ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero in Python [Fixed]
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero in Python
- ZeroDivisionError: integer modulo by zero
- ZeroDivisionError: division by zero in Python
# ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero in Python
The Python "ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero" occurs when we try to
divide a floating-point number by 0.
To solve the error, use an if statement to check if the number you are
dividing by is not zero, or handle the error in a try/except block.
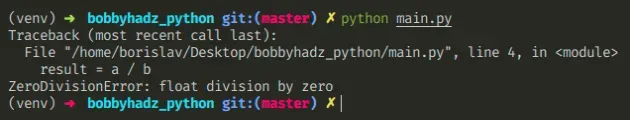
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
a = 15.0 b = 0 # ⛔️ ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero result = a / b
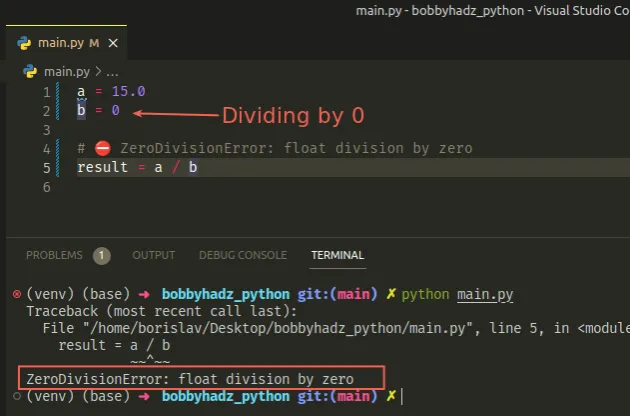
It's unclear what value is expected when we divide by 0, so Python throws an
error.
When we divide a number by 0, the result tends towards infinity.
# Checking if the value we are dividing by is not 0
One way to solve the error is to check if the value we are dividing by is not
0.
a = 15.0 b = 0 if b != 0: result = a / b else: result = 0 print(result) # 👉️ 0
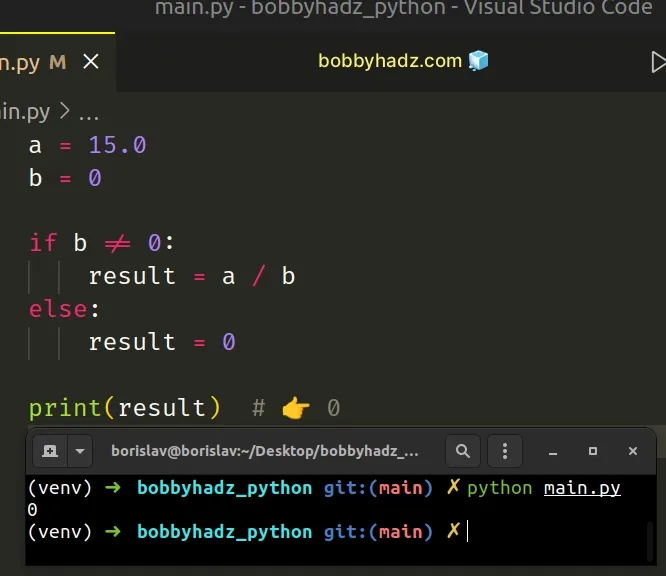
We check if the b variable doesn't store a 0 value and if it doesn't, we
divide a by b.
result variable to 0. Note that this could be any other value that suits your use case.If setting the result variable to 0 if b is equal to 0 suits your use
case, you can shorten this to a single line.
a = 15.0 b = 0 result = b and a / b print(result) # 👉️ 0
The expression x and y first evaluates x, and if x is falsy, its value is
returned, otherwise, y is returned.
0 is a falsy value, it gets returned if the b variable in the example stores a 0 value, otherwise, the result of dividing a by b is returned.# Using a try/except statement to handle the error
Alternatively, you can use a try/except statement.
a = 15.0 b = 0 try: result = a / b except ZeroDivisionError: result = 0 print(result) # 👉️ 0
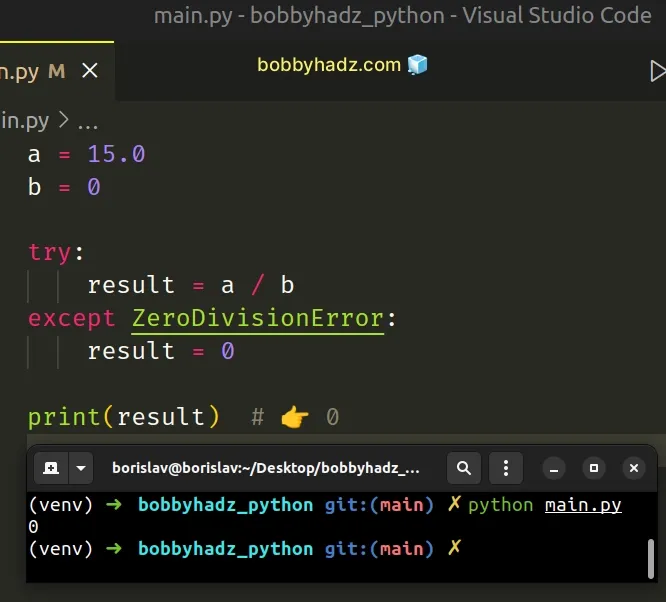
We try to divide a by b and if we get a ZeroDivisionError, the except
block sets the result variable to 0.
