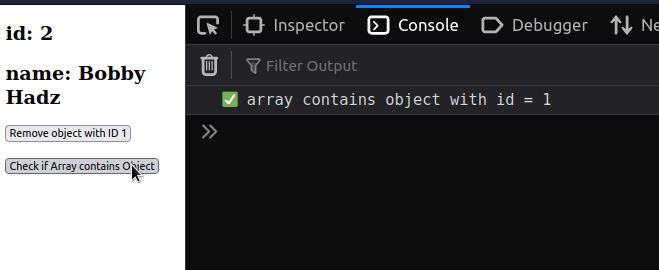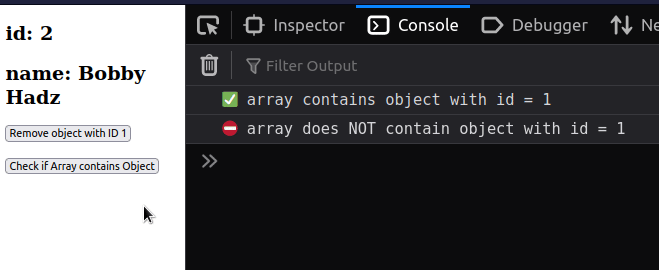
We added an onClick event listener to a button, so every time it's clicked,
its handleClick function is invoked.
We used the some() method to check if the object exists in the array in the
handleClick function.
const handleClick = () => { const isFound = employees.some(element => { return element.id === 1; }); if (isFound) { console.log('✅ array contains object with id = 1'); } else { console.log( '⛔️ array does NOT contain object with id = 1', ); } };
If the object is
removed from the array, the
isFound variable stores a false value.
# Check if a primitive value exists in an Array in React
Use the Array.includes() method to check if a primitive value exists in an
array.
The includes() method will return true if the value exists in an array and
false otherwise.
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const [names, setNames] = useState(['bobby', 'hadz', 'alice']); // ✅ Check if array contains string if (names.includes('bobby')) { console.log('✅ array contains string'); } // ✅ Check if array contains string on click const handleClick = () => { if (names.includes('bobby')) { console.log('✅ array contains string'); } }; return ( <div> {names.map((name, index) => { return ( <div key={index}> <h2>{name}</h2> </div> ); })} <br /> <button onClick={() => setNames(name => name !== 'bobby')}> Remove element </button> <br /> <br /> <button onClick={handleClick}>Click</button> </div> ); }; export default App;
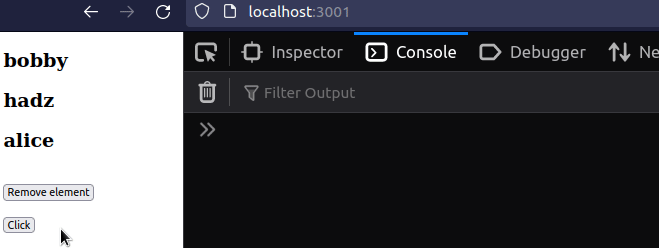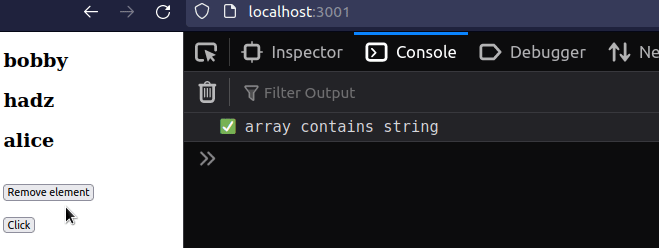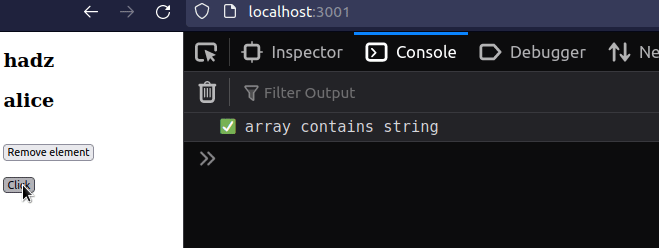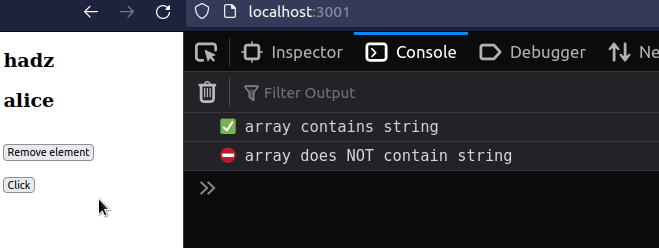
The code sample checks if a primitive value, such as a string, a number or a boolean exists in an array.
The includes() method returns true if the value exists in the array and
false otherwise.
if (names.includes('bobby')) { console.log('✅ array contains string'); }
Note that the includes() method is case-sensitive.
If you need to check if an array contains a string in a case-insensitive manner,
use the Array.some() method.
const names = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']; const str = 'BOBBY'; const isFound = names.some( name => name.toLowerCase() === str.toLowerCase(), ); console.log(isFound); // 👉️ true
We used the Array.some() method to iterate over the array.
On each iteration, we convert both strings to lowercase to perform a case-insensitive comparison.
The some() method will return true if the string is contained in the array
and false otherwise.

