How to Divide without a remainder in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# Divide without a remainder in Python
Use the floor division operator // to divide without a remainder.
The floor division operator will always return an integer and is like using
mathematical division with the floor() function applied to the result.
result_1 = 30 // 6 print(result_1) # 👉️ 5 print(type(result_1)) # 👉️ <class 'int'> result_2 = 30 / 6 print(result_2) # 👉️ 5.0 print(type(result_2)) # 👉️ <class 'float'>
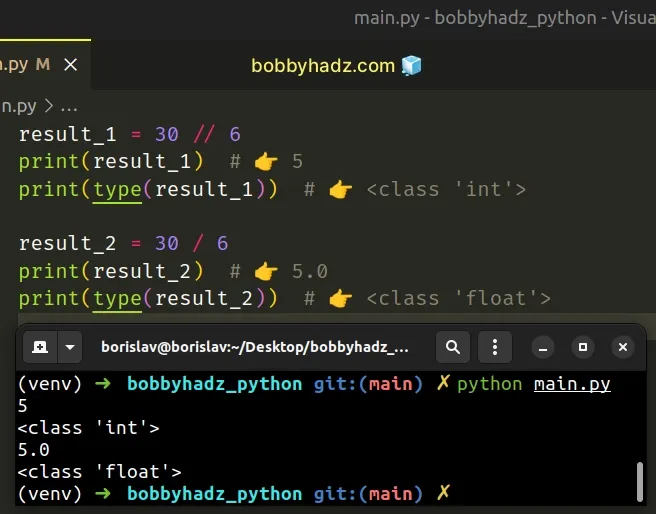
We used the floor division // operator to return an integer from integer
division.
/ of integers yields a float, while floor division // of integers result in an integer.The result of using the floor division operator is that of a mathematical
division with the floor() function applied to the result.
print(11 // 2) # 👉️ 5 print(11 / 2) # 👉️ 5.5
# Using math.floor()
You can use the
math.floor()
method in a similar way to how we used the floor division // operator.
import math result_1 = math.floor(11 / 2) print(result_1) # 👉️ 5 result_2 = 11 / 2 print(result_2) # 👉️ 5.5
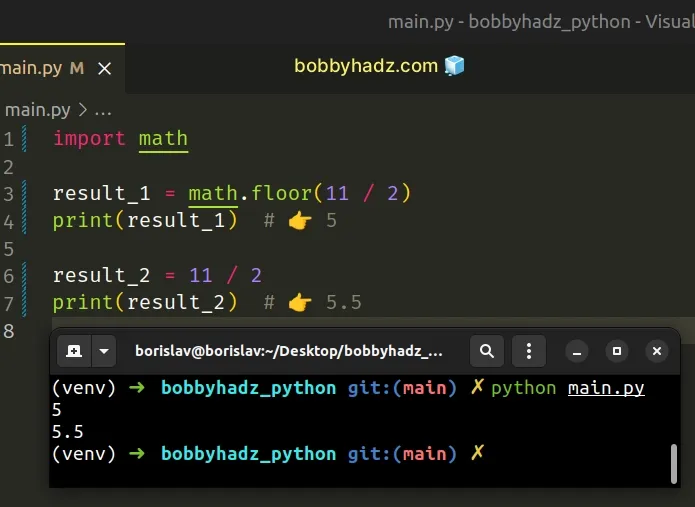
The math.floor() method returns the largest integer less than or equal to the provided number.
# Using math.ceil()
There is also a math.ceil() method.
import math result_1 = math.ceil(11 / 2) print(result_1) # 👉️ 6 result_2 = 11 / 2 print(result_2) # 👉️ 5.5
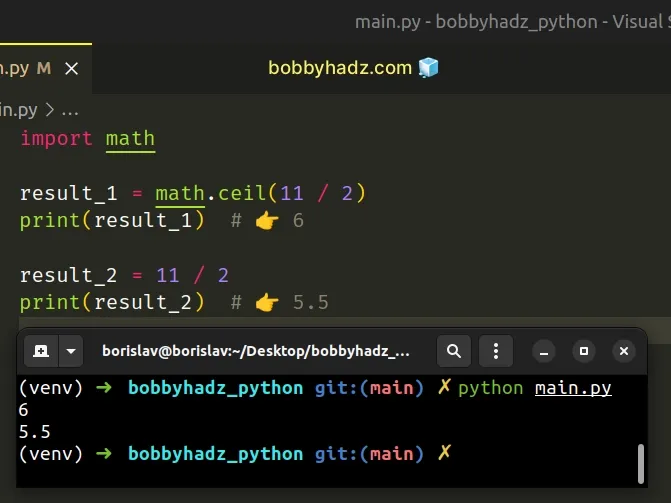
The math.ceil() method returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to the provided number.
# Using round()
You can also use the round() function if you want to round to the nearest
integer when dividing.
result_1 = round(15 / 4) print(result_1) # 👉️ 4 result_2 = 15 / 4 print(result_2) # 👉️ 3.75
The round() function takes the following 2 parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
number | the number to round to ndigits precision after the decimal |
ndigits | the number of digits after the decimal, the number should have after the operation (optional) |
The round function returns the number rounded to ndigits precision after the
decimal point.
If ndigits is omitted, the function returns the nearest integer.
# Divide without a remainder using int()
You can also use the int() class to remove the division decimal.
The int() class truncates floating-point numbers toward zero, so it will
return an int that represents the number without the decimal places.
result_1 = int(7 / 2) print(result_1) # 👉️ 3 result_2 = int(-7 / 2) print(result_2) # 👉️ -3
We used the int() class to remove the division decimal.
The int class returns an integer object constructed from the provided number or string argument.
int() class truncates toward zero.This approach allows us to remove the division decimal from a negative number and get a predictable result.
result_2 = int(-7 / 2) # 👉️ = -3.5 print(result_2) # 👉️ -3
# Divide without a remainder using math.trunc()
Alternatively, you can use the math.trunc() method.
The math.trunc() method removes the fractional part and returns the integer
part of the given number.
import math result_1 = math.trunc(7 / 2) print(result_1) # 👉️ 3 result_2 = math.trunc(-7 / 2) print(result_2) # 👉️ -3
The math.trunc() method takes a number, removes its fractional part and returns its integer part.
The math.trunc() method rounds towards zero.
print(math.trunc(3.45)) # 👉️ 3 print(math.trunc(-3.45)) # 👉️ -3
This approach achieves the same result as passing the result from the division
to the int() class.