# Figure out where the variable got set to 0
The best way to solve the error is to figure out where the variable gets
assigned a 0 and check whether that's the expected behavior.
Here are some common ways you might get a zero value unexpectedly.
print(int()) # 👉️ 0 print(int(0.9)) # 👉️ 0
You might also get a zero value if you multiply any number by 0.
num_1 = 5 num_2 = num_1 * 0 print(num_2) # 👉️ 0
Make sure you haven't assigned the result of multiplying a number by 0 to a
variable.
# Handling a number from user input with a try/except statement
If you need to take a number from user input, use a try/except statement to
handle the potential ZeroDivisionError.
num_1 = 15.0 try: num_2 = int(input('Enter a number: ')) result = num_1 / num_2 print(f'The result of the division is: {result}') except (ZeroDivisionError, ValueError): print('Specify a positive integer value')
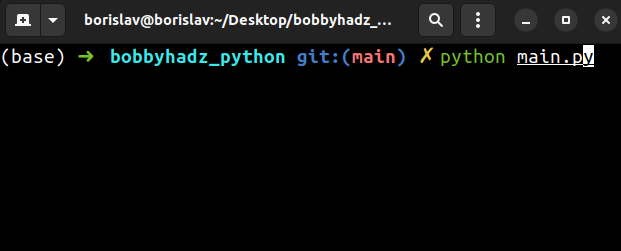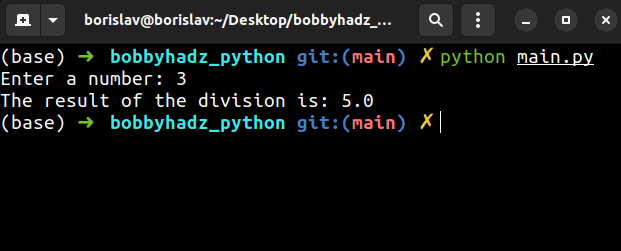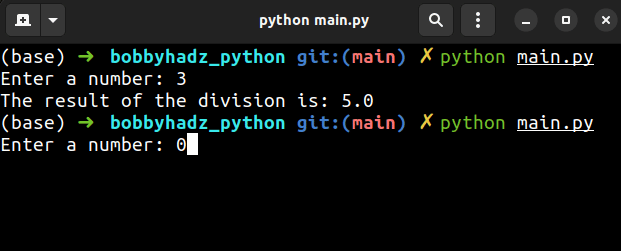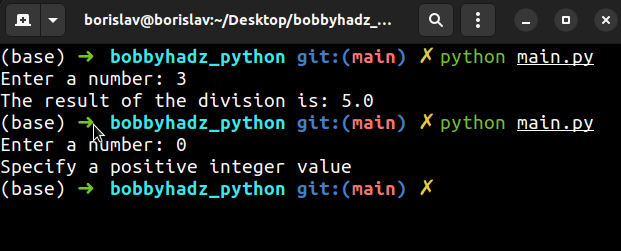
If the user passes an invalid integer, a ValueError is raised and is then
handled by the except block.
Similarly, if the user enters 0, a ZeroDivisionError is raised and is
handled by the except block.
Otherwise, the result of the division gets printed in the try block.
# Table of Contents
# ZeroDivisionError: integer modulo by zero in Python
The Python "ZeroDivisionError: integer division or modulo by zero" occurs when
we use the modulo % operator with an integer and a zero.
To solve the error, figure out where the 0 comes from and correct the
assignment.
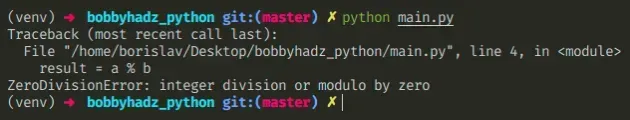
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
a = 6 b = 0 # ⛔️ ZeroDivisionError: integer division or modulo by zero # ZeroDivisionError: integer modulo by zero result = a % b
We tried using the modulo % operator with a zero.
It's unclear what value is expected when we divide by 0, so Python throws an
error.
When we divide a number by 0, the result tends towards infinity.
# Figuring out where the variable got assigned a zero value
The best way to solve the error is to figure out where the 0 value comes from
and correct the assignment.
Here are some unexpected sources of 0.
import random print(int()) # 👉️ 0 print(int(0.9)) # 👉️ 0 print(random.randint(0, 10)) # 👉️ 0 print(list(range(0, 5))) # 👉️ [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
If you use the random.randint() method or the range() class, make sure to
start from 1, and not from 0.
import random print(random.randint(1, 10)) # 👉️ 4 # 👇️ [1, 2, 3, 4] print(list(range(1, 5)))
# Check if the value is not 0 before using modulo
You can also conditionally check if the variable doesn't store a 0 value
before using the modulo operator.
a = 6 b = 0 if b != 0: result = a % b else: # 👇️ This runs print('b is equal to 0')
The if statement checks if the b variable doesn't store a 0 value before
using the modulo % operator.
# Using a try/except statement to handle the error
Alternatively, you can use a try/except statement.
a = 6 b = 0 try: result = a % b print(result) except ZeroDivisionError: pass
We use the modulo operator and if we get a ZeroDivisionError, the except
block is run.
You can set the result variable to a value that suits your use case in the
except block or simply pass.
The modulo (%) operator returns the remainder from the division of the first value by the second.
print(10 % 2) # 👉️ 0 print(10 % 4) # 👉️ 2
If the value on the right-hand side is zero, the operator raises a
ZeroDivisionError exception.
The left and right-hand side values may also be floating point numbers.
If the left-hand side value is a float and the right-hand side value is 0, you
would get a "ZeroDivisionError: float modulo" error.
# ⛔️ ZeroDivisionError: float modulo print(10.5 % 0) # 👉️ 0
# ZeroDivisionError: division by zero in Python
The Python "ZeroDivisionError: division by zero" occurs when we try to divide
a number by 0.
To solve the error, use an if statement to check if the number you are
dividing by is not zero, or handle the error in a try/except block.
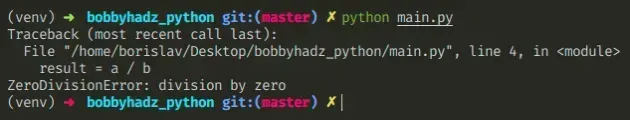
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
a = 5 b = 0 # ⛔️ ZeroDivisionError: division by zero result = a / b
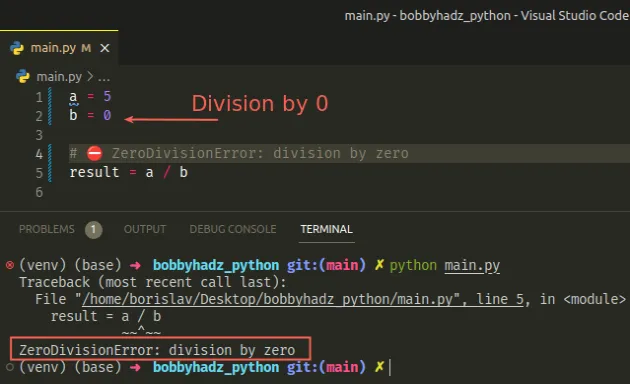
It's unclear what value is expected when we divide by 0, so Python throws an
error.
When we divide a number by 0, the result tends towards infinity.
# Checking if the value you are dividing by is not zero
One way to solve the error is to check if the value we are dividing by is not
0.
a = 5 b = 0 if b != 0: result = a / b else: result = 0 print(result) # 👉️ 0
We check if the b variable doesn't store a 0 value and if it doesn't, we
divide a by b.
result variable to 0. Note that this could be any other value that suits your use case.If setting the result variable to 0, if b is equal to 0 suits your use
case, you can shorten this to a single line.
a = 5 b = 0 result = b and a / b print(result) # 👉️ 0
The expression x and y first evaluates x, and if x is falsy, its value is
returned, otherwise, y is returned.
0 is a falsy value, it gets returned if the b variable in the example stores a 0 value, otherwise the result of dividing a by b is returned.# Using a try/except statement to handle the error
Alternatively, you can use a try/except statement.
a = 5 b = 0 try: result = a / b except ZeroDivisionError: result = 0 print(result) # 👉️ 0
The try/except block is known as "asking for forgiveness, rather than
permission".
We try to divide a by b and if we get a ZeroDivisionError, the except
block sets the result variable to 0.
The best way to solve the error is to figure out where the variable gets
assigned a 0 and check whether that's the expected behavior.
Here are some common ways you might get a zero value unexpectedly.
print(int()) # 👉️ 0 print(int(0.9)) # 👉️ 0
You might also get a zero value by multiplying a number by 0.
I've also written an article on how to check if a number is divisible by another number.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

